Diego Rivera, Man at the Crossroads/Man, Controller of the Universe, 1933
By Robert J. Burrowes
Developing the tradition charted by C. Wright Mills in his 1956 classic The Power Elite, in his latest book, Professor Peter Phillips starts by reviewing the transition from the nation state power elites described by authors such as Mills to a transnational power elite centralized on the control of global capital.
Thus, in his just-released study Giants: The Global Power Elite, Phillips, a professor of political sociology at Sonoma State University in the USA, identifies the world’s top seventeen asset management firms, such as BlackRock and J.P Morgan Chase, each with more than one trillion dollars of investment capital under management, as the ‘Giants’ of world capitalism. The seventeen firms collectively manage more than $US41.1 trillion in a self-invested network of interlocking capital that spans the globe.
This $41 trillion represents the wealth invested for profit by thousands of millionaires, billionaires and corporations. The seventeen Giants operate in nearly every country in the world and are ‘the central institutions of the financial capital that powers the global economic system’. They invest in anything considered profitable, ranging from ‘agricultural lands on which indigenous farmers are replaced by power elite investors’ to public assets (such as energy and water utilities) to war.
In addition, Phillips identifies the most important networks of the Global Power Elite and the individuals therein. He names 389 individuals (a small number of whom are women and a token number of whom are from countries other than the United States and the wealthier countries of Western Europe) at the core of the policy planning nongovernmental networks that manage, facilitate and defend the continued concentration of global capital. The Global Power Elite perform two key uniting functions, he argues: they provide ideological justifications for their shared interests (promulgated through their corporate media), and define the parameters of action for transnational governmental organizations and capitalist nation-states.
More precisely, Phillips identifies the 199 directors of the seventeen global financial Giants and offers short biographies and public information on their individual net wealth. These individuals are closely interconnected through numerous networks of association including the World Economic Forum, the International Monetary Conference, university affiliations, various policy councils, social clubs, and cultural enterprises. For a taste of one of these clubs, see this account of The Links in New York. As Phillips observes: ‘It is certainly safe to conclude they all know each other personally or know of each other in the shared context of their positions of power.’
The Giants, Phillips documents, invest in each other but also in many hundreds of investment management firms, many of which are near-Giants. This results in tens of trillions of dollars coordinated in a single vast network of global capital controlled by a very small number of people. ‘Their constant objective is to find enough safe investment opportunities for a return on capital that allows for continued growth. Inadequate capital-placement opportunities lead to dangerous speculative investments, buying up of public assets, and permanent war spending.’
Because the directors of these seventeen asset management firms represent the central core of international capital, ‘Individuals can retire or pass away, and other similar people will move into their place, making the overall structure a self-perpetuating network of global capital control. As such, these 199 people share a common goal of maximum return on investments for themselves and their clients, and they may seek to achieve returns by any means necessary – legal or not…. the institutional and structural arrangements within the money management systems of global capital relentlessly seek ways to achieve maximum return on investment, and … the conditions for manipulations – legal or not – are always present.’
Like some researchers before him, Phillips identifies the importance of those transnational institutions that serve a unifying function. The World Bank, International Monetary Fund, G20, G7, World Trade Organization (WTO), World Economic Forum (WEF), Trilateral Commission, Bilderberg Group, Bank for International Settlements, Group of 30 (G30), the Council on Foreign Relations and the International Monetary Conference serve as institutional mechanisms for consensus building within the transnational capitalist class, and power elite policy formulation and implementation. ‘These international institutions serve the interests of the global financial Giants by supporting policies and regulations that seek to protect the free, unrestricted flow of capital and debt collection worldwide.’
But within this network of transnational institutions, Phillips identifies two very important global elite policy-planning organizations: the Group of Thirty (which has 32 members) and the extended executive committee of the Trilateral Commission (which has 55 members). These nonprofit corporations, which each have a research and support staff, formulate elite policy and issue instructions for their implementation by the transnational governmental institutions like the G7, G20, IMF, WTO, and World Bank. Elite policies are also implemented following instruction of the relevant agent, including governments, in the context. These agents then do as they are instructed. Thus, these 85 members (because two overlap) of the Group of Thirty and the Trilateral Commission comprise a central group of facilitators of global capitalism, ensuring that ‘global capital remains safe, secure, and growing’.
So, while many of the major international institutions are controlled by nation-state representatives and central bankers (with proportional power exercised by dominant financial supporters such as the United States and European Union countries), Phillips is more concerned with the transnational policy groups that are nongovernmental because these organizations ‘help to unite TCC power elites as a class’ and the individuals involved in these organizations facilitate world capitalism. ‘They serve as policy elites who seek the continued growth of capital in the world.’
Developing this list of 199 directors of the largest money management firms in the world, Phillips argues, is an important step toward understanding how capitalism works globally today. These global power elite directors make the decisions regarding the investment of trillions of dollars. Supposedly in competition, the concentrated wealth they share requires them to cooperate for their greater good by identifying investment opportunities and shared risk agreements, and working collectively for political arrangements that create advantages for their profit-generating system as a whole.
Their fundamental priority is to secure an average return on investment of 3 to 10 percent, or even more. The nature of any investment is less important than what it yields: continuous returns that support growth in the overall market. Hence, capital investment in tobacco products, weapons of war, toxic chemicals, pollution, and other socially destructive goods and services are judged purely by their profitability. Concern for the social and environmental costs of the investment are non-existent. In other words, inflicting death and destruction are fine because they are profitable.
So what is the global elite’s purpose? In a few sentences Phillips characterizes it thus: The elite is largely united in support of the US/NATO military empire that prosecutes a repressive war against resisting groups – typically labeled ‘terrorists’ – around the world. The real purpose of ‘the war on terror’ is defense of transnational globalization, the unimpeded flow of financial capital around the world, dollar hegemony and access to oil; it has nothing to do with repressing terrorism which it generates, perpetuates and finances to provide cover for its real agenda. This is why the United States has a long history of CIA and military interventions around the world ostensibly in defense of ‘national interests’.
Wealth and Power
An interesting point that emerges for me from reading Phillips thoughtful analysis is that there is a clear distinction between those individuals and families who have wealth and those individuals who have (sometimes significantly) less wealth (which, nevertheless, is still considerable) but, through their positions and connections, wield a great deal of power. As Phillips explains this distinction, ‘the sociology of elites is more important than particular elite individuals and their families’. Just 199 individuals decide how more than $40 trillion will be invested. And this is his central point. Let me briefly elaborate.
There are some really wealthy families in the world, notably including the families Rothschild (France and the United Kingdom), Rockefeller (USA), Goldman-Sachs (USA), Warburgs (Germany), Lehmann (USA), Lazards (France), Kuhn Loebs (USA), Israel Moses Seifs (Italy), Al-Saud (Saudi Arabia), Walton (USA), Koch (USA), Mars (USA), Cargill-MacMillan (USA) and Cox (USA). However, not all of these families overtly seek power to shape the world as they wish.
Similarly, the world’s extremely wealthy individuals such as Jeff Bezos (USA), Bill Gates (USA), Warren Buffett (USA), Bernard Arnault (France), Carlos Slim Helu (Mexico) and Francoise Bettencourt Meyers (France) are not necessarily connected in such a way that they exercise enormous power. In fact, they may have little interest in power as such, despite their obvious interest in wealth.
In essence, some individuals and families are content to simply take advantage of how capitalism and its ancilliary governmental and transnational instruments function while others are more politically engaged in seeking to manipulate major institutions to achieve outcomes that not only maximize their own profit and hence wealth but also shape the world itself.
So if you look at the list of 199 individuals that Phillips identifies at the centre of global capital, it does not include names such as Bezos, Gates, Buffett, Koch, Walton or even Rothschild, Rockefeller or Windsor (the Queen of England) despite their well-known and extraordinary wealth. As an aside, many of these names are also missing from the lists compiled by groups such as Forbes and Bloomberg, but their absence from these lists is for a very different reason given the penchant for many really wealthy individuals and families to avoid certain types of publicity and their power to ensure that they do.
In contrast to the names just listed, in Phillips’ analysis names like Laurence (Larry) Fink (Chairman and CEO of BlackRock), James (Jamie) Dimon (Chairman and CEO of JPMorgan Chase) and John McFarlane (Chairman of Barclays Bank), while not as wealthy as those listed immediately above, wield far more power because of their positions and connections within the global elite network of 199 individuals.
Predictably then, Phillips observes, these three individuals have similar lifestyles and ideological orientations. They believe capitalism is beneficial for the world and while inequality and poverty are important issues, they believe that capital growth will eventually solve these problems. They are relatively non-expressive about environmental issues, but recognize that investment opportunities may change in response to climate ‘modifications’. As millionaires they own multiple homes. They attended elite universities and rose quickly in international finance to reach their current status as giants of the global power elite. ‘The institutions they manage have been shown to engage in illegal collusions with others, but the regulatory fines by governments are essentially seen as just part of doing business.’
In short, as I would characterize this description: They are devoid of a legal or moral framework to guide their actions, whether in relation to business, fellow human beings, war or the environment and climate. They are obviously typical of the elite.
Any apparent concern for people, such as that expressed by Fink and Dimon in response to the racist violence in Charlottesville, USA in August 2017, is simply designed to promote ‘stability’ or more precisely, a stable (that is, profitable) investment and consumer climate.
The lack of concern for people and issues that might concern many of us is also evident from a consideration of the agenda at elite gatherings. Consider the International Monetary Conference. Founded in 1956, it is a private yearly meeting of the top few hundred bankers in the world. The American Bankers Association (ABA) serves as the secretariat for the conference. But, as Phillips notes: ‘Nothing on the agenda seems to address the socioeconomic consequences of investments to determine the impacts on people and the environment.’ A casual perusal of the agenda at any elite gathering reveals that this comment applies equally to any elite forum. See, for example, the agenda of the recent WEF meeting in Davos. Any talk of ‘concern’ is misleading rhetoric.
Hence, in the words of Phillips: The 199 directors of the global Giants are ‘a very select set of people. They all know each other personally or know of each other. At least 69 have attended the annual World Economic Forum, where they often serve on panels or give public presentations. They mostly attended the same elite universities, and interact in upperclass social setting[s] in the major cities of the world. They all are wealthy and have significant stock holdings in one or more of the financial Giants. They are all deeply invested in the importance of maintaining capital growth in the world. Some are sensitive to environmental and social justice issues, but they seem to be unable to link these issues to global capital concentration.’
Of course, the global elite cannot manage the world system alone: the elite requires agents to perform many of the functions necessary to control national societies and the individuals within them. ‘The interests of the Global Power Elite and the TCC are fully recognized by major institutions in society. Governments, intelligence services, policymakers, universities, police forces, military, and corporate media all work in support of their vital interests.’
In other words, to elaborate Phillips’ point and extend it a little, through their economic power, the Giants control all of the instruments through which their policies are implemented. Whether it be governments, national military forces, ‘military contractors’ or mercenaries (with at least $200 billion spent on private security globally, the industry currently employs some fifteen million people worldwide) used both in ‘foreign’ wars but also likely deployed in future for domestic control, key ‘intelligence’ agencies, legal systems and police forces, major nongovernment organizations, or the academic, educational, ‘public relations propaganda’, corporate media, medical, psychiatric and pharmaceutical industries, all instruments are fully responsive to elite control and are designed to misinform, deceive, disempower, intimidate, repress, imprison (in a jail or psychiatric ward), exploit and/or kill (depending on the constituency) the rest of us, as is readily evident.
Defending Elite Power
Phillips observes that the power elite continually worries about rebellion by the ‘unruly exploited masses’ against their structure of concentrated wealth. This is why the US military empire has long played the role of defender of global capitalism. As a result, the United States has more than 800 military bases (with some scholars suggesting 1,000) in 70 countries and territories. In comparison, the United Kingdom, France, and Russia have about 30 foreign bases. In addition, US military forces are now deployed in 70 percent of the world’s nations with US Special Operations Command (SOCOM) having troops in 147 countries, an increase of 80 percent since 2010. These forces conduct counterterrorism strikes regularly, including drone assassinations and kill/capture raids.
‘The US military empire stands on hundreds of years of colonial exploitation and continues to support repressive, exploitative governments that cooperate with global capital’s imperial agenda. Governments that accept external capital investment, whereby a small segment of a country’s elite benefits, do so knowing that capital inevitably requires a return on investment that entails using up resources and people for economic gain. The whole system continues wealth concentration for elites and expanded wretched inequality for the masses….
‘Understanding permanent war as an economic relief valve for surplus capital is a vital part of comprehending capitalism in the world today. War provides investment opportunity for the Giants and TCC elites and a guaranteed return on capital. War also serves a repressive function of keeping the suffering masses of humanity afraid and compliant.’
As Phillips elaborates: This is why defense of global capital is the prime reason that NATO countries now account for 85 percent of the world’s military spending; the United States spends more on the military than the rest of the world combined.
In essence, ‘the Global Power Elite uses NATO and the US military empire for its worldwide security. This is part of an expanding strategy of US military domination around the world, whereby the US/ NATO military empire, advised by the power elite’s Atlantic Council, operates in service to the Transnational Corporate Class for the protection of international capital everywhere in the world’.
This entails ‘further pauperization of the bottom half of the world’s population and an unrelenting downward spiral of wages for 80 percent of the world. The world is facing economic crisis, and the neoliberal solution is to spend less on human needs and more on security. It is a world of financial institutions run amok, where the answer to economic collapse is to print more money through quantitative easing, flooding the population with trillions of new inflation-producing dollars. It is a world of permanent war, whereby spending for destruction requires further spending to rebuild, a cycle that profits the Giants and global networks of economic power. It is a world of drone killings, extrajudicial assassinations, death, and destruction, at home and abroad.’
Where is this all heading?
So what are the implications of this state of affairs? Phillips responds unequivocally: ‘This concentration of protected wealth leads to a crisis of humanity, whereby poverty, war, starvation, mass alienation, media propaganda, and environmental devastation are reaching a species-level threat. We realize that humankind is in danger of possible extinction’.
He goes on to state that the Global Power Elite is probably the only entity ‘capable of correcting this condition without major civil unrest, war, and chaos’ and elaborates an important aim of his book: to raise awareness of the importance of systemic change and the redistribution of wealth among both the book’s general readers but also the elite, ‘in the hope that they can begin the process of saving humanity.’ The book’s postscript is a ‘A Letter to the Global Power Elite’, co-signed by Phillips and 90 others, beseeching the elite to act accordingly.
‘It is no longer acceptable for you to believe that you can manage capitalism to grow its way out of the gross inequalities we all now face. The environment cannot accept more pollution and waste, and civil unrest is everywhere inevitable at some point. Humanity needs you to step up and insure that trickle-down becomes a river of resources that reaches every child, every family, and all human beings. We urge you to use your power and make the needed changes for humanity’s survival.’
But he also emphasizes that nonviolent social movements, using the Universal Declaration of Human Rights as a moral code, can accelerate the process of redistributing wealth by pressuring the elite into action.
Conclusion
Peter Phillips has written an important book. For those of us interested in understanding elite control of the world, this book is a vital addition to the bookshelf. And like any good book, as you will see from my comments both above and below, it raised more questions for me even while it answered many.
As I read Phillips’ insightful and candid account of elite behavior in this regard, I am reminded, yet again, that the global power elite is extraordinarily violent and utterly insane: content to kill people in vast numbers (whether through starvation or military violence) and destroy the biosphere for profit, with zero sense of humanity’s now limited future. See ‘The Global Elite is Insane Revisited’ and ‘Human Extinction by 2026? A Last Ditch Strategy to Fight for Human Survival’ with more detailed explanations for the violence and insanity here: ‘Why Violence?’ and ‘Fearless Psychology and Fearful Psychology: Principles and Practice’.
For this reason I do not share his faith in moral appeals to the elite, as articulated in the letter in his postscript. It is fine to make the appeal but history offers no evidence to suggest that there will be any significant response. The death and destruction inflicted by elites is highly profitable, centuries-old and ongoing. It will take powerful, strategically-focused nonviolent campaigns (or societal collapse) to compel the necessary changes in elite behavior. Hence, I fully endorse his call for nonviolent social movements to compel elite action where we cannot make the necessary changes without their involvement. See ‘A Nonviolent Strategy to End Violence and Avert Human Extinction’ and Nonviolent Campaign Strategy.
I would also encourage independent action, in one or more of several ways, by those individuals and communities powerful enough to do so. This includes nurturing more powerful individuals by making ‘My Promise to Children’, participating in ‘The Flame Tree Project to Save Life on Earth’ and signing the online pledge of ‘The People’s Charter to Create a Nonviolent World’.
Fundamentally, Giants: The Global Power Elite is a call to action. Professor Peter Phillips is highly aware of our predicament – politically, socially, economically, environmentally and climatically – and the critical role played by the global power elite in generating that predicament.
If we cannot persuade the global power elite to respond sensibly to that predicament, or nonviolently compel it to do so, humanity’s time on Earth is indeed limited.
Biodata: Robert J. Burrowes has a lifetime commitment to understanding and ending human violence. He has done extensive research since 1966 in an effort to understand why human beings are violent and has been a nonviolent activist since 1981. He is the author of ‘Why Violence?’ http://tinyurl.com/whyviolence His email address is flametree@riseup.net and his website is here. http://robertjburrowes.wordpress.com
Robert J. Burrowes
P.O. Box 68
Daylesford, Victoria 3460
Australia
Email: flametree@riseup.net
Websites:
Nonviolence Charter
Flame Tree Project to Save Life on Earth
‘Why Violence?’
Feelings First
Nonviolent Campaign Strategy
Nonviolent Defense/Liberation Strategy
Anita: Songs of Nonviolence
Robert Burrowes
Global Nonviolence Network






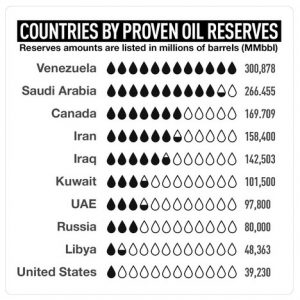 First of all, oil refineries were not built in Venezuela, but in Trinidad and in the southern U.S. Gulf Coast states. This enabled U.S. oil companies – or the U.S. Government – to leave Venezuela without a means of “going it alone” and pursuing an independent policy with its oil, as it needed to have this oil refined. It doesn’t help to have oil reserves if you are unable to get this oil refined so as to be usable.
First of all, oil refineries were not built in Venezuela, but in Trinidad and in the southern U.S. Gulf Coast states. This enabled U.S. oil companies – or the U.S. Government – to leave Venezuela without a means of “going it alone” and pursuing an independent policy with its oil, as it needed to have this oil refined. It doesn’t help to have oil reserves if you are unable to get this oil refined so as to be usable.