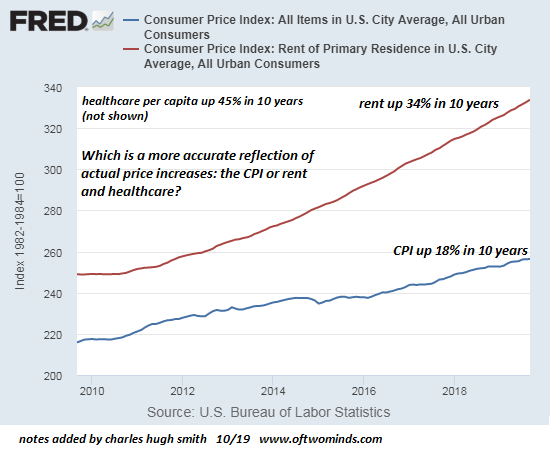
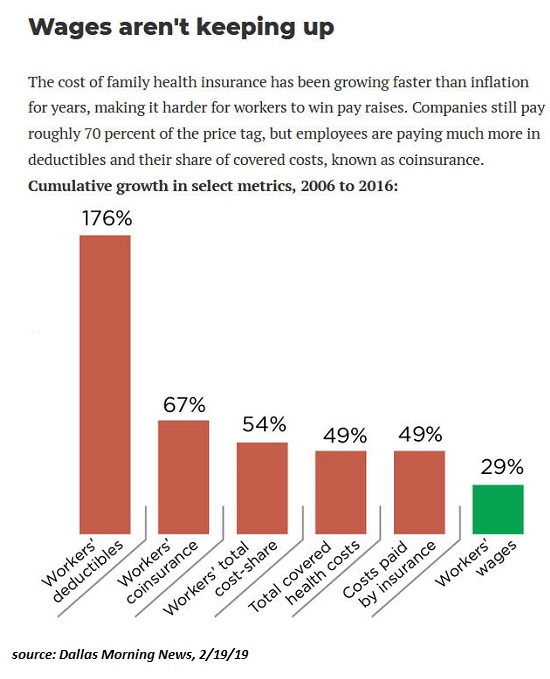
Who’s Who of Prominent Economists Agree: Inequality Harms Economic Growth
By WashingtonsBlog
A who’s who of prominent liberal and conservative economists in government and academia have now said that runaway inequality harms economic growth, including:
- Former U.S. Secretary of Labor and UC Berkeley professor Robert Reich
- Global economy and development division director at Brookings and former economy minister for Turkey, Kemal Dervi
- Societe Generale investment strategist and former economist for the Bank of England, Albert Edwards
- Michael Niemira, chief economist at the International Council of Shopping Centers
- Former executive director of the Joint Economic Committee of Congress, senior policy analyst in the White House Office of Policy Development, and deputy assistant secretary for economic policy at the Treasury Department, Bruce Bartlett
- Deputy Division Chief of the Modeling Unit in the Research Department of the IMF, Michael Kumhof
Even the father of free market economics – Adam Smith – didn’t believe that inequality should be a taboo subject.
Numerous investors and entrepreneurs agree that runaway inequality hurts the economy, including:
How Bad Is It?
So how bad is it, really?
Inequality in America today is twice as bad as in ancient Rome, worse than it was in Tsarist Russia, Gilded Age America, modern Egypt, Tunisia or Yemen, many banana republics in Latin America, and worse than experienced by slaves in 1774 colonial America. (More stunning facts.)
It’s Not an Accident … It’s Policy
Extreme inequality helped cause the Great Depression, the current financial crisis … and the fall of the Roman Empire . Bad government policy – which favors the fatcats at the expense of the average American – is largely responsible for our runaway inequality.
And yet the powers-that-be in Washington and Wall Street are accelerating the redistribution of wealth from the lower, middle and more modest members of the upper classes to the super-elite.
Defenders of the status quo pretend that this inequality is something outside of our control … like a force of nature. They argue that it’s due to technological innovation or something else outside of policy-makers’ control.
In reality, inequality is rising due to bad policy.
Nobel prize winning economist Joe Stiglitz said recently:
Inequality is not inevitable. It is not … like the weather, something that just happens to us. It is not the result of the laws of nature or the laws of economics. Rather, it is something that we create, by our policies, by what we do.
We created this inequality—chose it, really—with [bad] laws …
Gaming the System to Pillage and Loot
The world’s top economic leaders have said for years that inequality is spiraling out of control and needs to be reduced. Why is inequality soaring even though world economic leaders have talked for years about the urgent need to reduce it?
Because they’re saying one thing but doing something very different. And both mainstream Democrats and mainstream Republicans are using smoke and mirrors to hide what’s really going on.
And it’s not surprising … Nobel winner Stiglitz says that inequality is caused by the use of money to shape government policies to benefit those with money. As Wikipedia notes:
A better explainer of growing inequality, according to Stiglitz, is the use of political power generated by wealth by certain groups to shape government policies financially beneficial to them. This process, known to economists as rent-seeking, brings income not from creation of wealth but from “grabbing a larger share of the wealth that would otherwise have been produced without their effort”
Rent seeking is often thought to be the province of societies with weak institutions and weak rule of law, but Stiglitz believes there is no shortage of it in developed societies such as the United States. Examples of rent seeking leading to inequality include
- the obtaining of public resources by “rent-collectors” at below market prices (such as granting public land to railroads, or selling mineral resources for a nominal price in the US),
- selling services and products to the public at above market prices (medicare drug benefit in the US that prohibits government from negotiating prices of drugs with the drug companies, costing the US government an estimated $50 billion or more per year),
- securing government tolerance of monopoly power (The richest person in the world in 2011, Carlos Slim, controlled Mexico’s newly privatized telecommunication industry).
(Background here, here and here.)
Stiglitz says:
One big part of the reason we have so much inequality is that the top 1 percent want it that way. The most obvious example involves tax policy …. Monopolies and near monopolies have always been a source of economic power—from John D. Rockefeller at the beginning of the last century to Bill Gates at the end. Lax enforcement of anti-trust laws, especially during Republican administrations, has been a godsend to the top 1 percent. Much of today’s inequality is due to manipulation of the financial system, enabled by changes in the rules that have been bought and paid for by the financial industry itself—one of its best investments ever. The government lent money to financial institutions at close to 0 percent interest and provided generous bailouts on favorable terms when all else failed. Regulators turned a blind eye to a lack of transparency and to conflicts of interest.
***
Wealth begets power, which begets more wealth …. Virtually all U.S. senators, and most of the representatives in the House, are members of the top 1 percent when they arrive, are kept in office by money from the top 1 percent, and know that if they serve the top 1 percent well they will be rewarded by the top 1 percent when they leave office. By and large, the key executive-branch policymakers on trade and economic policy also come from the top 1 percent. When pharmaceutical companies receive a trillion-dollar gift—through legislation prohibiting the government, the largest buyer of drugs, from bargaining over price—it should not come as cause for wonder. It should not make jaws drop that a tax bill cannot emerge from Congress unless big tax cuts are put in place for the wealthy. Given the power of the top 1 percent, this is the way you would expect the system to work.
Former Sectretary of Labor Robert Reich recently noted:
When so much wealth accumulates at the top, with money comes the capacity to control politics… It’s not that people are rich, it’s that they abuse their wealth … The wealthy contribute to political candidates and the access that their contributions buy entrenches inequality by securing subsidies, bailouts and policies that lead to even greater inequality.
Bloomberg reports:
The financial industry spends hundreds of millions of dollars every election cycle on campaign donations and lobbying, much of which is aimed at maintaining the subsidy [to the banks by the public]. The result is a bloated financial sector and recurring credit gluts.
Indeed, the big banks literally own the Federal Reserve. And they own Washington D.C. politicians, lock stock and barrel. See this, this, this and this.
Two leading IMF officials, the former Vice President of the Dallas Federal Reserve, and the the head of the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, Moody’s chief economist and many others have all said that the United States is controlled by an “oligarchy” or “oligopoly”, and the big banks and giant financial institutions are key players in that oligarchy.
The chairman of the Department of Economics at George Mason University says that it is inaccurate to call politicians prostitutes. Specifically, he says that they are more correct to call them “pimps”, since they are pimping out the American people to the financial giants.
Economics professor Randall Wray writes:
Thieves … took over the whole economy and the political system lock, stock, and barrel.
No wonder the government has saved the big banks at taxpayer expense, chosen the banks over the little guy, and said no to helping Main Street … while continuing to throw trillions at the giant banks.
No wonder crony capitalism has gotten even worse under Obama than under Bush.
No wonder big Wall Street players are continuing to loot taxpayer money and public resources.
No wonder the big banks continue to manipulate every market and commit crime after crime and … and profit handsomely from it, while law-abiding citizens slide further and further behind.
Yet Obama is prosecuting fewer financial crimes than Bush, or his father, or Ronald Reagan.
No wonder:
All of the monetary and economic policy of the last 3 years has helped the wealthiest and penalized everyone else. See this, this and this.
***
Economist Steve Keen says:
“This is the biggest transfer of wealth in history”, as the giant banks have handed their toxic debts from fraudulent activities to the countries and their people.
Stiglitz said in 2009 that Geithner’s toxic asset plan “amounts to robbery of the American people”.
And economist Dean Baker said in 2009 that the true purpose of the bank rescue plans is “a massive redistribution of wealth to the bank shareholders and their top executives”.
Without the government’s creation of the too big to fail banks (they’ve gotten much bigger under Obama), the Fed’s intervention in interest rates and the markets (most of the quantitative easing has occurred under Obama), and government-created moral hazard emboldening casino-style speculation (there’s now more moral hazard than ever before) … things wouldn’t have gotten nearly as bad.
As we wrote in March 2009:
The bailout money is just going to line the pockets of the wealthy, instead of helping to stabilize the economy or even the companies receiving the bailouts:
- A lot of the bailout money is going to the failing companies’ shareholders
- Indeed, a leading progressive economist says that the true purpose of the bank rescue plans is “a massive redistribution of wealth to the bank shareholders and their top executives”
- The Treasury Department encouraged banks to use the bailout money to buy their competitors, and pushed through an amendment to the tax laws which rewards mergers in the banking industry (this has caused a lot of companies to bite off more than they can chew, destabilizing the acquiring companies)
As we pointed out in 2008:
The game of capitalism only continues as long as everyone has some money to play with. If the government and corporations take everyone’s money, the game ends.The fed and Treasury are not giving more chips to those who need them: the American consumer. Instead, they are giving chips to the 800-pound gorillas at the poker table, such as Wall Street investment banks. Indeed, a good chunk of the money used by surviving mammoth players to buy the failing behemoths actually comes from the Fed.
Quantitative Easing
It is well-documented that quantitative easing increases inequality (and see this and this.)
Quantitative easing doesn’t help Main Street or the average American. It only helps big banks, giant corporations, and big investors.
The Federal Reserve has been doing quantitative easing for 5 years … and inequality has shot up over the last 5 years. It’s not a coincidence.
Subsidies to Giant, Wealthy Corporations
Massive subsidies to big corporations is also part of the problem. Indeed, some financial analysts say that the taxpayer subsidy to the giant banks alone is $780 billion per year.
The average American family pays $6,000/year in subsidies to giant corporations.
This is a direct transfer of wealth from the little guy to the big guy … which increases inequality.
Goosing the Stock Market
Moreover, the Fed has more or less admitted that it is putting almost all of its efforts into boosting the stock market.
Robert Reich has noted:
Some cheerleaders say rising stock prices make consumers feel wealthier and therefore readier to spend. But to the extent most Americans have any assets at all their net worth is mostly in their homes, and those homes are still worth less than they were in 2007. The “wealth effect” is relevant mainly to the richest 10 percent of Americans, most of whose net worth is in stocks and bonds.
AP writes:
The recovery has been the weakest and most lopsided of any since the 1930s.After previous recessions, people in all income groups tended to benefit. This time, ordinary Americans are struggling with job insecurity, too much debt and pay raises that haven’t kept up with prices at the grocery store and gas station. The economy’s meager gains are going mostly to the wealthiest.
Workers’ wages and benefits make up 57.5 percent of the economy, an all-time low. Until the mid-2000s, that figure had been remarkably stable — about 64 percent through boom and bust alike.
David Rosenberg points out:
The “labor share of national income has fallen to its lower level in modern history … some recovery it has been – a recovery in which labor’s share of the spoils has declined to unprecedented levels.”
The above-quoted AP article further notes:
Stock market gains go disproportionately to the wealthiest 10 percent of Americans, who own more than 80 percent of outstanding stock, according to an analysis by Edward Wolff, an economist at Bard College.
Indeed, as we reported in 2010:
As of 2007, the bottom 50% of the U.S. population owned only one-half of one percent of all stocks, bonds and mutual funds in the U.S. On the other hand, the top 1% owned owned 50.9%.***
(Of course, the divergence between the wealthiest and the rest has only increased since 2007.)
Professor G. William Domhoff demonstrated that the richest 10% own 98.5% of all financial securities, and that:
The top 10% have 80% to 90% of stocks, bonds, trust funds, and business equity, and over 75% of non-home real estate. Since financial wealth is what counts as far as the control of income-producing assets, we can say that just 10% of the people own the United States of America.
Tyler Durden notes:
In today’s edition of Bloomberg Brief, the firm’s economist Richard Yamarone looks at one of the more unpleasant consequences of Federal monetary policy: the increasing schism in wealth distribution between the wealthiest percentile and everyone else. … “To the extent that Federal Reserve policy is driving equity prices higher, it is also likely widening the gap between the haves and the have-nots….The disparity between the net worth of those on the top rung of the income ladder and those on lower rungs has been growing. According to the latest data from the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances, the total wealth of the top 10 percent income bracket is larger in 2009 than it was in 1995. Those further down have on average barely made any gains. It is likely that data for 2010 and 2011 will reveal an even higher percentage going to the top earners, given recent increases in stocks.” Alas, this is nothing new, and merely confirms speculation that the Fed is arguably the most efficient wealth redistibution, or rather focusing, mechanism available to the status quo. This is best summarized in the chart below comparing net worth by income distribution for various percentiles among the population, based on the Fed’s own data. In short: the richest 20% have gotten richer in the past 14 years, entirely at the expense of everyone else.

***
Lastly, nowhere is the schism more evident, at least in market terms, than in the performance of retail stocks:
Saks chairman Steve Sadove recently remarked, “I’ve been saying for several years now the single biggest determinant of our business overall, is how’s the stock market doing.” Privately-owned Neiman- Marcus reported “In New York City, business at Bergdorf Goodman continues to be extremely strong.”
In contrast, retail giant Wal-Mart talks of its “busiest hours” coming at midnight when food stamps are activated and consumers proceed through the check-outs lines with baby formula, diapers, and other groceries. Wal-Mart has posted a decline in same-store sales for eight consecutive quarters.
As CNN Money pointed out in 2011, “Wal-Mart’s core shoppers are running out of money much faster than a year ago …” This trend has only gotten worse: The wealthy are doing great … but common folks can no longer afford to shop even at Wal-Mart, Sears, JC Penney or other low-price stores.
Durden also notes:
Another indication of the increasing polarity of US society is the disparity among consumer confidence cohorts by income as shown below, and summarized as follows: “The increase in equity prices has raised consumer spirits, particularly among higher-income consumers. The Conference Board’s Consumer Confidence index for all income levels bottomed in February/March of 2009. The recovery since then has been notable across the board, but nowhere as much as for those making $50,000 or more.”

Business Week notes:
Barry Ritholtz, [CIO of Ritholtz Wealth, and popular financial blogger], says millions of potential investors may conclude, as they did after the Great Depression, that the market is a rigged game for insiders. Such seismic shifts in popular sentiment can have lasting effects. The Dow Jones industrial average didn’t regain its September 1929 peak of 355.95 until 1954. “You’re going to lose a generation of investors,” says Ritholtz. “And that’s how you end up with a 25-year bear market. That’s the risk if people start to think there is no economic justice.”
Americans know that the system is rigged against them. See this. We know that the government is giving Wall Street crooks a pass. 70% of Americans know that the government’s economic policies have thrown money at the banks and hosed the people.
In such an environment, the average American has largely gotten out of stocks and other investments.
Over-Financialization
When a country’s finance sector becomes too large finance, inequality rises. As Wikipedia notes:
[Economics professor] Jamie Galbraith argues that countries with larger financial sectors have greater inequality, and the link is not an accident.
Government policy has been encouraging the growth of the financial sector for decades:

(Economist Steve Keen has also shown that “a sustainable level of bank profits appears to be about 1% of GDP”, and that higher bank profits leads to a ponzi economy and a depression).
Unemployment and Underemployment
A major source of inequality is unemployment, underemployment and low wages.

Government policy has created these conditions. And the pretend populist Obama – who talks non-stop about the importance of job-creation – actually doesn’t mind such conditions at all.
The“jobless recovery” that the Bush and Obama governments have engineered is a redistribution of wealth from the little guy to the big boys.
The New York Times notes:
Economists at Northeastern University have found that the current economic recovery in the United States has been unusually skewed in favor of corporate profits and against increased wages for workers.
In their newly released study, the Northeastern economists found that since the recovery began in June 2009 following a deep 18-month recession, “corporate profits captured 88 percent of the growth in real national income while aggregate wages and salaries accounted for only slightly more than 1 percent” of that growth.
The study, “The ‘Jobless and Wageless Recovery’ From the Great Recession of 2007-2009,” said it was “unprecedented” for American workers to receive such a tiny share of national income growth during a recovery.
***
The share of income growth going to employee compensation was far lower than in the four other economic recoveries that have occurred over the last three decades, the study found.
Obama apologists say Obama has created jobs. But the number of people who have given up and dropped out of the labor force has skyrocketed under Obama (and see this).

And the jobs that have been created have been low-wage jobs.

For example, the New York Times noted in 2011:
The median pay for top executives at 200 big companies last year was $10.8 million. That works out to a 23 percent gain from 2009.
***
Most ordinary Americans aren’t getting raises anywhere close to those of these chief executives. Many aren’t getting raises at all — or even regular paychecks. Unemployment is still stuck at more than 9 percent.
***
“What is of more concern to shareholders is that it looks like C.E.O. pay is recovering faster than company fortunes,” says Paul Hodgson, chief communications officer for GovernanceMetrics International, a ratings and research firm.
According to a report released by GovernanceMetrics in June, the good times for chief executives just keep getting better. Many executives received stock options that were granted in 2008 and 2009, when the stock market was sinking.
Now that the market has recovered from its lows of the financial crisis, many executives are sitting on windfall profits, at least on paper. In addition, cash bonuses for the highest-paid C.E.O.’s are at three times prerecession levels, the report said.
***
The average American worker was taking home $752 a week in late 2010, up a mere 0.5 percent from a year earlier. After inflation, workers were actually making less.
AP pointed out that the average worker is not doing so well:
Unemployment has never been so high — 9.1 percent — this long after any recession since World War II. At the same point after the previous three recessions, unemployment averaged just 6.8 percent.
– The average worker’s hourly wages, after accounting for inflation, were 1.6 percent lower in May than a year earlier. Rising gasoline and food prices have devoured any pay raises for most Americans.
– The jobs that are being created pay less than the ones that vanished in the recession. Higher-paying jobs in the private sector, the ones that pay roughly $19 to $31 an hour, made up 40 percent of the jobs lost from January 2008 to February 2010 but only 27 percent of the jobs created since then.
Alan Greenspan noted:
Large banks, who are doing much better and large corporations, whom you point out and everyone is pointing out, are in excellent shape. The rest of the economy, small business, small banks, and a very significant amount of the labour force, which is in tragic unemployment, long-term unemployment – that is pulling the economy apart.
Money Being Sucked Out of the U.S. Economy … But Big Bucks Are Being Made Abroad
Part of the widening gap is due to the fact that most American companies’ profits are driven by foreign sales and foreign workers. As AP noted in 2010:
Corporate profits are up. Stock prices are up. So why isn’t anyone hiring?
Actually, many American companies are — just maybe not in your town. They’re hiring overseas, where sales are surging and the pipeline of orders is fat.
***
The trend helps explain why unemployment remains high in the United States, edging up to 9.8% last month, even though companies are performing well: All but 4% of the top 500 U.S. corporations reported profits this year, and the stock market is close to its highest point since the 2008 financial meltdown.
But the jobs are going elsewhere. The Economic Policy Institute, a Washington think tank, says American companies have created 1.4 million jobs overseas this year, compared with less than 1 million in the U.S. The additional 1.4 million jobs would have lowered the U.S. unemployment rate to 8.9%, says Robert Scott, the institute’s senior international economist.
“There’s a huge difference between what is good for American companies versus what is good for the American economy,” says Scott.
***
Many of the products being made overseas aren’t coming back to the United States. Demand has grown dramatically this year in emerging markets like India, China and Brazil.
Government policy has accelerated the growing inequality. It has encouraged American companies to move their facilities, resources and paychecks abroad. And some of the biggest companies in America have a negative tax rate … that is, not only do they pay no taxes, but they actually get tax refunds.
And a large percentage of the bailouts went to foreign banks (and see this). And so did a huge portion of the money from quantitative easing. More here and here.
Capital Gains and Dividends
According to a 2013 study published by a researcher at the U.S. Congressional Research Service:
The largest contributor to increasing income inequality…was changes in income from capital gains and dividends.
Business Insider explains:
Drastic income inequality growth in the United States is largely derived from changes in the way the U.S. government taxes income from capital gains and dividends, according to a new study by Thomas Hungerford of the non-partisan Congressional Research Service.
Essentially, what Democrats have been saying about income inequality — that it’s in a large part due to favorable taxation and deduction policies for high income Americans — is largely right
***
The study … conclusively found that the wealthy benefitted from low tax rates on investment income, which in turn caused their wealth to grow faster.
Essentially, taxing capital gains as ordinary income would make the playing field more fair, and reduce over time income inequality.
Joseph Stiglitz noted in 2011:
Lowering tax rates on capital gains, which is how the rich receive a large portion of their income, has given the wealthiest Americans close to a free ride.
Indeed, the Tax Policy center reports that the top 1% took home 71% of all capital gains in 2012.
Ronald Reagan’s budget director, assistant secretary of treasury, and domestic policy director all say that the Bush tax cuts were a huge mistake. See this and this.