
By John & Nisha Whitehead
Source: The Rutherford Institute
We’re not living the American dream.
We’re living a financial nightmare.
The U.S. government is funding its existence with a credit card.
The government—and that includes the current administration—is spending money it doesn’t have on programs it can’t afford, and “we the taxpayers” are the ones being forced to foot the bill for the government’s fiscal insanity.
According to the number crunchers with the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, the government is borrowing roughly $6 billion a day.
As the Editorial Board for the Washington Post warns:
“The nation has reached a hazardous moment where what it owes, as a percentage of the total size of the economy, is the highest since World War II. If nothing changes, the United States will soon be in an uncharted scenario that weakens its national security, imperils its ability to invest in the future, unfairly burdens generations to come, and will require cuts to critical programs such as Social Security and Medicare. It is not a future anyone wants.”
Let’s talk numbers, shall we?
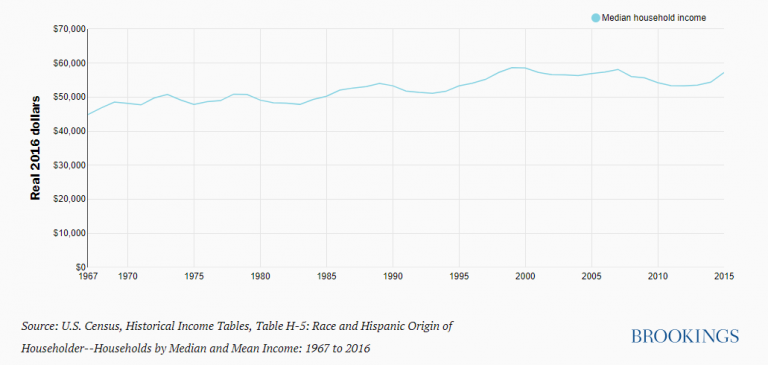
The national debt (the amount the federal government has borrowed over the years and must pay back) is $31 trillion and will grow another $19 trillion by 2033. That translates to roughly $246,000 per taxpayer or $94,000 for every single person in the country.
The bulk of that debt has been amassed over the past two decades, thanks in large part to the fiscal shenanigans of four presidents, 10 sessions of Congress and two wars.
It’s estimated that the amount this country owes is now 130% greater than its gross domestic product (all the products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the citizens).
In other words, the government is spending more than it brings in.
The U.S. ranks as the 12th most indebted nation in the world, with much of that debt owed to the Federal Reserve, large investment funds and foreign governments, namely, Japan and China.
Interest payments on the national debt are estimated to top $395 billion this year, which is significantly more than the government spends on veterans’ benefits and services, and according to Pew Research Center, more than it will spend on elementary and secondary education, disaster relief, agriculture, science and space programs, foreign aid, and natural resources and environmental protection combined.
According to the Committee for a Reasonable Federal Budget, the interest we’ve paid on this borrowed money is “nearly twice what the federal government will spend on transportation infrastructure, over four times as much as it will spend on K-12 education, almost four times what it will spend on housing, and over eight times what it will spend on science, space, and technology.”
In ten years, those interest payments will exceed our entire military budget.
This is financial tyranny.
We’ve been sold a bill of goods by politicians promising to pay down the national debt, jumpstart the economy, rebuild our infrastructure, secure our borders, ensure our security, and make us all healthy, wealthy and happy.
None of that has come to pass, and yet we’re still being loaded down with debt not of our own making while the government remains unrepentant, unfazed and undeterred in its wanton spending.
Indeed, the national deficit (the difference between what the government spends and the revenue it takes in) remains at more than $1.5 trillion.
If Americans managed their personal finances the way the government mismanages the nation’s finances, we’d all be in debtors’ prison by now.
Despite the government propaganda being peddled by the politicians and news media, however, the government isn’t spending our tax dollars to make our lives better.
We’re being robbed blind so the governmental elite can get richer.
In the eyes of the government, “we the people, the voters, the consumers, and the taxpayers” are little more than pocketbooks waiting to be picked.
“We the people” have become the new, permanent underclass in America.
Consider: The government can seize your home and your car (which you’ve bought and paid for) over nonpayment of taxes. Government agents can freeze and seize your bank accounts and other valuables if they merely “suspect” wrongdoing. And the IRS insists on getting the first cut of your salary to pay for government programs over which you have no say.
We have no real say in how the government runs, or how our taxpayer funds are used, but we’re being forced to pay through the nose, anyhow.
We have no real say, but that doesn’t prevent the government from fleecing us at every turn and forcing us to pay for endless wars that do more to fund the military industrial complex than protect us, pork barrel projects that produce little to nothing, and a police state that serves only to imprison us within its walls.
If you have no choice, no voice, and no real options when it comes to the government’s claims on your property and your money, you’re not free.
It wasn’t always this way, of course.
Early Americans went to war over the inalienable rights described by philosopher John Locke as the natural rights of life, liberty and property.
It didn’t take long, however—a hundred years, in fact—before the American government was laying claim to the citizenry’s property by levying taxes to pay for the Civil War. As the New York Times reports, “Widespread resistance led to its repeal in 1872.”
Determined to claim some of the citizenry’s wealth for its own uses, the government reinstituted the income tax in 1894. Charles Pollock challenged the tax as unconstitutional, and the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in his favor. Pollock’s victory was relatively short-lived. Members of Congress—united in their determination to tax the American people’s income—worked together to adopt a constitutional amendment to overrule the Pollock decision.
On the eve of World War I, in 1913, Congress instituted a permanent income tax by way of the 16th Amendment to the Constitution and the Revenue Act of 1913. Under the Revenue Act, individuals with income exceeding $3,000 could be taxed starting at 1% up to 7% for incomes exceeding $500,000.
It’s all gone downhill from there.
Unsurprisingly, the government has used its tax powers to advance its own imperialistic agendas and the courts have repeatedly upheld the government’s power to penalize or jail those who refused to pay their taxes.
While we’re struggling to get by, and making tough decisions about how to spend what little money actually makes it into our pockets after the federal, state and local governments take their share (this doesn’t include the stealth taxes imposed through tolls, fines and other fiscal penalties), the government continues to do whatever it likes—levy taxes, rack up debt, spend outrageously and irresponsibly—with little thought for the plight of its citizens.
To top it all off, all of those wars the U.S. is so eager to fight abroad are being waged with borrowed funds. As The Atlantic reports, “U.S. leaders are essentially bankrolling the wars with debt, in the form of purchases of U.S. Treasury bonds by U.S.-based entities like pension funds and state and local governments, and by countries like China and Japan.”
Of course, we’re the ones who have to repay that borrowed debt.
For instance, American taxpayers have been forced to shell out more than $5.6 trillion since 9/11 for the military industrial complex’s costly, endless so-called “war on terrorism.” That translates to roughly $23,000 per taxpayer to wage wars abroad, occupy foreign countries, provide financial aid to foreign allies, and fill the pockets of defense contractors and grease the hands of corrupt foreign dignitaries.
Mind you, that’s only a portion of what the Pentagon spends on America’s military empire.
The United States also spends more on foreign aid than any other nation, with nearly $300 billion disbursed over a five-year period. More than 150 countries around the world receive U.S. taxpayer-funded assistance, with most of the funds going to the Middle East, Africa and Asia. That price tag keeps growing, too.
As Forbes reports, “U.S. foreign aid dwarfs the federal funds spent by 48 out of 50 state governments annually. Only the state governments of California and New York spent more federal funds than what the U.S. sent abroad each year to foreign countries.”
Most recently, the U.S. has allocated nearly $115 billion in emergency military and humanitarian aid for Ukraine since the start of the Russia invasion.
As Dwight D. Eisenhower warned in a 1953 speech, this is how the military industrial complex continues to get richer, while the American taxpayer is forced to pay for programs that do little to enhance our lives, ensure our happiness and well-being, or secure our freedoms.
This is no way of life.
Yet it’s not just the government’s endless wars that are bleeding us dry.
We’re also being forced to shell out money for surveillance systems to track our movements, money to further militarize our already militarized police, money to allow the government to raid our homes and bank accounts, money to fund schools where our kids learn nothing about freedom and everything about how to comply, and on and on.
There was a time in our history when our forebears said “enough is enough” and stopped paying their taxes to what they considered an illegitimate government. They stood their ground and refused to support a system that was slowly choking out any attempts at self-governance, and which refused to be held accountable for its crimes against the people. Their resistance sowed the seeds for the revolution that would follow.
Unfortunately, in the 200-plus years since we established our own government, we’ve let bankers, turncoats and number-crunching bureaucrats muddy the waters and pilfer the accounts to such an extent that we’re back where we started.
Once again, we’ve got a despotic regime with an imperial ruler doing as they please.
Once again, we’ve got a judicial system insisting we have no rights under a government which demands that the people march in lockstep with its dictates.
And once again, we’ve got to decide whether we’ll keep marching or break stride and make a turn toward freedom.
But what if we didn’t just pull out our pocketbooks and pony up to the federal government’s outrageous demands for more money?
What if we didn’t just dutifully line up to drop our hard-earned dollars into the collection bucket, no questions asked about how it will be spent?
What if, instead of quietly sending in our tax checks, hoping vainly for some meager return, we did a little calculating of our own and started deducting from our taxes those programs that we refuse to support?
As I make clear in my book Battlefield America: The War on the American People and in its fictional counterpart The Erik Blair Diaries, if we don’t have the right to decide what happens to our hard-earned cash, then we don’t have any rights at all.















 AQ: I was trying to explain the shift in the middle class as an imaginative category. The middle class used to equal solid, fixed, stable. Temporally it was about gratification later, but your life wasn’t miserable while you were waiting for it. It wasn’t like OK, total slog, but you’re going to get that pension. We have to now think of it as a shaken category, an unstable category, and that’s a big shift. When we visualize the middle class, we’re visualizing the white picket fence, like the blue sky on the cover of the book. But it’s really this truck being squeezed between two houses.
AQ: I was trying to explain the shift in the middle class as an imaginative category. The middle class used to equal solid, fixed, stable. Temporally it was about gratification later, but your life wasn’t miserable while you were waiting for it. It wasn’t like OK, total slog, but you’re going to get that pension. We have to now think of it as a shaken category, an unstable category, and that’s a big shift. When we visualize the middle class, we’re visualizing the white picket fence, like the blue sky on the cover of the book. But it’s really this truck being squeezed between two houses.