By Charles Hugh Smith
Source: Of Two Minds
So what are conventional pundits missing today? I would start with three dynamics.
Only old people experienced real recessions–those in 1973-74 and 1980-82. Recessions since then have been shorter and less systemic.
In the good old days, a recession laid waste to entire industries which never recovered their previous employment. People who were laid off couldn’t find another job. Major sectors of the economy dried up and blew away. Jobs were scarce and there was an oversupply of people looking for work.
We’re told consumer confidence is in the dumps and everyone expects the worst: recession! Oh Lordy. Interestingly, there isn’t much evidence of this near-panic behaviorally. Everyone’s tightening their belts and battening down the hatches, but it’s not the cliff-dive we see in a real recession.
There’s certainly a lot of froth to be scraped off the latte, but what I’m curious about are the armatures of the economy and what I’m seeing is the crowd ignoring key dynamics because they’re so busy pushing the Recessionary Play-Doh into the old playboard.
The entire notion that there is a hard and fast line indicating “recession” is not realistic or useful. The economy dropped 1% for two quarters in a row, quick hit the alarm, go to DefCon 1. Uh, OK, right.
The more useful approach is to look at data points as mostly signal noise that fail to reflect or illuminate the core dynamics of the economy. Here’s an example: the stagflation of the 1970s is a hot topic as the financial punditry compares then to now, seeking evidence of similarities strong enough to predict a Lost Decade ahead.
One key factor that’s rarely (if ever) mentioned was the staggering cost of cleaning up America’s industrial sector and polluted skies and waterways at the same time that the Cold War required the U.S. to strengthen its allies by allowing them unfettered access to the U.S. marketplace–exports to the U.S. that had a price advantage due to the dominance of the dollar and the relative weakness of allies’ currencies.
1972 exchange rates indicate that the Japanese yen was 302 to $1–an enormous advantage when compared to recent exchange rates of around 110 yen to the USD.
What few current pundits seem to grasp is the dominant dynamic of the entire era of 1945-1992 was the Cold War with the Soviet Union and its client states and allies. Strengthening allies’ economies was a core goal and so the costs to the domestic economy had to be absorbed: there was no choice.
The costs of cleaning up the nation and its vast industrial base was an enormous drag on the economy. The value of the trillions of dollars (in current dollars) invested was not in boosting profits, it was in restoring what had been heedlessly destroyed and damaged by rampant dumping of waste and pollutants and improving the health and well-being of the citizenry.
Check out the smog in early 1970s TV series filmed in Los Angeles for a taste of what was cleaned up.
But in a mind-boggling failure of conventional economics, our financial punditry is blind to the impact of the most consequential economic realities of the 1970s–the Cold War and the lengthy, painful, costly clean-up of the nation and its industrial base–on stagflation.
One reason for this abject failure is these dynamics were difficult to measure, so they weren’t measured.We only manage what we measure and so if we don’t measure it, it doesn’t exist. If we measure things in a no-longer-relevant manner, for example GDP, we continue to act as if this misguided measure is of supreme importance when the reality is it’s dangerously misleading.
So what are conventional pundits missing today? I would start with three dynamics:
1. For the first time in multiple generations, there is a structural scarcity of labor. For a variety of reasons, there are fewer people willing to do the work at the offered wage than there are jobs. This is not temporary, it is demographic and social, not simply economic. All the supposedly easy fixes– automate everything, etc.–are not that easy.
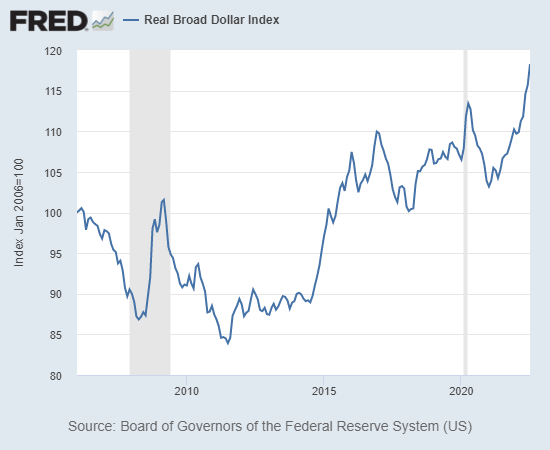
2. The strength of the U.S. dollar is exporting inflation, to the benefit of the domestic economy. After offshoring critical supply chains–a disaster that will take years to reverse–now the U.S. is offshoring inflation and the resulting demand destruction.
3. Global capital flows are reversing. capital flowed from the Core to the Periphery to reap the gains of globalization. Now the flow is reversing and capital is flowing from the Periphery to the Core to preserve capital and lock in lower-risk returns. What looks expensive to those earning U.S. dollars may look cheap and secure to those fleeing depreciating currencies and assets.
In my analysis, these are consequential dynamics that merit little attention in conventional financial analysis.
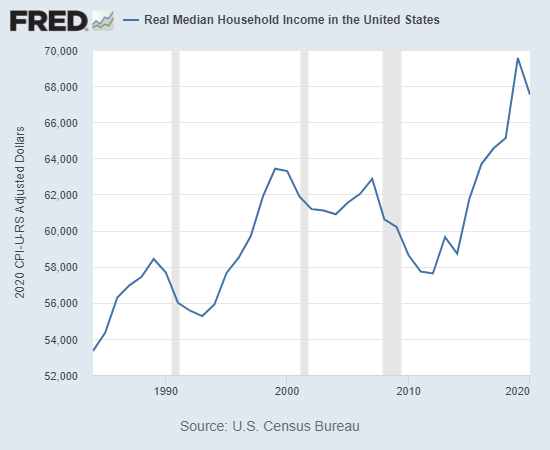
There is much more to say but glance at these two charts: real (i.e. adjusted for official inflation) median household income and real Broad U.S. Dollar Index.
If we’re not measuring or pondering the core structural dynamics of the economy, we’re not going to make sense of no-longer-relevant data. This is a most peculiar recession, and few seem to be asking if the reason is we’re missing what’s changed structurally.
Charts courtesy of St. Louis Federal Reserve Database (FRED))