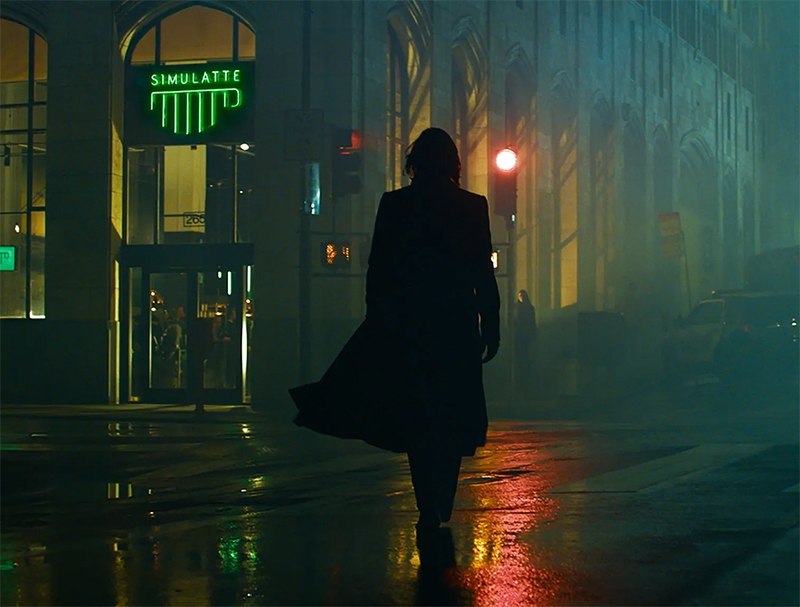By John Semley
Source: The Baffler
“It was an embarrasser; what did I want? I hadn’t thought that far ahead. Me, caught without a program!”
—Bruce Bethke, “Cyberpunk” (1983)
Held annually in a downtown L.A. convention center so massive and glassy that it served as a futurist backdrop for the 1993 sci-fi action film Demolition Man and as an intergalactic “Federal Transport Hub” in Paul Verhoeven’s 1997 space-fascism satire Starship Troopers, the Electronic Entertainment Expo, a.k.a. “E3,” is the trade show of the future. Sort of.
With “electronic entertainment” now surpassing both music and movies (and, indeed the total earnings of music and movies combined), the future of entertainment, or at least entertainment revenue, is the future of video games. Yet it’s a future that’s backward-looking, its gaze locked in the rearview as the medium propels forward.
Highlights of E3’s 2019 installment included more details around a long-gestating remake of the popular PlayStation 1-era role-playing game Final Fantasy VII, a fifth entry in the demon-shooting franchise Doom, a mobile remake of jokey kids side-scroller Commander Keen, and playable adaptations of monster-budget movie franchises like Star Wars and The Avengers. But no title at E3 2019 garnered as much attention as Cyberpunk 2077, the unveiling of which was met with a level of slavish mania one might reserve for a stadium rock concert, or the ceremonial reveal of an efficacious new antibiotic.
An extended trailer premiere worked to whet appetites. Skyscrapers stretched upward, slashed horizontally with long windows of light and decked out with corporate branding for companies called “DATA INC.” and “softsys.” There were rotating wreaths of bright neon billboards advertising near-futuristic gizmos and gee-gaws, and, at the street level, sketchy no-tell motels and cars of the flying, non-flying, and self-piloting variety. In a grimy, high-security bunker, a man with a buzzcut, his face embedded with microchips, traded blows with another, slightly larger man with a buzzcut, whose fists were robotically augmented like the cyborg Special Forces brawler Jax from Mortal Kombat. The trailer smashed to its title, and to wild applause from congregated gamers and industry types.
Then, to a chug-a-lug riff provided by Swedish straight-edge punkers Refused (recording under the nom de guerre SAMURAI) that sounded like the sonic equivalent of a can of Monster energy drink, an enormous freight-style door lifted, revealing, through a haze of pumped-out fog, a vaguely familiar silhouette: a tall, lean-muscular stalk, scraggly hair cut just above the shoulders. Over the PA system, in smoothly undulating, bass-heavy movie trailer tones, a canned voice announced: “Please welcome . . . Keanu Reeves.” Applause. Pitchy screams. Hysterics in the front row prostrating themselves in Wayne’s World “we’re not worthy!” fashion. “I gotta talk to ya about something!” Reeves roared through the din. Dutifully reading from a teleprompter, he plugged Cyberpunk 2077’s customizable characters and its “vast open world with a branching storyline,” set in “a metropolis of the future where body modification has become an obsession.”
More than just stumping for Cyberpunk 2077, Reeves lent his voice and likeness to the game as a non-playable character (NPC) named “Johnny Silverhand,” who is described in the accompanying press materials as a “legendary rockerboy.” A relative newbie to the world of blockbuster Xbox One games, Reeves told the audience at E3 that Cyberpunk piqued his interest because he’s “always drawn to fascinating stories.” The comment is a bit rich—OK, yes, this is a trade show pitch, but still—considering that such near-futuristic, bodily augmented, neon-bathed dystopias are hardly new ground for Reeves. His appearance in Cyberpunk 2077 serves more to lend the game some genre cred, given Reeves’s starring roles in canonical sci-fi films such as Johnny Mnemonic (1995) and the considerably more fantastic Matrix trilogy (1999-2003)—now quadrilogy; with an anticipated fourth installment announced just recently. Like many of E3 2019’s other top-shelf titles, Cyberpunk 2077 looked forward by reflecting back, conjuring its tech-noir scenario from the nostalgic ephemera of cyberpunk futures past.
This was hardly lost among all the uproar and excitement. Author William Gibson, a doyenne of sci-fi’s so-called “cyberpunk” subgenre, offered his own withering appraisal of Cyberpunk 2077, tweeting that the game was little more than a cloned Grand Theft Auto, “skinned-over with generic 80s retro-future” upholstery. “[B]ut hey,” Gibson added, a bit glibly, “that’s just me.” One would imagine that, at least in the burrows of cyberpunk fandom, Gibson’s criticism carries considerable weight.
After all, the author’s 1984 novel Neuromancer is a core text in cyberpunk literature. Gibson also wrote the screenplay for Johnny Mnemonic, adapted from one of his own short stories, which likewise developed the aesthetic and thematic template for the cyberpunk genre: future dystopias in which corporations rule, computer implants (often called “wetware”) permit access to expansive virtual spaces that unfold before the user like a walk-in World Wide Web, scrappy gangs of social misfits unite to hack the bad guys’ mainframes, and samurai swords proliferate, along with Yakuza heavies, neon signs advertising noodle bars in Kanji, and other fetish objects imported from Japanese pop culture. Gibson dissing Cyberpunk 2077 is a bit like Elvis Presley clawing out of his grave to disparage the likeness of an aspiring Elvis impersonator.
Gibson’s snark speaks to a deeper malaise that has beset cyberpunk. A formerly lively genre that once offered a clear, if goofy, vision of the future, its structures of control, and the oppositional forces undermining those authoritarian edifices, it has now been clouded by a kind of self-mythologizing nostalgia. This problem was diagnosed as early as 1991 by novelist Lewis Shiner, himself an early cyberpunk-lit affiliate.
“What cyberpunk had going for it,” Shiner wrote in a New York Times op-ed titled “Confessions of an Ex-Cyberpunk, “was the idea that technology did not have to be intimidating. Readers in their teens and 20’s responded powerfully to it. They were tired of hearing how their home computers were tempting them into crime, how a few hackers would undermine Western civilization. They wanted fiction that could speak to the sense of joy and power that computers gave them.”
That sense of joy had been replaced, in Shiner’s estimation, by “power fantasies” (think only of The Matrix, in which Reeves’s moonlighting hacker becomes a reality-bending god), which offer “the same dead-end thrills we get from video games and blockbuster movies” (enter, in due time, the video games and blockbuster movies). Where early cyberpunk offerings rooted through the scrap heap of genre, history, and futurist prognostication to cobble together a genre that felt vital and original, its modern iterations have recourse only to the canon of cyberpunk itself, smashing together tropes, clichés, and old-hat ideas that, echoing Gibson’s complaint, feel pathetically unoriginal.
As Refused (in their pre-computer game rock band iteration) put it on the intro to their 1998 record The Shape of Punk to Come: “They told me that the classics never go out of style, but . . . they do, they do.”
Blade Ran
The word was minted by author Bruce Bethke, who titled a 1980 short story about teenage hackers “Cyberpunk.” But cyberpunk’s origins can be fruitfully traced back to 1968, when Philip K. Dick published Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?, a novel that updated the speculative fiction of Isaac Asimov’s Robot series for the psychedelic era. It’s ostensibly a tale about a bounty hunter named Rick Deckard chasing rogue androids in a post-apocalyptic San Francisco circa 1992. But like Dick’s better stories, it used its ready-made pulp sci-fi premise to flick at bigger questions about the nature of sentience and empathy, playing to a readership whose conceptions of consciousness were expanding.
Ridley Scott brought Dick’s story to the big screen with a loose 1982 film adaptation, Blade Runner, which cast Harrison Ford as Deckard and pushed its drizzly setting ahead to 2019. With its higher order questions about what it means to think, to feel, and to be free—and about who, or what, is entitled to such conditions—Blade Runner effectively set a cyberpunk template: the billboards, the neon, the high-collared jackets, the implants, the distinctly Japanese-influenced mise-en-scène extrapolated from Japan’s 1980s-era economic dominance. It is said that William Gibson saw Blade Runner in theaters while writing Neuromancer and suffered something of a crisis of conscience. “I was afraid to watch Blade Runner,” Gibson told The Paris Review in 2011. “I was right to be afraid, because even the first few minutes were better.” Yet Gibson deepened the framework established by Blade Runner with a crucial invention that would come to define cyberpunk as much as drizzle and dumpsters and sky-high billboards. He added another dimension—literally.
Henry Case, Gibson establishes early on, “lived for the bodiless exultation of cyberspace.” As delineated in Neuromancer, cyberspace is an immersive, virtual dimension. It’s a fully realized realm of data—“bright lattices of logic unfolding across that colorless void”—which hackers can “jack into” using strapped-on electrodes. That the matrix is “bodiless” is a key concept, both of Neuromancer and of cyberpunk generally. It casts the Gibsonian idea of cyberspace against another of the genre’s hallmarks: the high-tech body mods flogged by Keanu Reeves during the Cyberpunk 2077 E3 demo.
Early in Neuromancer, Gibson describes these sorts of robotic, cyborg-like implants and augmentations. A bartender called Ratz has a “prosthetic arm jerking monotonously” that is “cased in grubby pink plastic.” The same bartender has implanted teeth: “a webwork of East European steel and brown decay.” Gibson’s intense, earthy descriptions of these body modifications cue the reader into the fundamental appeal of Neuromancer’s matrix, in which the body itself becomes utterly immaterial. Authors from Neal Stephenson (Snow Crash) to Ernest Cline (Ready Player One, which is like a dorkier Snow Crash, if such a thing is conceivable), further developed this idea of what theorist Fredric Jameson called “a whole parallel universe of the nonmaterial.”
As envisioned in Stephenson’s Snow Crash, circa 1992, this parallel universe takes shape less as some complex architecture of unfathomable data, and more as an immersive, massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG). Stephenson’s “Metaverse”—a “moving illustration drawn by [a] computer according to specifications coming down the fiber-optic cable”—is not a supplement to our real, three-dimensional world of physical bodies, but a substitute for it. Visitors navigate the Metaverse using virtual avatars, which are infinitely customizable. As Snow Crash’s hero-protagonist, Hiro Protagonist (the book, it should be noted, is something of a satire), describes it: “Your avatar can look any way you want it to . . . If you’re ugly, you can make your avatar beautiful. If you’ve just gotten out of bed, your avatar can still be wearing beautiful clothes and professionally applied makeup. You can look like a gorilla or a dragon or a giant talking penis in the Metaverse.”
Beyond Meatspatial Reasoning
The Metaverse seems to predict the wide-open, utopian optimism of the internet: that “sense of joy and power” Lewis Shiner was talking about. It echoes early 1990s blather about the promise of a World Wide Web free from corporate or government interests, where users could communicate with others across the globe, forge new identities in chat rooms, and sample from a smorgasbord of lo-res pornographic images. Key to this promise was, to some extent, forming new identities and relationships by leaving one’s physical form behind (or jacked into a computer terminal in a storage locker somewhere).
Liberated from such bulky earthly trappings, we’d be free to pursue grander, more consequential adventures inside what Gibson, in Neuromancer, calls “the nonspace of the mind.” Elsewhere in cyberpunk-lit, bodies are seen as impediments to the purer experience of virtuality. After a character in Cory Doctorow’s Down and Out in the Magic Kingdom unplugs from a bracingly real simulation immersing him in the life of Abraham Lincoln, he curses the limitations of “the stupid, blind eyes; the thick, deaf ears.” Or, as Case puts it in Neuromancer, the body is little more than “meat.”
In Stephenson’s Metaverse, virtual bodies don’t even obey the tedious laws of physics that govern our non-virtual world. In order to manage the high amount of pedestrian traffic within the Metaverse and prevent users from bumping around endlessly, the complicated computer programming permits avatars simply to pass through one another. “When things get this jammed together,” Hiro explains, “the computer simplifies things by drawing all of the avatars ghostly and translucent so you can see where you’re going.” Bodies—or their virtual representations—waft through one another, as if existing in the realm of pure spirit. There is an almost Romantic bent here (Neuromancer = “new romancer”). If the imagination, to the Romantics, opened up a gateway to deep spiritual truth, here technology serves much the same purpose. Philip K. Dick may have copped something of the 1960s psychedelic era’s ethos of expanding the mind to explore the radiant depths of the individual soul, spirit, or whatever, but cyberpunk pushed that ethos outside, creating a shared mental non-space accessible by anyone with the means—a kind of Virtual Commons, or what Gibson calls a “consensual hallucination.”
Yet outside this hallucination, bodies still persist. And in cyberpunk, the physical configurations of these bodies tend to express their own utopian dimension. Bruce Bethke claimed that “cyberpunk” resulted from a deliberate effort to “invent a new term that grokked the juxtaposition of punk attitudes and high technology.” Subsequent cyberpunk did something a bit different, not juxtaposing but dovetailing those “punk attitudes” with high-tech. (“Low-life, high-tech” is a kind of a cyberpunk mantra.) Neuromancer’s central heist narrative gathers a cast of characters—hacker Henry Case, a cybernetically augmented “Razorgirl” named Molly Millions, a drug-addled thief, a Rastafari pilot—that can be described as “ragtag.” The major cyberpunk blockbusters configure their anti-authoritarian blocs along similar lines.
In Paul Verhoeven’s cyberpunk-y action satire Total Recall, a mighty construction worker-cum-intergalactic-spy (Arnold Schwarzenegger) joins a Martian resistance led by sex workers, physically deformed “mutants,” little people, and others whose physical identities mirror their economic alienation and opposition to a menacing corporate-colonial overlord named Cohaagen.
In Johnny Mnemonic, Keanu Reeves’s businesslike “mnemonic courier” (someone who ferries information using computer implants embedded in the brain) is joined by a vixenish bodyguard (Dina Meyer’s Jane, herself a version of Neuromancer’s Molly Millions), a burly doctor (Henry Rollins), and a group of street urchin-like “Lo-Teks” engaged in an ongoing counterinsurgency against the mega-corporation Pharmakom. Both Mnemonic and Recall rely on cheap twists, in which a figure integral to the central intrigue turns out to be something ostensibly less- or other-than-human. Total Recall has Kuato, a half-formed clairvoyant mutant who appears as a tumorous growth wriggling in the abdomen of his brother. Even more ludicrously, Mnemonic’s climax reveals that the Lo-Teks’ leader is not the resourceful J-Bone (Ice-T), but rather Jones, a computer-augmented dolphin. In cyberpunk, the body’s status as “dead meat” to be transcended through computer hardware and neurological implantation offers a corollary sense of freedom.
The idea of the cybernetic body as a metaphor for the politicized human body was theorized in 1985, cyberpunk’s early days, by philosopher and biologist Donna Haraway. Dense and wildly eclectic, by turns exciting and exasperating, Haraway’s “Cyborg Manifesto” is situated as an ironic myth, designed to smash existing oppositions between science and nature, mind and body. Haraway was particularly interested in developing an imagistic alternative to the idea of the “Goddess,” so common to the feminism of the time. Where the Goddess was backward-looking in orientation, attempting to connect women to some prelapsarian, pre-patriarchal state of nature, the cyborg was a myth of the future, or at least of the present. “Cyborg imagery,” she writes, “can suggest a way out of the maze of dualisms in which we have explained our bodies and our tools to ourselves.” Part machine and part flesh, Haraway visualizes the cyborg as a being that threatens existing borders and assumes responsibility for building new ones.
Though they are not quite identical concepts, Haraway’s figure of the cyborg and the thematics of cyberpunk share much in common. A character like Gibson’s Molly Millions, for example, could be described as a cyborg, even if she is still essentially gendered as female (the gender binary was one of the many “dualisms” Haraway believed the cyborg could collapse). Cyborgs and cyberpunk are connected in their resistance to an old order, be it political and economic (as in Neuromancer, Johnny Mnemonic, etc.) or metaphysical (as in Haraway). The cyborg and the cyberpunk both dream of new futures, new social relationships, new bodies, and whole new categories of conceptions and ways of being.
The historical problem is that, for the most part, these new categories and these new relationships failed to materialize, as cyberpunk’s futures were usurped and commodified by the powers they had hoped to oppose.
Not Turning Japanese
In an introduction to the Penguin Galaxy hardcover reissue of Neuromancer, sci-fi-fantasy writer Neil Gaiman ponders precisely how the 1980s cyberpunk visions came to shape the future. “I wonder,” he writes, “to what extent William Gibson described a future, and how much he enabled it—how much the people who read and loved Neuromancer made the future crystallize around his vision.”
It’s a paradox that dogs most great sci-fi writers, whose powers for Kuato-style clairvoyance have always struck me as exaggerated. After all, it’s not as if, say, Gene Roddenberry literally saw into the future, observed voice-automated assistants of the Siri and Alexa variety, and then invented his starship’s speaking computers. It’s more that other people saw the Star Trek technology and went along inventing it. The same is true of Gibson’s matrix or Stephenson’s Metaverse, or the androids of Asimov and Dick. And the realization of many technologies envisioned by cyberpunk—including the whole concept of the internet, which now operates not as an escapist complement to reality, but an essential part of its fabric, like water or heat—has occurred not because of scrappy misfits and high-tech lowlifes tinkering in dingy basements, but because of gargantuan corporate entities. Or rather, the cyberpunks have become the corporate overlords, making the transition from the Lo-Teks to Pharmakom, from Kuato to Cohaagen. In the process, the genre and all its aspirations have been reduced to so much dead meat. This is what Shiner was reacting to when, in 1991, he renounced his cyberpunk affiliations, or when Bruce Bethke, who coined the term, began referring to “cyberpunk” as “the c-word.”
The commodification of the cool is a classic trick of capitalism, which has the frustrating ability to mutate faster than the forces that oppose it. Yet even this move toward commodification and corporatization is anticipated in much cyberpunk. “Power,” for Neuromancer’s Henry Case, “meant corporate power.” Gibson goes on: “Case had always taken it for granted that the real bosses, the kingpins in a given industry, would be both more and less than people.” For Case (and, it follows, Gibson, at least at the time of his writing), this power had “attained a kind of immortality” by evolving into an organism. Taking out one-or-another malicious CEO hardly matters when lines of substitutes are waiting in the wings to assume the role.
It’s here that cyberpunk critiques another kind of body. Not the ruddy human form that can be augmented and perfected by prosthetics and implants, but the economic body. Regarding the economy as a holistic organism—or a constituent part of one—is an idea that dates back at least as far as Adam Smith’s “invisible hand.” The rhetoric of contemporary economics is similarly biological. An edifying 2011 argument in Al Jazeera by Paul Rosenberg looked at the power of such symbolic conceptions of the economy. “The organic metaphor,” Rosenberg writes, “tells people to accept the economy as it is, to be passive, not to disturb it, to take a laissez faire attitude—leave it alone.”
This idea calls back to another of cyberpunk’s key aesthetic influences: the “body economic” of Japan in the 1980s. From the 2019 setting of 1982’s Blade Runner, to the conspicuous appearance of yakuza goons in Gibson’s stories, to Stephenson’s oddly anachronistic use of “Nipponese” in Snow Crash, cyberpunk’s speculative futures proceed from the economic ascendency of 1980s Japan, and the attendant anxiety that Japan would eventually eclipse America as an economic powerhouse. This idea, that Japan somehow is (or was) the future, has persisted all the way up to Cyberpunk 2077’s aesthetic template, and its foregrounding of villains like the shadowy Arasaka Corporation. It suggests that, even as it unfolds nearly sixty years from our future, the blockbuster video game is still obsessed with a vision of the future past.
Indeed, it’s telling that as the robust Japanese economy receded in the 1990s, its burly body giving up the proverbial ghost, that Japanese cinema became obsessed with avenging spirits channeled into the present by various technologies (a haunted video cassette in Hideo Nakata’s Ringu, the internet itself in Kiyoshi Kurosawa’s Kairo, etc.). But in the 1980s, Japan’s economic and technologic dominance seemed like a foregone conclusion. In a 2001 Time article, Gibson called Japan cyberpunk’s “de facto spiritual home.” He goes on:
I remember my first glimpse of Shibuya, when one of the young Tokyo journalists who had taken me there, his face drenched with the light of a thousand media-suns—all that towering, animated crawl of commercial information—said, “You see? You see? It is Blade Runner town.” And it was. It so evidently was.
Gibson’s analysis features one glaring mistake. His insistence that “modern Japan simply was cyberpunk” is tethered to its actual history as an economic and technological powerhouse circa the 1980s, and not from its own science-fictional preoccupations. “It was not that there was a cyberpunk movement in Japan or a native literature akin to cyberpunk,” he writes. Except there so evidently was.
The Rusting World
Even beyond the limp, Orwellian connotations, 1984 was an auspicious year for science-fiction. There was Neuromancer, yes. But 1984 also saw the first collected volume of Akira, a manga written and illustrated by Katsuhiro Otomo. Originally set, like Blade Runner, in 2019, Akira imagines a cyberpunk-y Neo-Tokyo, in which motorcycle-riding gangs do battle with oppressive government forces. Its 1988 anime adaptation was even more popular, in both Japan and the West. (The film’s trademark cherry red motorcycle has been repeatedly referenced in the grander cyberpunk canon, appearing in Steven Spielberg’s film adaptation of Ready Player One and, if pre-release hype is to believed, in Cyberpunk 2077 itself.) In 2018, the British Film Institute hailed Akira, accurately, as “a vital cornerstone of the cyberpunk genre.”
Japan has plenty of other, non-Akira cyberpunk touchstones. As a cinematic subgenre, Japanese cyberpunk feels less connected to the “cyber” and more to the spirit of “punk,” whether in the showcasing of actual Japanese punk rock bands (as in 1982’s Burst City) or the films’ own commitment to a rough-hewn, low-budget, underground aesthetic. Chief among the latter category of films is Shinya Tsukamoto’s Tetsuo: The Iron Man, which was shot on 16mm over a grueling year-and-a-half, mostly in and around Tetsuo actress and cinematographer Kei Fujiwara’s apartment, which also housed most of the film’s cast and crew.
Unlike the Western cyberpunk classics, Tsukamoto’s vision of human-machine hybridization is demonstrably more nightmarish. The film follows two characters, credited as the Salaryman (Tomorowo Taguchi) and the Guy (a.k.a. “The Metal Fetishist,” played by writer/director/producer/editor Tsukamoto himself), bound by horrifying mutations, which see their flesh and internal organs sprouting mechanical hardware.
In its own way, Tetsuo works as a cyberpunk-horror allegory for the Japanese economy. As the Salaryman and the Fetishist learn to accept the condition of their mechanization, they merge together, absorbing all the inorganic matter around them, growing enormously like a real-world computer virus or some terrifying industrial Katamari. Their mission resonates like a perverse inversion of Japan’s post-industrial promise. As Tsukamoto’s Fetishist puts it: “We can rust the whole world and scatter it into the dust of the universe.”
Like Haraway’s development of the cyborg as a metaphoric alternative to the New Age “goddess,” Tetsuo’s titular Iron Man can offer a similar corrective. If cyberpunk has become hopelessly obsessed with its own nostalgia, recycling all its 1980s bric-a-brac endlessly, then we need a new model. Far from the visions of Gibson, in which technology provides an outlet for a scrappy utopian impulse that jeopardizes larger corporate-political dystopias, Tetsuo is more pessimistic. It sees the body—both the individual physical body and the grander corpus of political economy—as being machine-like. Yet, as Rosenberg notes in his Al Jazeera analysis of economic rhetoric, it may be more useful to conceive of the economy not as a “body” or an organism but as a machine. The body metaphor is conservative, “with implications that tend toward passivity and acceptance of whatever ills there may be.” Machines, by contrast, can be fixed, greased, re-oriented. They are, unlike bodies, a thing separate from us, and so subject to our designs.
Cybernetic implants and cyborg technology are not some antidote to corporate hegemony. The human does not meld with technology to transcend the limitations of humanity. Rather, technology and machinery pose direct threats to precisely that condition. We cannot, in Tsukamoto’s film, hack our way to a better future, or technologically augment our way out of collective despair. Technology—and the mindless rush to reproduce it—are, to Tsukamoto, the very conditions of that despair. Even at thirty years old, Tetsuo offers a chilling vision not of the future, or of 1980s Japan, but of right now: a present where the liberating possibilities of technology have been turned inside-out; where hackers become CEOs whose platforms bespoil democracy; where automation offers not the promise of increased wealth and leisure time, but joblessness, desperation, and the wholesale redundancy of the human species; where the shared hallucination of the virtual feels less than consensual.
There’s nothing utopian about the model of cyberpunk developed in Tetsuo: The Iron Man. It is purely dystopian. But this defeatism offers clarity. And in denying the collaborative, collectivist, positive vision of a technological future in favor of a vision of identity-destroying, soul-obliterating horror, Tsukamoto’s stone-cold classic of Japanese cyberpunk invites us to imagine our own anti-authoritarian, anti-corporate arrangements. The enduring canon of American-style cyberpunk may have grown rusty. It has been caught, as Bethke put it in his genre-naming story, “without a program.” But the genre’s gnarlier, Japanese iterations have plenty to offer, embodying sci-fi’s dream of imagining a far-off future as a deep, salient critique of the present. It is only when we accept this cruel machinery of the present that we can freely contemplate how best to tinker with its future.
Left to peddle such a despairing vision in a packed-out L.A. convention center, even cyberpunk’s postmortem poster boy Keanu Reeves would be left with little to say but a resigned, bewildered, “Woah . . .”