
By Dmitry Orlov
Source: Club Orlov
Most people are familiar with the game Monopoly. Its goal is to teach capitalist kiddies a valuable lesson about capitalism; namely, that in running a business it isn’t useful to shoot for some happy modicum of accommodation with your competitors or to strive for a sustainable steady state. Instead, what you need to do to survive (never mind win) is to grow as quickly as possible and eat up your competitors alive, or you’ll get eaten up yourself. That’s not just a game; that’s exactly how capitalism actually works, and if that doesn’t work for you (it doesn’t for most people) then that’s exactly how capitalism doesn’t work.
And so the Waltons couldn’t just run Walmart as a mart; they had to make it into a global empire—just in order to survive. Now, most governments in the world realize that this sort of unbridled capitalism is harmful and seek to regulate it. For instance, Russia has a Federal Antimonopoly Service. The US Justice Department has an Antitrust Division, which is aptly named if its mission is to destroy Americans’ trust in their government’s ability to regulate business. It also has a website which currently says: “Due to the lapse in appropriations, Department of Justice websites will not be regularly updated.” Perhaps that’s all right for a country that seeks to monopolize everything—international finance and law, defense procurement and, of course, the dispensation of “freedom and democracy” and “universal values.”
Most people are also familiar with the concept of national debt. The federal debt of the US government currently equals… never mind; it’s going up much faster than you can write it down. If you want to watch it go up real time, you can look it up here. The exact number is useless: if you take a snapshot of it—say, $21,921,420,945,123.00—that will no longer be the payoff amount by the time you write out the check, and if you write out the check, no matter who you are, it will bounce. But it won’t even get that far: if you mail that check to the US Treasury Department, they wouldn’t be able to deposit it because “Due to the lapse in appropriations…” (You get the picture.)
The debt goes up all the time, and the rate at which it goes up is accelerating. The concept of acceleration may not be intuitive for some of you, so let me explain. Debt goes up with some speed. Acceleration is the amount by which that speed increases, measured in, for example, dollars per minute per minute. Calculating it is a fun little arithmetic exercise. During Barak Obama’s reign it went up by $8.6 trillion, starting from $11.6 trillion and gong up to $20.2 trillion. Trump plans to add $4.8 trillion during his first three years. (Relevant numbers can be looked up here).
Thus, Obama’s velocity was $8.6 trillion over 8 years—roughly $1 trillion per year or $2 million per minute while Trump’s velocity is roughly $1.6 trillion per year or a little over $3 million per minute. Therefore, the acceleration is only a few cents per minute per minute—but it sure adds up! Acceleration tends to sneak up on you. For instance, if you want to gain some intuitive appreciation for acceleration due to gravity (9.81m or 32 feet per second per second) then try jumping off a chair while keeping your knees straight. You can also ponder the fact that satellites that fall out of Earth’s orbit tend to burn up on reentry as they decelerate due to friction with the atmosphere.
Any sane, numerate person can tell you that increases in debt are fine provided your revenues are increasing significantly faster, but if that’s not the case then the eventual result is bankruptcy. And that is most definitely not the case. Hence the name of this board game is National Bankruptcy. But I am not sure what the objective of the game should be. Is it to go bankrupt as quickly and efficiently as possible, or is to go bankrupt as slowly and painfully as possible?
I am quite sure that players who aren’t on a path to national bankruptcy would prefer to keep it that way, and would furthermore prefer to be rid of all sovereign debt issued by whoever is going to go bankrupt before that happens. (Russia seems to have that problem solved already while China is far behind.) In any case, I am a very serious person who doesn’t like jokes and doesn’t have time to play games, board games included, so I’ll leave it to others to ponder such questions. Still, the board game metaphor seems useful for discussing this topic.
One problem with playing this game is the problem of scale. People have a problem appreciating such huge numbers. They are familiar with what a dollar is, but what’s a trillion? Here it is, represented as double-stacked pallets of $100 bills.
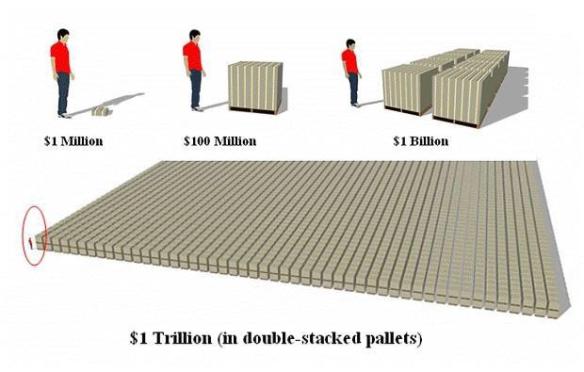
That seems a bit cumbersome for our board game. Reasonable values for the chips in our National Bankruptcy game would be $100 billion, $500 billion and $1 trillion. We could use a few $5 trillion and $10 trillion chips too, though not too many because I doubt that the game would go on long enough to make them useful.
I propose that for the sake of this game we introduce a handy new unit called a “piffle” which is equal to $100 billion. A trillion is 10 piffles, 10 trillion is 100 piffles. Then our chips can be 1, 5, 10, 50 and 100 piffles. Piffles allow us to express various huge quantities without going through any arithmetic contortions. US federal debt is currently 220 piffles. US trade deficit for 2018 was 6 piffles while the US defense budget was 7 piffles. For 2019 the federal budget deficit (covered by increased borrowing) is 10 piffles and rising while tax revenues are just 3 piffles and falling. The interest payment on federal debt is 3 piffles but with rising interest rates it’s going to 5 piffles within a few years.
Speaking of rising interest rates… just today Trump wished for 0% interest rates again, like Obama had while he was running up his 80 piffles’ worth of debt. But now it’s hovering around 3% and is unlikely to go down no matter what Trump wishes. Why? Well, here’s the reason. The US imports much more than it exports because it can’t afford to or lacks the ability to make all the stuff it needs; that’s why there are 6 piffles’ worth of trade deficit. When other nations sell to the US more than they buy, they end up holding lots of piffles, and since the US needs lots of piffles (remember, the budget deficit is 10 piffles) it makes plenty of sense to borrow that money right back. A little while back it was possible to borrow it back at 0% interest because the US was powerful enough to threaten those who refused to play this game with military annihilation (cue pictures of bombed-out Libya and Iraq). But times have changed, and unless the US bribes its debt-holders with 3% interest rate or better—no deal.
How have times changed? There are two effects worth mentioning. First, the military annihilation threat isn’t working any more. Yes, the US still spends a stunning, record-shattering sum of 7 piffles on defense, but none of that is working. Call it the free money effect. When people spend their own hard-earned money, they tend to be careful with it, but if it’s somebody else’s money that they got for free never intending to pay it back, then they tend to throw caution to the wind. And so US military spending has become less and less effective over time, in one of two ways: procurement costs have gone through the roof, and the resulting products have become useless.
In terms of procurement costs, the purchasing parity between the US and (just as an example) Russia seems to be at least ten to one: to get the same result, the US has to spend at least ten times more than Russia. And so although Russia spends well less than 1 piffle on defense, its military is far more effective. In terms of product uselessness, the Pentagon now resembles a woman who has a closet jam-packed with expensive designer labels but has absolutely nothing to wear because her entire wardrobe is no longer fashionable. There is the entire set of aircraft carriers none of which can operate close enough to enemy shores to be of any use at all because they can be readily sunk using hypersonic rockets launched from very far away. There are the stockpiles of Tomahawk cruise missiles which can’t make it past Soviet-era air defense systems (with a few electronics and software upgrades). There are the Patriot air defense systems which are useless even for stopping Soviet-era SCUD missiles, never mind anything more modern.
Add to this Russia’s (and soon China’s) new hypersonic weapons with conventional payloads and new air and space defense systems such as the S-400: these provide what’s known as “escalation dominance.” Suppose the US does something unspeakably nasty and Russia and/or China decide to teach it a lesson. They now have the ability to blow up any target within the US without getting anywhere near it and without placing any of their military assets at risk.
They could, for instance, take out the US electric grid in a way that will take many months to get it back on line. They can then reliably intercept anything that the US tries to retaliate with. Of course, the US can become suicidal—that’s always a risk—and launch a full-on nuclear first strike, then sit back and wait to be completely obliterated along with much of the rest of the planet. But that’s not a military strategy, that’s pure suicide, and the officers in charge of military strategy tend to be emotionally stable family men who look forward to playing with their grandchildren upon retirement.
So, why then should the US continue to spend 7 piffles on defense? The sad answer is that it will go bankrupt whether it zeroes out the defense budget or not. If the defense budget goes to 0, then there is still 3 piffles’ worth of budget deficit left, plus those 6 piffles of trade deficit aren’t going anywhere but up. But what about MAGA?—you might ask—What about firing up US manufacturing, bringing the jobs back and exporting our way out of this? After all, if we turn those 6 piffles of trade deficit into 6 piffles of trade surplus, suddenly it all works out and bankruptcy becomes avoidable.
No, sorry, that just not realistic. You see, in order to get an industrial economy going again the US needs several things. It needs cheap energy, cheap labor, low cost of doing business and readily available markets, both domestic and export. And the US doesn’t have any of these. In terms of energy—and oil is by far the most important form of energy—in 2019 the US will import exactly as much oil as it did in 1998—around 8 million barrels a day. Yes, the shale oil industry has sprung up in the meantime, and the US is currently producing 11.5 million barrels per day. But also in the meantime US oil consumption has gone up a lot—to 20 million barrels a day, which is a stunning 20% of the world’s consumption for 4.4% of the world’s population.
And so the oil deficit is still very much there. Plus the shale oil patch has never made any money but has accumulated over 2 piffles’ worth of debt and has spent over a piffle’s worth more than it made. With interest rates going up they are unlikely to be able to borrow enough to keep up the same hectic drilling rate, and with declines from existing wells at over half a million barrels per day per month it won’t take many months to whittle down that 11.5 million barrels per day, forcing the US to either boost imports or cut consumption.
But the oil price has gone down a lot lately, so there shouldn’t be a problem in any case, right? Again, sorry, no. Peak Oil for most countries has come and gone. There is now only a handful of countries left that are able to meaningfully boost oil production: Russia, Canada (mostly tar sands), Iran, Iraq, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait and Brazil. Russia has recently announced that it isn’t planning to boost production. Saudi Arabia is a huge oil producer but does not seem to have any spare capacity left. Canada’s tar sands patch is a money-losing environmental disaster. Iran and Iraq (call them Iranq, since they are both Shia Moslem, are politically aligned and neither loves America too much) aren’t exactly going to gallop to the rescue. That leaves UAE, Kuwait and Brazil, and if you add them all up together that’s nowhere near enough. So, get ready for oil price spikes, followed by a wave of demand destruction, followed by oil price collapses, followed by supply destruction—you know, the usual.
Moving on to labor. In order to stay competitive, the US will need to lower its median wage a lot. It has to be lower than what the Chinese and the Southeast Asians earn because the US needs to outcompete them to steal their export market share. Without various other major changes this will cause US workers to either rebel or starve to death in short order. The changes involve nationalizing medicine and education to drive down their costs by a factor of 1000 or so, converting to public transportation and pretty much banning the use of private cars to make transportation affordable, putting up high-rises right next to factories for affordable worker housing and so on. That’s a lot of piffles’ worth of effort!
The cost of doing business is a tough one too. The US spends way more on courts and lawyers, insurance and regulatory compliance than most other countries, and the regulatory maze that entrepreneurs have to run in order to run even a small and simple business is very costly and absolutely confounding. How does one take a machete to that whole ridiculous, corrupt scheme? I have no idea. It’s an imponderable. The Chinese would probably just call it a “cultural revolution,” round up all the lawyers and the bureaucrats, make them wear dunce caps and sandwich boards that say “I am what is wrong with this country” and march them in procession while pelting them with rocks and beating them with sticks. Something like that…
Finally, there is the question of export markets. What exactly is the US going to export more effectively than other countries are exporting already? China out-manufactures just about anybody on the planet and isn’t about to give up its spot. Russia exports grain and other foodstuffs (all non-GMO, unlike the US), nuclear and space technology, defense technology (that actually works) and much else. Pakistan and India, and various other countries, export textiles. The world is full up with product. It’s consumers to bankrupt that are in short supply. And if the US cuts its labor rates to make itself competitive, then its consumer base will shrink rather dramatically.
So it looks like bankruptcy is it, no use fighting it. But what should the US do in the meantime? I suggest that it should put up some really huge walls—just for the sake of leaving behind some spectacular ruins for future generations to marvel at. The one along the southern border seems to be going up already, but there should be at least two more. There needs to be a wall along the Mason-Dixon line, because given the heated state of US politics there needs to be a way to prevent people from trying to reenact the Civil War (a misnomer, that!) with actual real weapons and live ammo. And there also needs to be a wall along the northern border, to keep various groups of armed troglodytes from escaping to Canada and ransacking it (it’s the least we can do for our peaceful northern neighbors). How much will these three walls cost? Glad you asked! They will cost roughly 0.005 piffles apiece, 0.015 piffles total—a truly piffling amount. That’s my 0.000000002 piffle’s worth. But, you know, it’s the thought that counts.
Oh, and if you want to actually design this National Bankruptcy board game, please resist the temptation to contact me about it. Seriously, I don’t like games, board games especially. I am a very serious person who doesn’t have time for such piffles.






