By Eric Zuesse
Source: Strategic Culture Foundation
The way that Congress and the President structured America’s coronavirus bailout legislation, the protections that go to the super-wealthy start immediately, but the protections that go to the neediest — the soaring numbers of unemployed, the increasingly endangered medical workers, etc. — require documentation which is creating delays that might soon cause many of these individuals to lose their homes, their cars, even their lives.
On April 17th, Matt Taibbi headlined “The Trickle-Up Bailout” and he noted that:
As we head into the second month of pandemic lockdown, two parallel narratives are developing about the financial rescue.
In one, ordinary people receive aid through programs that are piecemeal, complex, and riddled with conditions.
A law freezing evictions applies to holders of government-backed mortgages only. “Disaster grants” are coming more slowly and in smaller amounts than expected; small businesses were disappointed to learn from the SBA early last week that aid would be limited to $1000 per employee.
That’s typical.
As I had already explained on April 14th:
America’s bailout package to overcome the coronavirus ‘recession’ is twofold:
One part is printing money for employees and consumers, so that they won’t be thrown out onto the streets for non-payment of debts such as mortgages, car-loans, credit cards, and student loans.
Another part is printing money for bondholders and stockholders, so that their investments will still have value and there won’t be panicked selling of them as corporations accumulate soaring losses because consumers are staying home and are cutting way back on expenses.
The top-down part of the bailout (the part for investors) will merely add to the wealth of the already-wealthy, while everybody else sinks financially into oblivion. (On April 9th, the Zero Hedge financial site explained in detail why even bailing out the airlines would hurt the economy more than help the economy.) The top-down part supplies the money to the corporations instead of to their employees and consumers, and is therefore supply-boosting instead of demand-boosting. Supplying money to the corporations that the Government selects to protect will enable those corporations to buy up assets and corporations which during the crisis are being auctioned off by the ones that go out of business, and this will leave the nation’s wealth in even fewer hands than before the epidemic struck.
The bottom-up part (the part for workers and consumers) will be exactly the opposite of that: it will help prevent another Great Depression. By boosting purchases, instead of bailing-out billionaires and such, it will enable the economy to keep functioning, and it will not increase the concentration of wealth.
However, employees and consumers don’t have many lobbyists, but billionaires do, and billionaires also own (through political donations and lobbyists) almost all members of Congress (and also the mainstream press), and they not only own, but are represented by, one inside the White House, who is surrounded there by others, and by representatives of others, so that the concerns of the wealthiest will be very well represented by America’s Government, and will end up dominating the bailouts, so that only the insiders, who are well-connected in Washington, will be protected. (And Joe Biden would be no improvement over Donald Trump, though his rhetoric is different.)
Already, we see, in the ‘news’-reports, that there is ‘chaos’ etc. in the U.S. Government’s response to the crisis, but what’s not being reported in the mainstream ‘news’-media is that there very much is method to this seeming madness, and it is the method of the well-practiced and well-funded takers, definitely not of their victims, from whom they (and their Government) have been, and now increasingly are, taking. The takers own the Deep State, and are protected by it. The vast bulk of the bailouts will go to them. The vast bulk of the bailouts will go to suppliers (investors), not to their workers and consumers.
So, as a general rule: the more that a person’s income depends upon investments, and the less that it depends upon their labor (wages), the more fully that the bailouts will compensate for the losses they’ll be suffering as a result of the coronavirus disruptions.
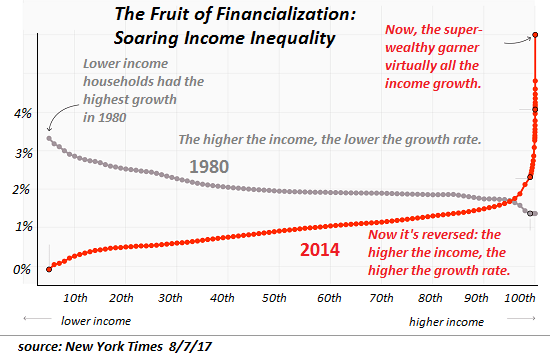
Here is a breakdown of the incomes that the super-rich receive (mainly from investments), versus the incomes that everybody else receive:

As can easily be seen there, only the super-rich (the top 1%, and most especially the top 0.1%) receive the majority of their incomes from investments (“Business income” and “Capital income”). Everybody else receives it mainly from “compensation” (wages), “retirement income,” and “Transfer income” (welfare).
Most of the benefits to the top 0.1% will be coming by means of monetary policy, via the Federal Reserve, not by means of fiscal policy — such as the payments to the unemployed (which are subject to many delays) and such as the $1,200-per-adult grants (which were the fastest to be paid because it’s the “helicopter money” that buys votes for the political incumbents, all of whom had voted for the bailouts).
The bailouts’ widely publicized part is the $2.2 trillion, since that includes whatever the public gets. However, that part is the smaller portion of the entire program. As CBS News reported on March 24th, “Top White House economic adviser Larry Kudlow said the price tag of economic stimulus amounts to roughly $6 trillion, which includes $2 trillion for direct assistance, and roughly $4 trillion in Federal Reserve lending power. Kudlow said this will be the single-largest such Main Street financial package in the history of the country.” Kudlow said it at a White House press conference. He mentioned there just in passing (at 1:36), that it’s a “six trillion-dollar program, four trillion dollars in lending power from the Fed, that’s a six trillion-dollar package …,” and the reporters in the White House press corps didn’t ask him anything about the Fed’s part, the $4 trillion portion (the program’s part that protects the billionaires); they evidently didn’t care about that, but only about the $2.2 trillion, which is actually the PR decoration on this $6T cake — the $2.2T that the public is interested in, the bait-part of the entire bailout-program. (Its hook won’t sink in until the readers’ children and grandchildren will be paying for it via their taxes in a stripped America.) However, on March 26th, Wall Street on Parade (WSP) — the best investigative-reporting source about Wall Street — headlined “Stimulus Bill Allows Federal Reserve to Conduct Meetings in Secret; Gives Fed $454 Billion Slush Fund for Wall Street Bailouts” and disclosed that even what Kudlow had called “Main Street” (the $2.2T part) included much for Wall Street; and WSP then rhetorically asked, “Why does the Federal Reserve need $454 billion from the U.S. taxpayer to bail out Wall Street when it has the power to create money out of thin air and has already dumped more than $9 trillion cumulatively in revolving loans to prop up Wall Street’s trading houses since September 17, 2019 – long before there was any diagnosis of coronavirus anywhere in the world?” They promptly answered this: “The Fed needs that money to create more Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) — the same device used by Enron to hide its toxic debt off its balance sheet before it went belly up.” Furthermore, the $454 billion, which WSP called “the money the Treasury is handing over to the Fed” is what CBS had reported “would result in ‘$4 trillion in Federal Reserve lending power’.” And U.S. taxpayers are guaranteeing 100% of these loans to investors — so, it’s “heads you win, tails we lose,” for taxpayers addressing billionaires, and “heads we win, tails you lose,” for billionaires addressing taxpayers. The billionaires win, the public loses. But the billionaires’ media don’t mention this fact, that investors get the guarantees, while the public takes all of the risks. However, what is an “investment” for, if non-investors are receiving its risks? It’s just legalized crime. And these are huge risks, and all or most of the $454 billion that the U.S. is lending to the Fed to guarantee private investors’ investments could be destroyed in the coronavirus-crisis. This is far more socialism for the super-rich than for the bottom 99%. The billionaires love socialism when they’re the ones who are getting the bailouts — the public taking on the risks that investors are supposed to assume. The issue for billionaires isn’t “socialism versus capitalism,” like they always say; it’s actually “socialism for us, and capitalism for everybody else.” That’s not “survival of the fittest,” for the wealthiest class; it’s instead their ordering their politicians to: protect our wealth, no matter what the cost to the public could turn out to be. And that’s precisely what the President and Congress did. Kudlow, however, said, instead, that the “package” would produce “a good rebound in the second half of the year.” Maybe for the billionaires it would.
Kudlow was simply being consistent with his own prior record. On 10 December 2007, he had headlined in National Review, “Bush Boom Continues: You can call it Goldilocks 2.0. But you can’t call it a recession.” And he closed by saying, “This sort of fiscal and monetary coordination will continue the Bush boom for years to come.” He’s good for the billionaires; and, so, today, he’s President Trump’s top economic advisor. He’s up there, because he’s wrong — not because he’s right. (If he had been right, he wouldn’t be there.)
After the immediate crisis is over, America will have a top 0.1% who are unscathed and whose mega-corporations will be selling not only what they had been selling before, but selling virtually everything that sells in the post-coronavirus world. For examples: what mom-and-pop businesses (including restaurants, B&Bs, etc.) had previously been selling, will, in the future, be supplied (to the extent that it remains being supplied at all) by McDonalds, Starbucks, Marriott, Amazon, Target, Walmart, and other megacorporations (controlled by billionaires), which will have been receiving, from the Fed, and from the Treasury, whatever they needed in order to carry their investors through the crisis-period. (And who are those investors? Look at that chart above, the recipients mainly of “Business income” and “Capital income” — the chief recipients of dividends, interest, and capital gains incomes.)
Furthermore: after the crisis, commercial real estate will be super-cheap, because of all the bankrupted mom-and-pop businesses. Wages also will decline, as the public become increasingly desperate, and the billionaires win increasing market-power. Therefore, not only will the megacorporations be selling a larger percentage of the national output, but their expenses will go down.
Consequently: America will have lots more poor people, and lots wealthier billionaires.
This, however, will be only a temporary situation, because the enormous spread of poverty will result in greatly decreased taxes coming into all levels of the U.S. Government. Bridges will collapse, potholes will proliferate, unendowed colleges will close, nervous breakdowns and heart-attacks will increase, and thus the public won’t be able to spend as much as they were spending before the crisis hit. And, so, although the megacorporations will be selling a larger percentage of national output, that national output will decline, because of the spreading poverty. Therefore, even the billionaires won’t necessarily become richer than they were before the crisis hit.
All of this outcome is unnecessary and results from corruption. The only reason why there is any bailout, at all, for investors (in anything other than pass-through entities), is the pervasive governmental corruption at the very top. If there were no corruption, then the only bailouts would be to individuals and pass-through businesses (which are individuals) — the “bottom-up” bailouts. America is a very corrupt country at the top, and that is the reason why it will collapse in the aftermath of the coronavirus crisis.
Ultimately, when the wealth-inequality is so extreme, the billionaires are selling mainly to each other, and the necessities for the public are less and less profitable to sell at all. The outcome will therefore be economic collapse, and perhaps even revolution.
The basic way to evaluate how well or poorly a nation’s Government is performing in this crisis is the country’s ratio of coronavirus cases to its total population, but if a given country has not yet reached its peak in its daily number of new cases, then that country’s ratio is probably still rising, in which instance, that country’s performance will probably turn out to have been less good than this ratio currently is showing it to be. And, conversely, the lower this ratio is, the better the performance of that country’s Government is shown to be in responding to Covid-19.
Here are the ten nations that have the largest numbers of cases at the present time, and the ratio of that number to their total population; and also shown here is the date when the daily number of new cases peaked (because if it hasn’t yet peaked, then this crucial ratio will probably be rising in that country):
Ratio of total cases divided by total population (the lower this number, the better):
USA = 740,928/330,000,000 = 0.00224523636 not yet peaked
SPAIN = 195,944/46,940,000 = 0.00417435023 peaked March 26th
ITALY = 178,972/60,360,000 = 0.0029650762 peaked March 19th
FRANCE = 152,578/66,990,000 = 0.00227762352 peaked April 3rd
GERMANY = 144,387/83,020,000 = 0.00173918332 peaked March 27th
UK = 120,067/66,650,000 = 0.00180145536 peaked April 10th
TURKEY = 86,306/82,000,000 = 0.00105251219 peaked April 11th
CHINA = 82,735/1,393,000,000 = 0.00005939339 peaked February 12th
IRAN = 82,211/81,800,000 = 0.00100502444 peaked March 30th
RUSSIA = 42,853/144,500,000 = 0.00029656055 not yet peaked
In addition, the following major countries might especially be noted, since the main reason they aren’t on that list is their being outstandingly good performers:
JAPAN = 10,797/126,500,000 = 0.00008535177 peaked April 11th
S. KOREA = 10,661/51,640,000 =0.00020644848 peaked March 3rd
The worst of all these performers appear currently to be, though not yet in any clear order: USA, Spain, and Italy.
The best appear to be, in order: China, Japan, and S. Korea.
The U.S. press has recently been particularly praising Denmark’s performance, and noting that Denmark’s coronavirus emergency legislation is more socialistic than Sweden’s is. However, both of those Scandinavian countries actually have very similar actual performance, thus far, in this crisis. In Denmark, the focus of the emergency legislation was on “saving jobs,” instead of on protecting investors. It’s a democratic socialist country, perhaps the most equalitarian in the world. Of course, that’s the exact opposite of dictatorial capitalism (fascism), which became America’s system after FDR died in 1945, and increasingly thereafter (hyper-imperialistic, military-industrial-complex or “MIC” dominated, like fascist regimes usually are), perpetrating coups and invasions, destroying Iran, Iraq, and many other countries, in order to expand its power and the wealth of its billionaires (like the fascist countries had done going into WW II). No cases of coronavirus-19 were reported in Denmark until February 27th. Denmark unanimously passed its emergency law on March 13th — drastically different bailout legislation from the one that America subsequently passed — in order to deal with the crisis. The daily number of Denmark’s new Covid-19 cases peaked on April 7th, and has been declining since that time. Its neighbor Sweden peaked on April 8th. Sweden’s emergency legislation is less strict about lockdowns, but relies more on individual discretion. However, since Sweden, like Denmark, is a democratic socialist country, individuals needn’t worry about paying medical bills, nor about being paid while on sick-leave. So, employees aren’t desperate to return to their places of work, such as in America; and, therefore, these countries don’t spread the infection as readily as in the U.S. and are thus far less likely to have recurring peaks and delayed terminations of the coronavirus crisis. (By contrast: in America, where losing one’s job can mean losing one’s health care, even sick employees may be inclined to stay on the job and perhaps infect customers.) And there are no corporate bailouts in either Denmark’s or Sweden’s legislation. Denmark’s Finance Minister, the Social Democrat (or democratic socialist) Nicolai Wammen was interviewed for 15 minutes on March 27th, by Christiane Amanpour, and he explained Denmark’s emergency law, which was overwhelmingly bottom-up, not top-down (such as America’s is).
Here, therefore, is the actual performance, thus far, of both of those two countries:
DENMARK = 7,384/5,806,000 = 0.00127178780 peaked April 7th
SWEDEN = 14,385/10,230,000 = 0.00140615835 peaked April 8th
Both of them are reasonably comparable to Germany, UK, Turkey, and Iran, but not as good as S. Korea, and not nearly as good as the two best, China and Japan.
In the final analysis, China and Japan could turn out to have the least-corrupt and best-run Governments; and the most corrupt Governments could turn out to be USA, Spain, and Italy. However, the performances of Brazil and some other nations in the southern hemisphere might yet turn out to be even worse than those of USA, Spain, and Italy, because the winter season has’t yet reached there.
On April 16th, Wall Street on Parade headlined “Here Are the Contracts Showing How $4.5 Trillion in Stimulus Was Outsourced to Wall Street” and described — and documented — what the Wall Street Journal and the rest of the financial press would not, which is the U.S. Government’s legalized money-laundering operation, via the Fed, transferring onto the American public almost all of the losses that America’s billionaires will be suffering from the coronavirus crash. Back on 21 January 2020, WSP described this money-laundering, in its earlier 2008 embodiment, this way: “The epic financial collapse on Wall Street in 2008 was, reduced to its basic terms, simply the end game of Wall Street banks’ efforts to monetize their frauds.” They noted: “On April 9, 2019, the nonprofit Wall Street watchdog, Better Markets, released a study titled: “Wall Street’s Six Biggest Bailed-Out Banks: Their RAP Sheets & Their Ongoing Crime Spree.” It should have made headlines on the front pages of every major newspaper in the U.S. Instead, it was effectively ignored by mainstream media.” (Incidentally: Obama repeatedly promised to prosecute banksters, but secretly protected them and prosecuted none of them, though their crimes had been monstrous. The billionaires’ thefts from the public are entirely bipartisan, supported by over 95% of Congress — the billionaires own the Presidents and members of Congress, and not only own virtually all of the news-media.) On April 20th, America’s National Public Radio (NPR) broadcast “Amid Pandemic, Italian Prosecutors Warn That Mafia Groups Are Cementing Their Power” and reported that Mafia bosses were buying up cheap some of Italy’s suddenly desperate small businesses. If the same thing is being done by America’s billionaires, that’s not yet being reported by their press — perhaps it will instead be reported by Italy’s press.
The Federal Reserve are controlled by and represent the banksters — Wall Street — who not only skim on their own accounts but work with and for the billionaires, some of whom are themselves banksters, but many of whom are operating hedge funds, private equity funds, and all types of FORTUNE 500 companies. Basically, Wall Street works for the billionaires. The billionaires run practically everything in America, except Main Street.
In the upcoming June 2020 issue of the neoconservative (pro-U.S.-imperialist) Democratic Party U.S. magazine, The Atlantic, their George Packer banners “We Are Living in a Failed State: The coronavirus didn’t break America. It revealed what was already broken.” That magazine blames this “failed state” on the (neoconservative) Republican Party, and so Packer’s phrase there “a dysfunctional government” links to an anti-Republican article, by one of the top officials in the liberal neoconserative U.S. Administration of the Democrat Barack Obama, titled “How Trump Designed His White House to Fail.” However, the actual cause of the gradual collapse, since 1945, of what had been U.S. President FDR’s largely democratic U.S.A., is the billionaires who own both Parties — it is bipartisan. This rot comes from both Parties’ billionaires. (The particular propaganda-operation, The Atlantic, happens to be controlled by the same Democratic Party billionaire who controls Apple corporation.) No billionaire will publish the reality. For example, Packer’s article said: “The second crisis, in 2008, intensified it [‘a bitterness toward the political class’]. At the top, the financial crash could almost be considered a success. Congress passed a bipartisan bailout bill that saved the financial system.” The presumption there is that the only way to restore the economy after a crash is to bail out the country’s billionaires. It’s a timely message, at this moment when the billionaires require their Government to bail them out, yet again. (I recently proposed one way to reduce the billionaires’ dictatorship over America.)
On April 17th, WSP headlined “Americans Are Paying a Tragic Price for Allowing Five Banks to Control the U.S. Economy” and closed by urging: “Americans need to use this time at home to call their Senators and Reps in Congress and demand the separation of federally-insured, deposit-taking banks from the casinos on Wall Street. We’re talking about nothing less than the survival of this country.” Needless to say, the ultimate beneficiaries of this public largesse — to America’s billionaires — don’t desire to publicize such writings, any more than they desire to publicize to the public their offshore bank accounts.
Unlike so much that’s in the billionaires’ ‘news’, the facts that are reported here are solidly documented (and linked-to), but the billionaires don’t report these facts. Thus, the masses don’t know these facts, and so the mass-violence, when it comes, won’t be focused against the billionaires. What you’re reading, here, is being kept secret by (not being published by) the billionaires’ media. So — if only to spread word that the cause of this is not “the Chinese” or “foreigners” or “the Jews” or some other amorphous ethnicity, who aren’t actually to blame — please email the URL (the web-address) atop this article, to all of your friends, as “FYI:”. It might stir some interesting conversations, especially if all the ‘news’ that they know comes from America’s billionaires — the same people who fund the country’s successful politicians, each and every election-year. The American Revolution did not come about by misinformed people. It came about by informed people. Misinformed people create only more problems.
So, that’s “FYI.” And thanks for reading here.