By Caitlin Johnstone
Source: CaitlinJohnstone.com
The Associated Press journalist who reported a US intelligence official’s false claim that Russia had launched missiles at Poland last week has been fired.
As we discussed previously, AP’s anonymously sourced report which said “A senior U.S. intelligence official says Russian missiles crossed into NATO member Poland, killing two people” went viral because of the massive implications of direct hot warfare erupting between Russia and the NATO alliance. AP subsequently retracted its story as the mainstream political/media class came to accept that it was in fact a Ukrainian missile that had struck Poland.
AP’s firing of reporter James LaPorta looks at this time to be the end point of any accountability for the circulation of this extremely dangerous falsehood. AP spokesperson Lauren Easton says no disciplinary action will be taken against the editors who waved the bogus story through, and to this day the public has been kept in the dark about the identity of the US official who fed such extremely egregious misinformation/disinformation to the public through the mainstream press.
It is utterly inexcusable for AP to continue to protect the anonymity of a government official who fed them such a profoundly significant falsehood. This didn’t just affect AP staff, it affected the whole world; we deserve to know what happened and who was responsible, and AP has no business obstructing that knowledge from us.
LaPorta’s firing looks like this is yet another instance where the least powerful person involved in a debacle is being made to take the fall for it. A powerful intelligence official will suffer no consequences for feeding false information to the press — thereby ensuring that it will happen again — and no disciplinary action will be taken against LaPorta’s superiors, despite the absolute buffoonery that subsequent reporting has revealed on their part.
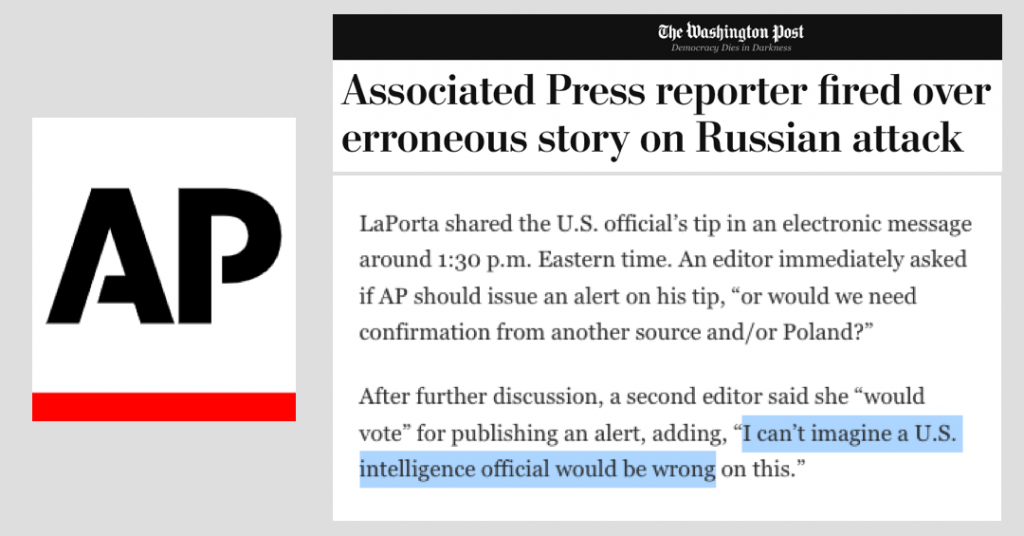
In an article titled “Associated Press reporter fired over erroneous story on Russian attack,” The Washington Post reports the following (emphasis added):
Internal AP communications viewed by The Post show some confusion and misunderstanding during the preparations of the erroneous report.
LaPorta shared the U.S. official’s tip in an electronic message around 1:30 p.m. Eastern time. An editor immediately asked if AP should issue an alert on his tip, “or would we need confirmation from another source and/or Poland?”
After further discussion, a second editor said she “would vote” for publishing an alert, adding, “I can’t imagine a U.S. intelligence official would be wrong on this.”
“I can’t imagine a US intelligence official would be wrong on this.”
Can you imagine not being able to imagine a US intelligence official being wrong? This would be an unacceptable position for any educated adult to hold, much less a journalist, still less an editor, and still less an editor of one of the most influential news agencies on earth.
These are the people who publish the news reports we read to find out what’s happening in the world. This is the baby-brained level of thinking these people are serving the public interest with.
Antiwar commentator Daniel Larison writes the following of the AP editor’s shocking quote:
Skepticism about official claims should always be the watchword for journalists and analysts. These are claims that need more scrutiny than usual rather than less. If you can’t imagine that an intelligence official could get something important wrong, whether by accident or on purpose, you are taking far too many things for granted that need to be questioned and checked out first.
Intelligence officials of many governments feed information to journalists and have done so practically ever since there was a popular press to feed information to, and that information certainly should not be trusted just because an official source hands it over. It is also always possible for intelligence officials to just get things wrong, whether it is because they are relying on faulty information or because they were too hasty in reaching conclusions about what they think they know.
Whether the AP’s source was feeding them a line or was simply mistaken, a claim as provocative and serious as this one should have been checked out much more thoroughly before it got anywhere near publication. The AP report in this case seems to have been a combination of a story that was “too good to check” and a culture of deference to official sources in which the editors didn’t feel compelled to make the effort to check.
Indeed, the only reason the press receive such explicit protections in the US Constitution is because they are supposed to hold the powerful to account. If the editors of a wildly influential news agency will just unquestioningly parrot whatever they are fed by government officials while simultaneously protecting those officials with anonymity, they are not holding the powerful to account, and are in fact not meaningfully different from state propagandists.
They are state propagandists. Which is probably why they are sipping lattes in the AP newsroom while Julian Assange languishes in prison.
As Jacobin’s Branko Marcetic observed, this is far from the first time AP has given the cover of anonymity to US government officials circulating bogus claims of potentially dangerous consequence, like the time it reported an official’s evidence-free assertion which later proved false that Iran had carried out an attack on four oil tankers off the coast of the United Arab Emirates, or the time it let another one anonymously claim that “Iran may try to take advantage of America’s troop withdrawals from Iraq and Afghanistan.”
So to recap —
- Powerful government official who fed AP a false story: Zero accountability
- AP editor who asked if a report should immediately be published upon receipt of the story: Zero accountability
- Second AP editor who says she can’t imagine a U.S. intelligence official would be wrong: Zero accountability
- Journalist who wrote the story: Singular accountability
In a sane society, power and responsibility would go hand in hand. A disaster would be blamed on the most powerful people involved in its occurrence. In our society it’s generally the exact opposite, with the rank-and-file taking all of the responsibility and none of the power.
Our rulers lie to us, propagandize us, endanger us, impoverish us, destroy journalism, start wars, kill our biosphere and make our world dark and confusing, and they suffer no consequences for it. We cannot allow them to continue holding all of the power and none of the responsibility. This is backwards and must end.



