By Charles Hugh Smith
Source: Of Two Minds
It’s time once again to check for Ministry of Propaganda updates, which like Windows and iOS is constantly being updated to counter new threats and enhance the user experience (heh).
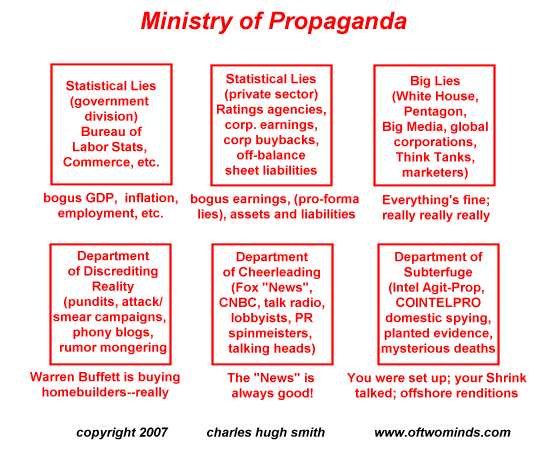
Much like the other operating systems that underpin our daily lives, the core functions of the MoP don’t change much. My chart from 2007 remains an instructive summary of MoP operations, with the only changes being Mr. Buffett is now buying oil companies and social media corporations are now major media players.
The core mission of the Ministry of Propaganda isn’t just to push a desirable narrative–it’s to mystify the underlying dynamics of a system that benefits the few at the expense of the many by promoting a self-serving worldview (weltanschauung) that explains how the world works in a way that protects the interests of those in power.
As science fiction author Philip K. Dick explains in the quote below, the MoP narrative isn’t just a cloak thrown over the underlying dynamics, it’s the creation of an entire universe / worldview, including contexts for understanding what’s going on, establishing what’s valuable and what isn’t, and what behaviors enhance status and which ones marginalize us.
The Ministry of Propaganda isn’t monolithic: various factions compete to push their self-serving narratives. As Dick noted, this includes governments, corporations, religious and political groups, each of which understands that once the populace accepts their worldview, their power is cemented in realms far above mere force.
A key mechanism in establishing a dominant worldview is the think-tank or equivalent self-serving body claiming authority over what’s true / false and important / unimportant. This can be authority over the “correct” interpretation of spiritual texts, economic policies, healthcare “standards of care,” geopolitical goals, etc.
Since humans are innately social, status-striving beings, hierarchies of authority and power are the air we breathe. Those who establish themselves as authorities don’t just gain power, they cement their power on the basis of their authority rather than on loyalty or competence.
The enormous powers of social media and traditional media to promote claims of authority have generated a deranging snarl of conflicting agendas and narratives. Various centers of power collaborate on pushing worldviews that benefit their interests, but this isn’t entirely coherent. The one thing all participants in the Ministry of Propaganda agree on is our power is deserved and must be defended against all threats, which includes hostile entities inside and outside the national borders.
This fragmented, constantly shifting cacophony of competing authorities is destabilizing. As the tectonic plates of worldviews collide, the edges crumble and people naturally seek the safety of some core set of beliefs, in effect “circling the wagons” in an attempt to restore some internal stability.
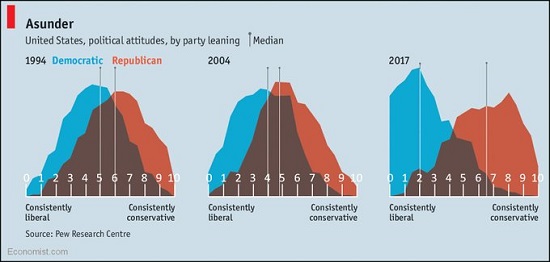
We see this in the intense political polarization of this era (see chart below). To make sense of the competing claims of authority, we reduce the perimeter of what’s defendable, putting more of the world into “outside enemies” (them) and reserving the “safe, trusted place” for fewer of “us.”
With so many competing factions in the Ministry of Propaganda, there’s a proliferation of propaganda such that there is literally nothing left but PR. In a universe constructed of nothing but agit-prop and PR, we all have our favorites examples. James Bond picks up his Nokia phone. Even though nobody’s seen a Nokia phone in ages, if you want to be cool like Bond, go buy a Nokia phone.
Marketing is the MoP’s entire universe. Everybody’s selling something to gain or maintain power, status, mindshare or the ultimate prize, the dominant worldview.
To ease the confusion, please download the latest updates from the Ministry. These updates replace all that misinformation, misdirection, and blatant marketing with the, ahem, facts, or the correct interpretation of the facts. (We had to destroy the village in order to save it. OK, got it.)
While it’s fun to sort all the propaganda into various boxes, we would do well to look for what all the marketers / MoP players seek to mystify. In my analysis, what must be mystified at all costs boils down to the unsustainability of 1) the current consumption of resources, 2) the current method of creating capital so the few can buy up the planet’s most valuable assets, 3) neocolonialism, the modern replacement for the old model of occupation and exploitation by force, and 4) neofeudalism, the economic / social /political arrangement in which the majority of the populace are modern-day serfs with extremely limited agency and power which they are told is limitless.
“You can be anything you choose to be!” Or at least your digital avatar can do so, and that’s practically as good as actually having agency and power in the real world. Or so we’re told, mindlessly, endlessly without pause or respite.
More on these topics in the coming weeks.