By Charles Hugh Smith
Source: Of Two Minds
Please study these charts as a means of understanding the inevitability of economic stagnation and a revolt of the decapitalized middle class.
I’ve been covering the decline of America’s middle class for over a decade with charts, data and commentary on the social depression that has accompanied the decline.
While there are many mutually reinforcing dynamics in this 45-year decline–demographics, global energy costs, financialization and globalization, to name a few– one term describes the accelerating erosion of America’s middle class: decapitalization.
To understand decapitalization, we need to start with the fundamentals of any economy between labor (wages) and capital and between investment and speculation. Although it’s tempting to oversimplify and demonize one or the other of these basics (speculators bad! etc.), they each provide an essential role in a healthy economy, one which is in dynamic equilibrium, a state analogous to a healthy ecosystem with constantly changing interactions of numerous species, individuals and inputs (weather, etc.). This variability enables the order of fluctuations (to use Ilya Prigogine’s profound phrase), a dynamic stability / equilibrium.
If labor’s share of the economy drops too low, the workforce cannot consume enough to support their households and the economy as a whole. If capital can no longer earn an attractive return, investment dries up and production stagnates. If speculators are not allowed to take on risk, liquidity dries up and risk crushes investment. But if speculation becomes the foundation of the economy’s “growth,” then the inevitable collapse of speculative bubbles will crash the economy.
In modern social-capitalist systems, the core stabilizer of the system is the wage-earning middle class which provides the stable workforce driving production and the stable pool of consumers needed to borrow money and consume enough to soak up the production of goods and services at a profit to producers.
Without a stable, dominant middle class, capital has few opportunities to invest in productive capacity. Without a stable, dominant middle class, the economy stagnates and is prone to collapse as it is far from equilibrium.
The process of middle class decline is best explained as decapitalization because the middle class is fundamentally a means of transforming labor into capital via savings and investment. The traditional ladder of social mobility from the working class to the middle class is one of capitalizing work: time and savings are invested in higher education, in effect capitalizing future labor by increasing productivity.
Capital isn’t limited to cash, land or tools; in an information economy, knowledge and skills are also capital, as is the social capital of social networking and relationships formed with mentors, suppliers, lenders, colleagues, investors, etc.
The second way to capitalize work is to save earnings and invest the savings in assets that produce income or gain value: a house, land, rental property, small business and income-producing financial assets such as bonds or dividend-paying stocks.
Thrift, investing, long-term planning and deferred consumption are all essential to capitalizing work by turning that labor into income-producing assets. As the household’s ownership of these assets that yield unearned income rises, so does their income and wealth. These increase the financial security of the household and build a nestegg which can be passed down to the next generation, improving their security via inheritance of income-producing assets.
As long as productivity is increasing the value of their labor, the middle class can leverage future earnings into assets by borrowing money to invest in assets: to buy a house, a mortgage is borrowed against future earnings. As long as the mortgage is a fixed-interest loan and income can be expected to rise with productivity, then this is a win-win situation: capital earns a predictable, low-risk return from the mortgage and the middle class household has stake in a family home, an asset which acts as a savings mechanism as the mortgage slowly pays down the debt and increases the household’s home equity–a form of savings.
The processes of decapitalization have upended this entire structure. In the systems context outlined above, our economy is out of balance and far from equilibrium and thus prone to collapse.
For the bottom 90%, which of course includes the middle class however you define it, it’s increasingly difficult to capitalize labor into capital. There are a number of factors driving this decapitalization:
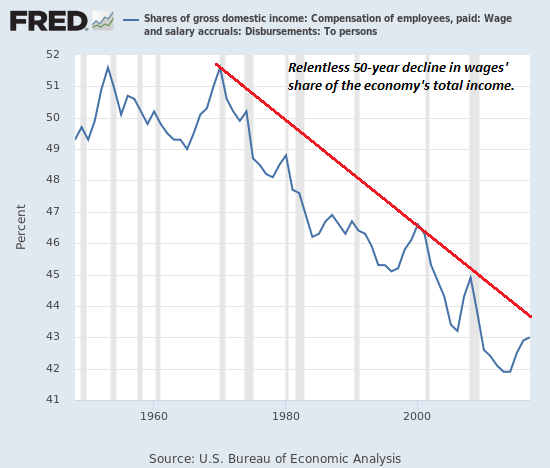
1. Wages’ share of the national income has continued a five-decade downtrend. (See chart below) National income since 1973 has shifted from labor (wages) to capital and more specifically, to debt and speculative gaming of the system, a.k.a. financialization.
Total household income in the U.S. in 2018 was $17.6 trillion. The decline in wages’ share of the national income from 1973 to 2018 is about 8.5%, which equals $1.5 trillion, the sum shifted from labor to capital every year. (See chart below)(source: https://www.statista.com/statistics/216756/us-personal-income/)
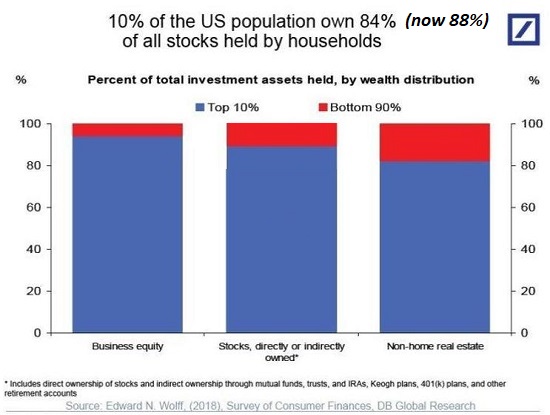
No, this is not a typo. As this RAND report documents, $50 trillion has been siphoned from labor (the lower 90% of the workforce) to the Financial Aristocracy and their technocrat lackeys (the top 10%) who own the vast majority of the capital (see charts below): Trends in Income From 1975 to 2018.
2. Within the workforce, wages have shifted to the top 10% who now earn 50% of all taxable income. (See RAND chart below) Financialization and globalization have decapitalized the skills of entire sectors of the workforce as automation and offshoring reduced the human capital of workers’ skills and experience and the value of their social capital. When the entire industry is offshored, skills and professional relationships lose their market value.
In a fully globalized economy, every worker producing tradable goods/services is competing with the entire global workforce, a reality that reduces wages in high-cost developed nations such as the U.S.
Financialization has heavily rewarded workers with specialized gaming the financial system skills and devalued every other skill as only the skills of financialization are highly profitable in a globalized, financialized economy.
3. As the high-wage jobs and capital shifted to coastal urban centers, middle class owners of homes and capital elsewhere saw the value of their assets decline. If a home valued at $100,000 in the late 1990s is now worth $150,000, the owners lost ground even with “official” inflation. In terms of real-world purchasing power, their home actually lost significant value in the past 23 years.
Meanwhile, middle class owners who bought their home in a coastal hot-spot for $100,000 23 years ago are now enjoying home valuations close to $1 million. Homes, along with every other asset, have been shifted into a casino where almost everyone is sorted into winners and losers, less often by skill and more often by luck.
For those who were too young to buy in 1997, sorry–the opportunity to buy a home for three times average middle class income is gone. The lucky generation who bought in the late 1990s in booming coastal magnets for global capital joined the top 10% and their colleagues in less desirable regions lost ground.
4. As capital siphoned off income and appreciation from labor (human and social capital), the gains accruing to capital accelerated. Those who already owned income-producing assets reaped both income and asset appreciation gains as yields on savings collapsed to near-zero as the Federal Reserve and other central banks dropped yields to near-zero in 2009 and kept them low for the following 13 years.
This had two devastating effects on the middle class: hundreds of billions of dollars that once flowed to savers and money markets disappeared, swallowed by the banks as a direct (and intentional) effect of the Fed’s ZIRP (zero-interest rate policy).
Since the Fed destroyed low-risk yields, anyone seeking any real yield (i.e. above inflation) would have to enter the casino and compete with hedge funds, insiders and the Financial Aristocracy. Very few middle class workers have the skills and experience to beat the pros in the casino, and so income and wealth accrued to those who already owned capital.
This is a key reason why the rich got richer and the poor got poorer. Those with capital accrued the majority of gains in income and wealth, leaving the bottom 90% in the dust.
A recent Foreign Affairs essay Monopoly Versus Democracy included these stunning statistics:
Ten percent of Americans now control 97 percent of all capital income in the country. Nearly half of the new income generated since the global financial crisis of 2008 has gone to the wealthiest one percent of U.S. citizens. The richest three Americans collectively have more wealth than the poorest 160 million Americans. (emphasis added.)
The 3% of income from capital collected by the bottom 90%–which includes the middle class– is basically signal noise: the middle class collects inconsequential crumbs of income from capital.
Prior to the Fed’s ZIRP and financialization of the economy, the middle class could both collect income from capital they owned and they could afford to acquire assets that yielded low-risk solid returns. Now they can do neither. Even worse, the puchasing power of their labor continues to decline, leaving them less able to save and buy assets.
This is why The Top 10% Is Doing Just Fine, The Middle Class Is Dying on the Vine. Please study these charts as a means of understanding the inevitability of economic stagnation and a revolt of the decapitalized middle class.