By Rajan Menon
Source: Intrepid Report
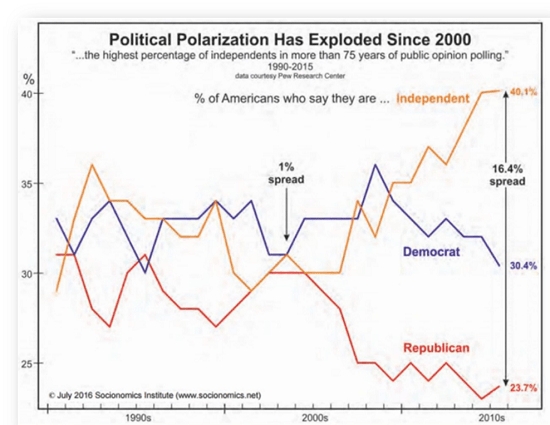
Despair about the state of our politics pervades the political spectrum, from left to right. One source of it, the narrative of fairness offered in basic civics textbooks — we all have an equal opportunity to succeed if we work hard and play by the rules; citizens can truly shape our politics — no longer rings true to most Americans. Recent surveys indicate that substantial numbers of them believe that the economy and political system are both rigged. They also think that money has an outsized influence on politics. Ninety percent of Democrats hold this view, but so do 80 percent of Republicans. And careful studies confirm what the public believes.
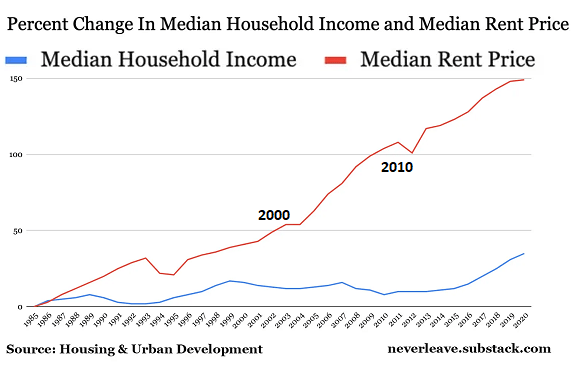
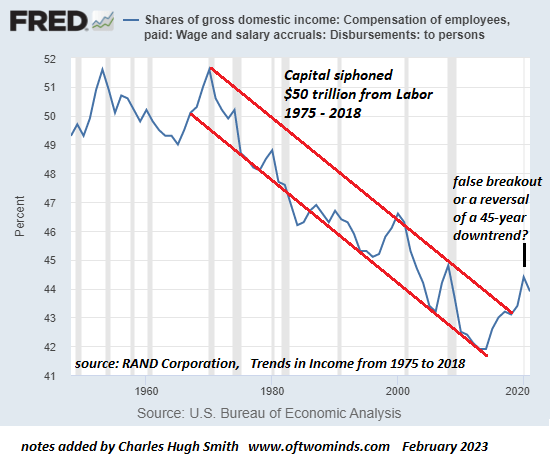
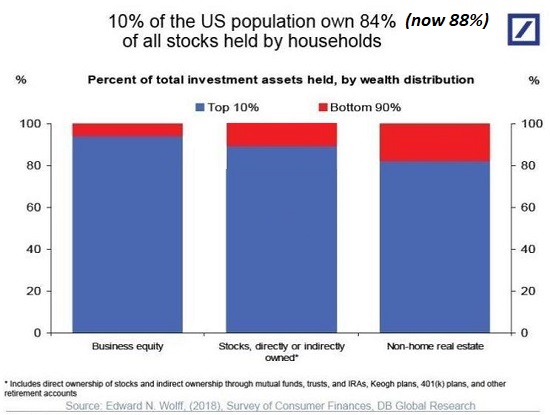
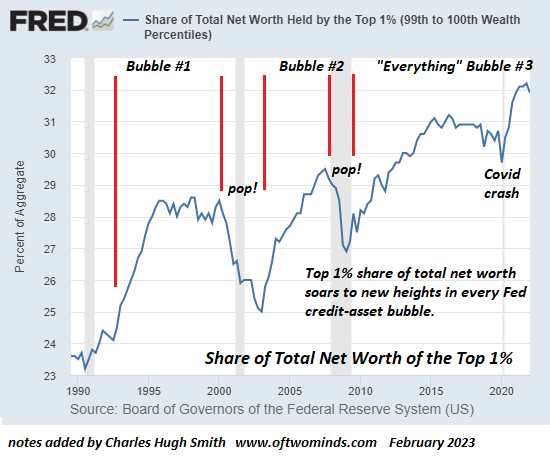
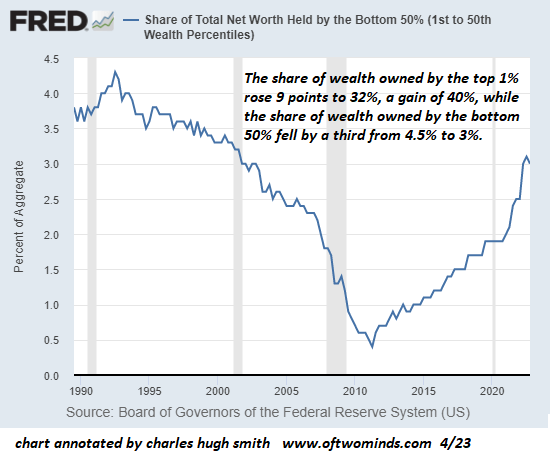
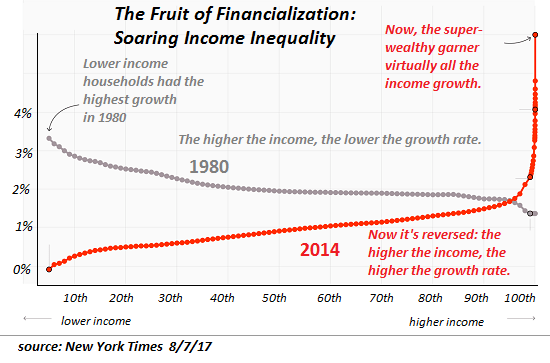
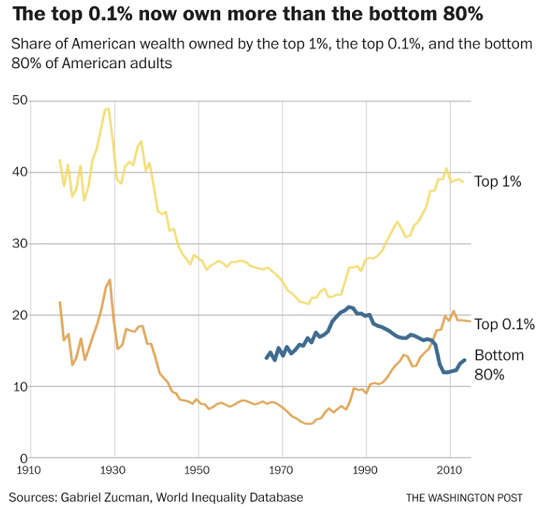
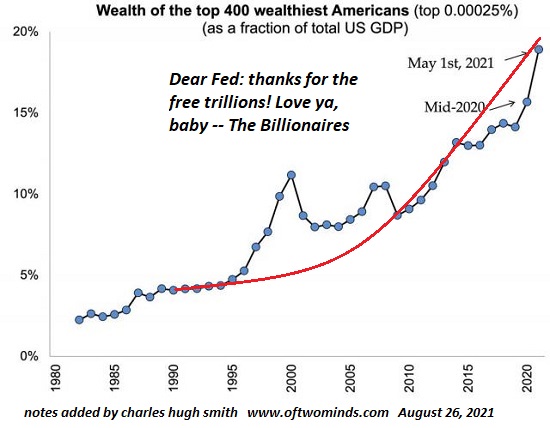
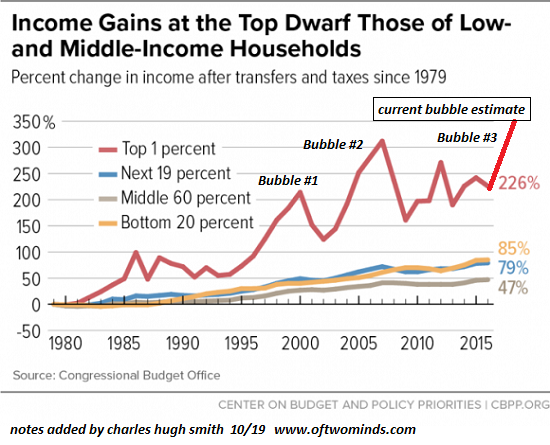
None of this should be surprising given the stark economic inequality that now marks our society. The richest 1 percent of American households currently account for 40 percent of the country’s wealth, more than the bottom 90 percent of families possess. Worse yet, the top 0.1 percent has cornered about 20percent of it, up from 7 percent in the mid-1970s. By contrast, the share of the bottom 90 percent has since then fallen from 35 percent to 25 percent. To put such figures in a personal light, in 2017, three men — Jeff Bezos, Warren Buffett, and Bill Gates — possessed more wealth ($248.5 billion) than the bottom 50 percent of Americans.
Over the last four decades, economic disparities in the U.S. increased substantially and are now greater than those in other wealthy democracies. The political consequence has been that a tiny minority of extremely wealthy Americans wields disproportionate influence, leaving so many others feeling disempowered.
What Money Sounds Like
Two recent headline-producing scandals highlight money’s power in society and politics.
The first involved super-affluent parents who used their wealth to get their manifestly unqualified children into highly selective colleges and universities that previously had reputations (whatever the reality) for weighing the merits of applicants above their parents’ wealth or influence.
The second concerned Texas Senator Ted Cruz’s reported failure to reveal, as election laws require, more than $1 million in low-interest loans that he received for his 2012 Senate campaign. (For that lapse, the Federal Election Commission (FEC) fined Senator Cruz a modest $35,000.) The funds came from Citibank and Goldman Sachs, the latter his wife’s longtime employer. News of those undisclosed loans, which also cast doubt on Cruz’s claim that he had funded his campaign in part by liquidating the couple’s assets, only added to the sense that favoritism now suffuses the politics of a country that once prided itself on being the world’s model democracy. (Journalists covering the story couldn’t resist pointing out that the senator had often lambasted Wall Street’s “crony capitalism” and excessive political influence.)
The Cruz controversy is just one reflection of the coming of 1 percent politics and 1 percent elections to America at a moment when the first billionaire has been ensconced in the Oval Office for more than two years, posing as a populist no less.
Since the Supreme Court’s 2010 ruling in Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission, money has poured into politics as never before. That’s because the Court ruled that no limits could be placed on corporate and union spending aimed at boosting or attacking candidates running for political office. Doing so, the justices determined in a 5-4 vote, would be tantamount to restricting individuals’ right to free speech, protected by the First Amendment. Then came the Court’s 2014 McCutcheon v. Federal Election Commission decision (again 5-4), which only increased money’s influence in politics by removing the aggregate limit on an individual’s contribution to candidates and to national party committees.
In an age when money drives politics, even ex-presidents are cashing in. Fifteen years after Bill Clinton departed the White House, he and Hillary had amassed a net worth of $75 million — a 6,150percent increase in their wealth. Barack and Michelle Obama’s similarly soared from $1.3 million in 2000 to $40 million last year — and they’re just warming up. Key sources of these staggering increases include sky-high speaking fees (often paid by large corporations), including $153 million for the Clintons between February 2001 and May 2016. George W. Bush also made tens of millions of dollars in this fashion and, in 2017, Obama received $400,000 for a single speech to a Wall Street firm.
No wonder average Americans believe that the political class is disconnected from their day-to-day lives and that ours is, in practice, a democracy of the rich in which money counts (and counts and counts).
Cash for College
Now let’s turn to what those two recent scandals tell us about the nexus between wealth and power in America.
First, the school scam. Parents have long hired pricey tutors to coach their children for the college admissions tests, sometimes paying them hundreds of dollars an hour, even $1,500 for 90 minutes of high-class prep. They’ve also long tapped their exclusive social and political connections to gin up razzle-dazzle internships to embellish those college applications. Anyone who has spent as much time in academia as I have knows that this sort of thing has been going on for a long time. So has the practice of“legacy admissions” — access to elite schools especially for the kids of alumni of substantial means who are, or might prove to be, donors. The same is true of privileged access to elite schools for the kids of mega-donors. Consider, for instance, that $2.5 million donation Charles Kushner made to Harvard in 1998, not long before his son Jared applied. Some of the folks who ran Jared’s high school noted that he wasn’t exactly a whiz-bang student or someone with sky-high SAT scores, but — surprise! — he was accepted anyway.
What’s new about the recent revelations is that they show the extent to which today’s deep-pocketed helicopter parents have gone into overdrive, using brazen schemes to corrupt the college admissions process yet more. One unnamed parent spent a cool $6.5 million to ensure the right college admitted his or her child. Others paid hefty amounts to get their kids’ college admissions test scores falsified or even hired proxies to take the tests for them. Famous actors and financial titans made huge payments to university sports coaches, who then lied to admissions officers, claiming that the young applicants were champions they had recruited in sports like water polo, crew, or tennis. (The kids may have known how to swim, row, or play tennis, but star athletes they were not.)
Of course, as figures on the growing economic inequality in this country since the 1970s indicate, the overwhelming majority of Americans lack the connections or the cash to stack the deck in such ways, even assuming they would do so. Hence, the public outrage, even though parents generally understand that not every aspirant can get into a top school — there aren’t enough spots — just as many know that their children’s future happiness and sense of fulfillment won’t depend on whether they attend a prestigious college or university.
Still, the unfairness and chicanery highlighted by the admissions scandal proved galling, the more so as the growing crew of fat cats corrupting the admissions process doubtless also preach the gospel of American meritocracy. Worse, most of their kids will undoubtedly present their fancy degrees as proof that quality wins out in our society, never mind that their starting blocks were placed so far ahead of the competition.
To add insult to injury, the same parents and children may even portray admissions policies designed to help students who lack wealth or come from underrepresented communities as violations of the principles of equal opportunity and fairness, democracy’s bedrock. In reality, students from low-income families, or even those of modest means, are startlingly less likely to be admitted to top private universities than those from households in the top 10 percent. In fact, applicants from families in the top 1 percent are now 77 times more likely than in the bottom 20 percent to land in an elite college, and 38 of those schools admit more kids from families in that top percentage than from the bottom 60 percent.
Buying Politics (and Politicians), American-Style
Now, let’s return to the political version of the same — the world in which Ted Cruz swims so comfortably. There, too, money talks, which means that those wealthy enough to gain access to, and the attention of, lawmakers have huge advantages over others. If you want political influence, whether as a person or a corporation, having the wealth needed to make big campaign contributions — to individuals or groups — and to hire top-drawer lobbyists makes a world of difference.
Official data on the distribution of family income in the United States show that the overwhelming majority of Americans can’t play that game, which remains the preserve of a tiny super-rich minority. In 2015, even with taxes and government-provided benefits included, households in the lowest 20 percent accounted for only about 5 percent of total income. Their average income — not counting taxes and government-provided assistance — was only $20,000. The share of the bottom 50 percent — families making $61,372 or less — dropped from 20 percent to 12 percent between 1978 and 2015. By contrast, families in the top 1 percent earned nearly 50 percent of total income, averaging $215,000 a year — and that’s only income, not wealth. The super-rich have plenty of the latter, those in the bottom 20 percent next to none.
Before we proceed, a couple of caveats about money and political clout. Money doesn’t always prevail. Candidates with more campaign funds aren’t guaranteed victory, though the time politicians spend raising cash leaves no doubt that they believe it makes a striking difference. In addition, money in politics doesn’t operate the way simple bribery does. The use of it in pursuit of political influence works more subtly, and often — in the new era opened by the Supreme Court — without the slightest need to violate the law.
Still, in Donald Trump’s America, who would claim that money doesn’t talk? If nothing else, from inaugural events — for Trump’s inaugural $107 million was raised from a host of wealthy donors with no limits on individual payments, 30 of which totaled $1 million or more — to gala fundraisers, big donors get numerous opportunities to schmooze with those whose campaigns they’ve helped bankroll. Yes, there’s a limit — currently $5,600 — on how much any individual can officially give to a single election campaign, but the ultra-wealthy can simply put their money into organizations formed solely to influence elections as well as into various party committees.
Individuals, companies, and organizations can, for instance, give money to political action committees (PACs) and Super PACs. Though bound by rules, both entities still have lots of leeway. PACs face no monetary limits on their independent efforts to shape elections, though they can’t accept corporate or union money or take more than $5,000 from individuals. They can provide up to $5,000 to individual election campaigns and $15,000 per party committee, but there’s no limit on what they can contribute in the aggregate. Super PACs have far more running room. They can rake in unlimited amounts from a variety of sources (as long as they’re not foreign) and, like PACs, can spend limitless sums to shape elections, providing they don’t give money directly to candidates’ campaigns.
Then there are the dark money groups, which can receive financial contributions from any source, American or foreign. Though their primary purpose is to push policies, not individual campaigns, they can engage in election-related work, provided that no more than half their funds are devoted to it. Though barred from donating to individual campaigns, they can pour unlimited money into Super PACs and, unlike PACs and Super PACs, don’t have to disclose who gave them the money or how much. Between 2008 and 2018, dark money groups spent $1 billion to influence elections.
In 2018, 2,395 Super PACs were working their magic in this country. They raised $1.6 billion and spent nearly $809 million. Nearly 78 percent of the money they received came from 100 donors. They, in turn, belonged to the wealthiest 1 percent, who provided 95 percent of what those Super PACs took in.
As the 2018 congressional elections kicked off, the four wealthiest Super PACs alone had $113.4 million on hand to support candidates they favored, thanks in substantial measure to business world donors. In that election cycle, 31 individuals ponied up more than $5 million apiece, while contributions from the top four among them ranged from almost $40 million to $123 million.
The upshot: if you’re running for office and advocate policies disliked by wealthy individuals or by companies and organizations with lots of cash to drop into politics, you know from the get-go that you now have a problem.
Wealth also influences political outcomes through the lobbying industry. Here again, there are rules, but even so, vast numbers of lobbyists and eye-popping amounts of lobbying money now are at the heart of the American political system. In 2018 alone, the 50 biggest lobbying outfits, largely representing big companies, business associations, and banks, spent $540 million, and the grand total for lobbying that year alone was $3.4 billion.
Nearly 350 of those lobbyists were former legislators from Congress. Officials departing from senior positions in the executive branch have also found artful ways to circumvent presidential directives that prohibit them from working as lobbyists for a certain number of years.
Do unions and public interest groups also lobby? Sure, but there’s no contest between them and corporations. Lee Drutman of the New America think tank notes that, for every dollar the former spent in 2015, corporate donors spent $34. Unsurprisingly, only one of the top 20 spenders on lobbying last year was a union or a public-interest organization.
The sums spent by individual companies to gain political influence can be breathtaking. Take now-embattled Boeing. It devoted $15 million to lobbying in 2018 — and that’s not counting its campaign contributions, using various channels. Those added another $8.4 million in the last two-and-a-half years. Yet Boeing only placed 11th among the top 20 corporate spenders on lobbying last year. Leading the pack: the U.S. Chamber of Commerce at $94.8 million.
Defenders of the status quo will warn that substantially reducing money’s role in American politics is sure to threaten democracy and civil liberties by ceding undue power to the state and, horror of horrors, putting us on the road to “socialism,” the right wing’s bogeyman du jour. This is ludicrous. Other democracies have taken strong steps to prevent economic inequality from subverting their politics and haven’t become less free as a result. Even those democracies that don’t limit political contributions have adopted measures to curb the power of money, including bans on television ads (a huge expense for candidates in American elections: $3 billion in 2018 alone just for access to local stations), free airtime to allow competitors to disseminate their messages, and public funds to ease the financial burden of election campaigns. Compared to other democracies, the United States appears to be in a league of its own when it comes to money’s prominence in politics.
Those who favor continuing business as usual like to point out that federal “matching funds” exist to help presidential candidates not be steamrolled by competitors who’ve raised mounds of money. Those funds, however, do no such thing because they come with stringent limits on total spending. Candidates who accept matching funds for a general election cannot accept contributions from individuals. Moreover, matching funds are capped at $20 million, which is a joke considering that Barack Obama and Mitt Romney spent a combined $1.2 billion in individual contributions alone during the 2012 presidential election. (Super PACs spent another $350 million to help Romney and $100 million to back Obama.)
A New American Tradition?
Rising income inequality, wage stagnation, and slowing social mobility hurt ordinary Americans economically, even as they confer massive social and political advantages on the mega-rich — and not just when it comes to college admissions and politics either.
Even the Economist, a publication that can’t be charged with sympathy for left-wing ideas, warned recently of the threat economic inequality poses to the political agency of American citizens. The magazine cited studies showing that, despite everything you’ve heard about the power of small donations in recent political campaigns, 1 percent of the population actually provides a quarter of all the money spent on politics by individuals and 80 percent of what the two major political parties raise. Thanks to their wealth, a minuscule economic elite as well as big corporations now shape policies, notably on taxation and expenditure, to their advantage on an unprecedented scale. Polls show that an overwhelming majority of Americans support stricter laws to prevent wealth from hijacking politics and want the Citizens United ruling overturned. But then just how much does the voice of the majority matter? Judging from the many failed efforts to pass such laws, not much.