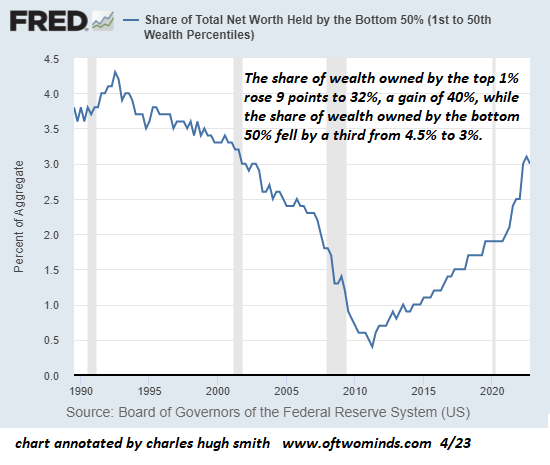
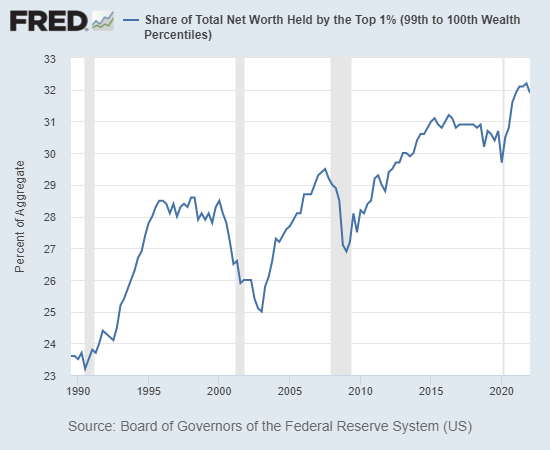
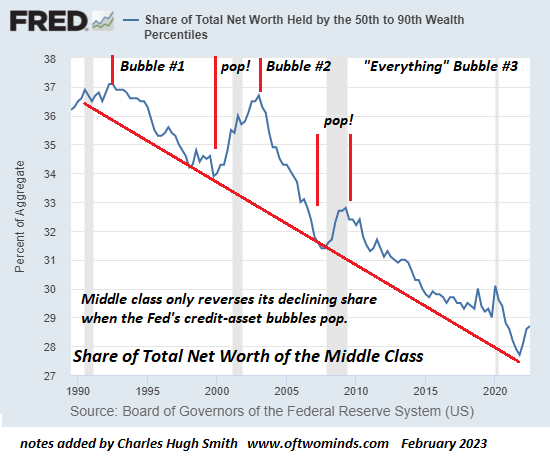
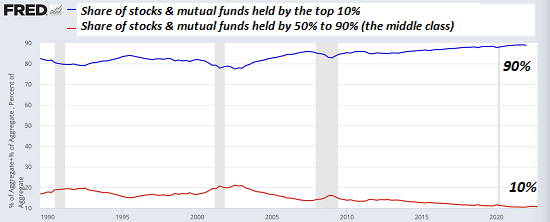
By Pepe Escobar
Source: The Unz Review
Prof. Michael Hudson’s new book, The Collapse of Antiquity: Greece and Rome as Civilization’s Oligarchic Turning Point is a seminal event in this Year of Living Dangerously when, to paraphrase Gramsci, the old geopolitical and geoeconomic order is dying and the new one is being born at breakneck speed.
Prof. Hudson’s main thesis is absolutely devastating: he sets out to prove that economic/financial practices in Ancient Greece and Rome – the pillars of Western Civilization – set the stage for what is happening today right in front of our eyes: an empire reduced to a rentier economy, collapsing from within.
And that brings us to the common denominator in every single Western financial system: it’s all about debt, inevitably growing by compound interest.
Ay, there’s the rub: before Greece and Rome, we had nearly 3,000 years of civilizations across West Asia doing exactly the opposite.
These kingdoms all knew about the importance of canceling debts. Otherwise their subjects would fall into bondage; lose their land to a bunch of foreclosing creditors; and these would usually try to overthrow the ruling power.
Aristotle succinctly framed it: “Under democracy, creditors begin to make loans and the debtors can’t pay and the creditors get more and more money, and they end up turning a democracy into an oligarchy, and then the oligarchy makes itself hereditary, and you have an aristocracy.”
Prof. Hudson sharply explains what happens when creditors take over and “reduce all the rest of the economy to bondage”: it’s what’s called today “austerity” or “debt deflation”.
So “what’s happening in the banking crisis today is that debts grow faster than the economy can pay. And so when the interest rates finally began to be raised by the Federal Reserve, this caused a crisis for the banks.”
Prof. Hudson also proposes an expanded formulation: “The emergence of financial and landholding oligarchies made debt peonage and bondage permanent, supported by a pro-creditor legal and social philosophy that distinguishes Western civilization from what went before. Today it would be called neoliberalism.”
Then he sets out to explain, in excruciating detail, how this state of affairs was solidified in Antiquity in the course of over 5 centuries. One can hear the contemporary echoes of “violent suppression of popular revolts” and “targeted assassination of leaders” seeking to cancel debts and “redistribute land to smallholders who have lost it to large landowners”.
The verdict is merciless: “What impoverished the population of the Roman Empire” bequeathed a “creditor-based body of legal principles to the modern world”.
Predatory oligarchies and “Oriental Despotism”
Prof Hudson develops a devastating critique of the “social darwinist philosophy of economic determinism”: a “self-congratulatory perspective” has led to “today’s institutions of individualism and security of credit and property contracts (favoring creditor claims over debtors, and landlord rights over those of tenants) being traced back to classical antiquity as “positive evolutionary developments, moving civilization away from ‘Oriental Despotism’”.
All that is a myth. Reality was a completely different story, with Rome’s extremely predatory oligarchies waging “five centuries of war to deprive populations of liberty, blocking popular opposition to harsh pro-creditor laws and the monopolization of the land into latifundia estates”.
So Rome in fact behaved very much like a “failed state”, with “generals, governors, tax collectors, moneylenders and carpet beggars” squeezing out silver and gold “in the form of military loot, tribute and usury from Asia Minor, Greece and Egypt.” And yet this Roman wasteland approach has been lavishly depicted in the modern West as bringing a French-style mission civilisatrice to the barbarians – while carrying the proverbial white man’s burden.
Prof. Hudson shows how Greek and Roman economies actually “ended in austerity and collapsed after having privatized credit and land in the hands of rentier oligarchies”. Does that ring a – contemporary – bell?
Arguably the central nexus of his argument is here:
“Rome’s law of contracts established the fundamental principle of Western legal philosophy giving creditor claims priority over the property of debtors – euphemized today as ‘security of property rights’. Public expenditure on social welfare was minimized – what today’s political ideology calls leaving matters to ‘the market’. It was a market that kept citizens of Rome and its Empire dependent for basic needs on wealthy patrons and moneylenders – and for bread and circuses, on the public dole and on games paid for by political candidates, who often themselves borrowed from wealthy oligarchs to finance their campaigns.”
Any similarity with the current system led by the Hegemon is not mere coincidence. Hudson: “These pro-rentier ideas, policies and principles are those that today’s Westernized world is following. That is what makes Roman history so relevant to today’s economies suffering similar economic and political strains.”
Prof. Hudson reminds us that Rome’s own historians – Livy, Sallust, Appian, Plutarch, Dionysius of Halicarnassus, among others – “emphasized the subjugation of citizens to debt bondage”. Even the Delphic Oracle in Greece, as well as poets and philosophers, warned against creditor greed. Socrates and the Stoics warned that “wealth addiction and its money-love was the major threat to social harmony and hence to society.”
And that brings us to how this criticism was completely expunged from Western historiography. “Very few classicists”, Hudson notes, follow Rome’s own historians describing how these debt struggles and land grabs were “mainly responsible for the Republic’s Decline and Fall.”
Hudson also reminds us that the barbarians were always at the gate of the Empire: Rome, in fact, was “weakened from within”, by “century after century of oligarchic excess.”
So this is the lesson we should all draw from Greece and Rome: creditor oligarchies “seek to monopolize income and land in predatory ways and bring prosperity and growth to a halt.” Plutarch was already into it: “The greed of creditors brings neither enjoyment nor profit to them, and ruins those whom they wrong. They do not till the fields which they take from their debtors, nor do they live in their houses after evicting them.”
Beware of pleonexia
It would be impossible to fully examine so many precious as jade offerings constantly enriching the main narrative. Here are just a few nuggets (And there will be more: Prof. Hudson told me, “I’m working on the sequel now, picking up with the Crusades.”)
Prof. Hudson reminds us how money matters, debt and interest came to the Aegean and Mediterranean from West Asia, by traders from Syria and the Levant, around 8th century B.C. But “with no tradition of debt cancellation and land redistribution to restrain personal wealth seeking, Greek and Italian chieftains, warlords and what some classicists have called mafiosi [ by the way, Northern European scholars, not Italians) imposed absentee land ownership over dependent labor.”
This economic polarization kept constantly worsening. Solon did cancel debts in Athens in the late 6th century – but there was no land redistribution. Athens’ monetary reserves came mainly from silver mines – which built the navy that defeated the Persians at Salamis. Pericles may have boosted democracy, but the eventful defeat facing Sparta in the Peloponnesian War (431-404 B.C.) opened the gates to a heavy debt-addicted oligarchy.
All of us who studied Plato and Aristotle in college may remember how they framed the whole problem in the context of pleonexia (“wealth addiction”) – which inevitably leads to predatory and “socially injurious” practices. In Plato’s Republic, Socrates proposes that only non-wealthy managers should be appointed to govern society – so they would not be hostages of hubris and greed.
The problem with Rome is that no written narratives survived. The standard stories were written only after the Republic had collapsed. The Second Punic War against Carthage (218-201 B.C.) is particularly intriguing, considering its contemporary Pentagon overtones: Prof. Hudson reminds us how military contractors engaged in large-scale fraud and fiercely blocked the Senate from prosecuting them.
Prof. Hudson shows how that “also became an occasion for endowing the wealthiest families with public land when the Rome state treated their ostensibly patriotic donations of jewelry and money to aid the war effort as retroactive public debts subject to repayment”.
After Rome defeated Carthage, the glitzy set wanted their money back. But the only asset left to the state was land in Campania, south of Rome. The wealthy families lobbied the Senate and gobbled up the whole lot.
With Caesar, that was the last chance for the working classes to get a fair deal. In the first half of the 1st century B.C. he did sponsor a bankruptcy law, writing down debts. But there was no widespread debt cancellation. Caesar being so moderate did not prevent the Senate oligarchs from whacking him, “fearing that he might use his popularity to ‘seek kingship’” and go for way more popular reforms.
After Octavian’s triumph and his designation by the Senate as Princeps and Augustus in 27 B.C., the Senate became just a ceremonial elite. Prof Hudson summarizes it in one sentence: “The Western Empire fell apart when there was no more land for the taking and no more monetary bullion to loot.” Once again, one should feel free to draw parallels with the current plight of the Hegemon.
Time to “uplift all labor”
In one of our immensely engaging email exchanges, Prof. Hudson remarked how he “immediately had a thought” on a parallel to 1848. I wrote in the Russian business paper Vedomosti: “After all, that turned out to be a limited bourgeois revolution. It was against the rentier landlord class and bankers – but was as yet a far cry from being pro-labor. The great revolutionary act of industrial capitalism was indeed to free economies from the feudal legacy of absentee landlordship and predatory banking — but it too fell back as the rentier classes made a comeback under finance capitalism.”
And that brings us to what he considers “the great test for today’s split”: “Whether it is merely for countries to free themselves from US/NATO control of their natural resources and infrastructure — which can be done by taxing natural-resource rent (thereby taxing away the capital flight by foreign investors who have privatized their natural resources). The great test will be whether countries in the new Global Majority will seek to uplift all labor, as China’s socialism is aiming to do.”
It’s no wonder “socialism with Chinese characteristics” spooks the Hegemon creditor oligarchy to the point they are even risking a Hot War. What’s certain is that the road to Sovereignty, across the Global South, will have to be revolutionary: “Independence from U.S. control is the Westphalian reforms of 1648 — the doctrine of non-interference in the affairs of other states. A rent tax is a key element of independence — the 1848 tax reforms. How soon will the modern 1917 take place?”
Let Plato and Aristotle weigh in: as soon as humanly possible.