By Charles Hugh Smith
Source: Of Two Minds
This is how we’ll end up with severe shortages of truly skilled labor and high unemployment of those who lack the necessary skills.
The labor force and the job market are referred to as if they were monolithic structures. But they’re not monolithic, they are complex aggregates of very different cohorts of age, skills, mobility, education, experience, opportunity, potential and motivation.
As a result, numbers such as the unemployment rate tell us very little about the labor force and the job market in terms of what matters going forward. So what does matter going forward?
1. Demographics–the aging and retirement of key sectors of the work force.
2. Skills and experience that will be increasingly scarce due to mismatched demand for skills that are diminishing as older workers retire.
3. What skills and experience will be demanded by re-industrialization, reshoring and expanding the electrification of the economy.
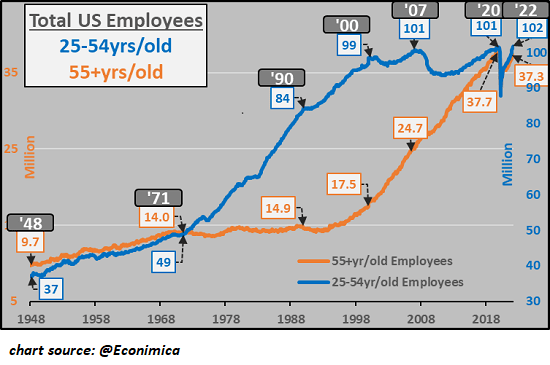
Consider these two charts of the US work force by age. (Courtesy of CH @econimica) In the first chart, Total US Employees, note that the prime working age work force (ages 25-54) has been flatlined for the past 20 years at 101-102 million. In contrast, the 55-and-older cohort of employees soared from 17 million to 37 million. This increase of 20 million accounts for virtually all growth in the employed work force.
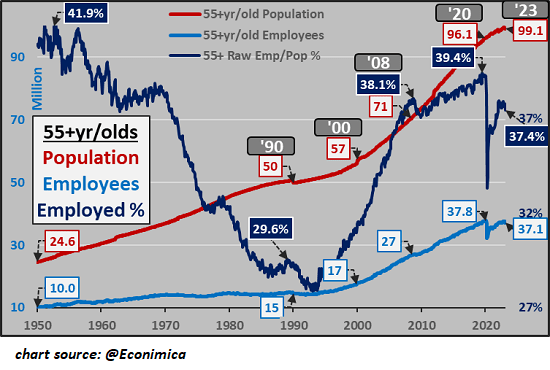
A funny thing happens as workers get old; they retire and leave the work force. Their skills and experience are no longer available to employers or the nation’s economy. The second chart shows the aging of the American populace, as the 55+ cohort increased from 57 million to 99 million since 2000, as the number of older employees skyrocketed from 17 million to 37 million.
While the total US population increased by 18% from 281 million in 2000 to 331 million today, the 55+ cohort increased 74% (from 57 million to 99 million).
The key takeaway here is the number of experienced workers who will retire in the next decade will track the explosive growth in the 55+ cohort. The general consensus is this will not be a problem because there are plenty of younger workers available to fill the vacated slots.
But this overlooks the qualitative and quantitative differences in the millions leaving the work force and those joining the work force. This is especially consequential in real-world jobs, i.e. all those jobs that require engaging real-world materials rather than staring at screens.
Though few analysts and commentators will admit to it, the implicit assumption is that the jobs that matter all involve staring at screens–processing data, finance, entertainment and shaping narrative make the world go round. All the real-world stuff (boring!) will magically get done by tax donkeys who are out of sight, out of mind.
This mindset has it backwards: it’s the real-world work of changing the industrial / energy / energy distribution foundation of the economy that matters going forward, not the staring-at-screens jobs.
What few seem to realize is the work force that’s aging and retiring is the cohort with the real-world skills. It’s a nice idea to remake the entire electrical grid of the nation to transport much larger quantities of electrical power, but who’s going to do all that work? Young people whose career goals are becoming YouTube influencers or day-traders? No. All the ChatAI bots in the world aren’t going to get the real work done, either.
In other words, there is a massive mismatch between the skills available to hire in the young-worker cohort and the skills and experience needed to rebuild the material, real-world foundations of the US economy. It’s well-known but apparently not worth worrying about that the average age of the US farmer is pushing 60 years of age. Nobody left to grow all our food? Hey, isn’t there a ChatAI bot to do all that for us? It can all be automated, right? No? Well, why not? Somebody out there, get it done! Food in super-abundance should be delivered to everyone staring at screens 24/7, it’s our birthright.
The average age of skilled tradespeople is also skewed to the aging work force. There is no easy way to quantify real-world skills gained by on-the-job experience. I suspect it follows a power-law distribution: the newly minted worker just out of school / apprenticeship can handle basic functions, but when tough problems arise, the number of workers with the requisite experience to diagnose and fix the problem diminishes rapidly.
This distribution presents an enormous problem for the economy and employers. Once the super-experienced workers who can solve any problem leave, they cannot be replaced by inexperienced workers. So when the really big problems arise, the systems will break down because those who knew how to deal with the problems are no longer available.
This is how you can have 10 million unemployed workers and 1 million unfilled positions that can’t be filled because few are truly qualified. You want to erect new electrical transmission lines? Nice, but you’re not going to get the job done with green workers accustomed to staring at screens. It takes years of hard labor to acquire even a bare minimum of the skills required. These are not assembly-line jobs that can be filled by unskilled labor, these are jobs in the messy real world, not a distribution center.
As I note in my book on Self-Reliance, individuals with a full spectrum of real-world skills are now extremely rare. Skills that were once common are now performed by specialists. We seem to have all the time in the world to stare at hundreds of cooking programs on TV but how many people actually prepare three meals a day, week in, week out, month in, month out, year in, year out? How many people know how to repair anything, build anything, or maintain a machine?
My direct experience is that many young people don’t know how to put air in the tires of the vehicle Mom and Dad gave them. Young people with graduate-level diplomas don’t know what a green bean plant looks like. (Eeew, gross, it grows in dirt?) The cultural value system that only values wealth, regardless of its source, and minting money from staring at screens has generated a fundamental mismatch between the skills that will be needed going forward and the skills being presented as oh-so-valuable.
Yes, there are many young workers with sharp real-world skills. The question is, are there enough?
This is how we’ll end up with severe shortages of truly skilled labor and high unemployment in the cohort of workers with few real-world skills and a surplus of skills for which there is limited demand. As a real-world experiment, go find a tough old rancher and ask them a series of questions about livestock, machinery, fencing, generators, etc., and then ask the average newly minted college graduate that followed the warped values embedded in our economy the same questions.
Of course the young worker can’t match the experience of the old worker, but do they have any experience at all of a spectrum of essential real-world skills? If not, do they have the requisite physical endurance and commitment needed to acquire real-world skills?
Who’s going to do all the real-world work going forward? A few people talk about it as an abstraction, but it’s not an issue to everyone focused on Federal Reserve policy or GDP. But eventually, the real world will matter more than staring at screens and day-trading, because when the systems break down due to lack of truly qualified employees, we’ll all wake up. But by then it will be too late. We’ll be staring at dead screens begging for somebody somewhere to restore power so we can continue playing with ChatAI to trade zero-day options.