By Stavroula Pabst and Max Blumenthal
Source: The Grayzone
Marketed as life-saving public health measures, lockdowns triggered death and economic devastation on a global scale while doing little to slow the spread of Covid-19. Now, they’re back with a vengeance.
In October 2021, it seemed as though the lockdowns that still paralyzed societies from Australia to New Zealand and Singapore were coming to an end, as these countries threw in the “Zero-COVID” towel following a year and a half of rolling restrictions and closures.
But with COVID-19 cases rising in Europe, several countries are implementing lockdowns all over again, often with clearly punitive motivations.
This November, Austria’s government announced that police would enforce a lockdown exclusively against unvaccinated citizens. Following days of massive protests, the policy was extended to everyone, with steep fines and even prison sentences to be imposed on those who refuse to comply, and a compulsory vaccination requirement tacked on for good measure.
Next door in Germany, where a new lockdown was announced this December for unvaccinated people, barring them from almost all public places except for pharmacies and supermarkets, Berlin is also weighing a vaccination mandate for all. One German constitutional lawyer has even proposed that refusers of the jab “be brought before the vaccinator by the police.”
Though statewide lockdowns have eased in Australia, the country is constructing internment camps for those who test positive for Covid, along with their Covid-negative “close contacts.” Harley Hodgson, an Australian held for 14 days in one such camp despite repeatedly testing negative for Covid, said of her experience: “You feel like you’re in prison. You feel like you’ve done something wrong. It’s inhumane what they’re doing.”
Initially marketed to the public as a means to “flatten the curve” and “slow the spread,” lockdowns now represent one of the most draconian aspects of the perverse New Normal that has metastasized amid an atmosphere of seemingly endless emergency.
While much of the public accepted such restrictions during the early days of the pandemic, they are now met with increasing resistance by citizens around the world who have suffered from economic devastation, homelessness, suicidal ideation, social isolation, domestic violence, addiction and the cancellation of routine medical procedures as a result of lockdowns.
The public health justification for these non-pharmaceutical interventions has not only been discredited in the eyes of millions across the globe, but by an array of scientific studies and data demonstrating that they likely caused more deaths than they prevented.
The lethal impact of lockdowns was particularly pernicious in the Global South, where hundreds of millions of the world’s most vulnerable people were driven into a cascading humanitarian crisis. As the World Food Program warned in 2020, “135 million people on earth are marching towards the brink of starvation” as a result of their economies shutting down to supposedly inhibit the spread of COVID-19.
In his book, The Covid Consensus, professor of African history at King’s College Toby Green chronicled the misery, migration outflow and mass death spawned by lockdowns imposed on populations from Africa to Latin America.
“Lockdowns were not a policy that made any sense in societies where many people live largely outside, and SARS-CoV-2 is a virus that circulates inside,” Green told The Grayzone. “Moreover, they made no sense in regions such as Africa where the population is much younger than in rich countries – they merely saw a massive shift of health burden from the global rich to the global young and poor.”
For most people on the planet, the economic and psychological harm experienced during the past 19 months was not the result of the pandemic per se, but of emergency-order restrictions governments imposed on them and justified as public health measures. In the Global North, such costly efforts did little more than delay the inevitable spread of COVID-19 while transferring wealth into the hands of Big Tech oligarchs who constitute the pandemic’s real “winners.”
Though public health scholars and some officials warned that lockdowns would do possibly irreparable damage to the global economy while only deepening the public health crisis, the politics of the Trump era enabled supporters of harsh restrictions to caricature critics as dangerous right-wing extremists.
“Discussion of the inevitable harm of lockdowns has been almost totally forbidden by most of the mainstream media and academia, while the left followed the lead of the Democratic Party, doing all it could to marginalize any discussion of the collateral damage of these measures,” Christian Parenti, professor of economics at the City University of New York and author of several books about policing and mass surveillance, commented to The Grayzone. “Any questioning of lockdown measures was cast as right wing, even fascist. But mostly the left just ignored the emerging facts, particularly regarding the carnage caused in the Global South.”
One of the most outspoken among the public health scholars sounding the alarm about the social cost of sweeping restrictions was Dr. Jay Bhattacharya, a professor of medicine at Stanford University. As a co-author of the Great Barrington Declaration, which advocated a strategy of focused protection instead of hard lockdown, Bhattacharya and his colleagues were subjected to social media censorship and mainstream media attacks.
“Lockdowns provided the illusion of control over a virus that was present in parts of the world and spreading far earlier than most officials believed,” Bhattacharya told The Grayzone. He added, “Much of the evidence that people have developed to argue that lockdowns work come from modelling studies that have proved incredibly inaccurate.”
Indeed, the initial inspiration for locking down the UK and parts of the US derived from a bunk model of projected fatalities that has since been discredited.
Lockdowns were inspired by bogus modelling by unqualified academics
On March 16, 2020, as the global consensus formed around implementing restrictions in some form, a professor from London’s Imperial College delivered a presentation to the British government that would prove pivotal. That academic, Neil Ferguson, introduced a model asserting that if the UK did not impose a harsh lockdown, 500,000 citizens would die of Covid-19 that year; and if it took only moderate steps to restrict public life, as Prime Minister Boris Johnson planned, 260,000 would die.
In either case, Ferguson insisted, the national healthcare system would be overwhelmed and the economy irreparably damaged. Within a week, Johnson’s government accepted Ferguson’s fatalistic model and locked down hard.
Around the same time, the Trump White House received a paper from Ferguson that envisioned a catastrophic death toll. His model predicted fatalities at a 25% higher rate than the CDC’s already stark projection: 2.2 million dead in the first year unless the US instituted lockdowns.
“What had the biggest impact in the model is social distancing, small groups, not going in public in large groups,” Dr. Deborah Birx, a leader of Trump’s coronavirus task force, referring to the Imperial College projection. The New York Times reported on March 16, the day the Trump administration received Ferguson’s paper: “White House Takes New Line After Dire Report On Death Toll.”
While Ferguson’s modelling succeeded in inspiring harsh lockdowns, it ultimately brought him public embarrassment. First, the professor was caught breaking the quarantine he personally inspired to enjoy a tryst with his lover – a married woman who complained that the lockdown “strained” her relationship with the professor. Then, as time went on, it became clear that Ferguson’s models had exaggerated the Covid-19 fatality rate by a factor of at least four.
“Yes, my prediction was off,” he admitted to the Times of London in August 2021. But by then, the damage was done.
This was not the first time Ferguson’s numbers had proven to be wildly off the mark. Back in 2001, Ferguson projected that as many as 50,000 could die from Mad Cow Disease. After a panicked government slaughter of some 6.5 million cattle, the mass death failed to come to fruition. (Only about 2,800 have died from Mad Cow in three decades).
In 2005, Ferguson was at it again, predicting up to 200 million global deaths from the bird flu. In the end, only a few hundred people died. Then in 2009, Ferguson warned that 65,000 could die from the swine flu in the UK alone. But when the dust cleared, he and his team were off by a factor of over 1000.
So why did governments across the Atlantic trust a serial exaggerator who appeared to have no formal training in epidemiology or computer modelling, and whose codes were buggier than a locust infestation?
Before briefings from Ferguson, leaders from Whitehall to Washington were already in a panic over the onset of the novel coronavirus. A haze of reporting in early 2020 made the coronavirus appear more deadly than it turned out to be, with some reports suggesting the fatality rate could rise to as high as seven percent.
Although it is now known that COVID-19 does not kill the vast majority of people it infects, with Infection Fatality Rates (IFR) of .15 percent overall and .05 percent for persons under 70, the confusion and uncertainty led many public health officials to act quickly. In reality, the coronavirus is a less lethal disease that spreads easily, making it harder to contain with human interventions.
Further, according to Toby Green of King’s College in London, British public health officials were easily seduced by the tech-centric presentation of academics like Ferguson.
“Let’s remember that in the UK, where Ferguson’s model first had its influence, Dominic Cummings, Boris Johnson’s advisor on Covid-19, had already written about the importance of a data-driven approach to policy,” Green explained. “Matt Hancock, the health minister, was also highly integrated into the tech sector through his family, which runs a tech business. So a computer-driven model [like Ferguson’s] was appealing.”
Somehow, the technocrats placed in charge of Covid-19 policy across the Atlantic demonstrated little concern for how the lockdowns they suddenly imposed would impact the economic and social wellbeing of the citizens they were supposed to protect.
A bonanza for tech oligarchs, “the equivalent of smoking 15 cigarettes a day” for the less fortunate
In the United States, lockdowns and various rolling restrictions triggered an economic catastrophe for working and poor people across the country, pushing those already on the financial precipice over the brink.
In the US in 2020, 40 percent of people making under $40,000 annually lost work, and almost three million women were driven out of the workforce due to an inability to balance work and caregiving and virtual learning obligations for children who could no longer attend in-person school or daycare. Dozens of airlines failed, and at least 200,000 small-businesses were shuttered.
Increased unemployment benefits and stimulus checks had a salutary effect on the economic well-being of average Americans, seeing personal savings rise 8 percent between 2019 and summer of 2021. But even if American poverty did not immediately surge, it may yet do so, now that stimulus checks, generous unemployment benefits, and the eviction moratorium have all been terminated by the administration of President Joe Biden.
As lockdowns drove inequality in the US, millions skipped routine medical care such as childhood vaccinations and cancer screenings, because the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommended that hospitals suspend non-essential and elective procedures. In May 2021, almost ten million routine screenings were missed in the United States, while other preventative health visits declined on a mass scale due to elective procedure suspensions, which may also lead to worsening public health problems in the long-term.
Due to the CDC’s recommendations, 1.4 million medical workers lost their jobs in April 2020. One medical record company estimated that screening for breast, colorectal, and cervical cancers dropped by 80% to 90% during March and April of 2020 compared to the same months in 2019. Now, the US is struggling with a surge of cancers and other ailments that went undetected because of overzealous and overly broad lockdowns.
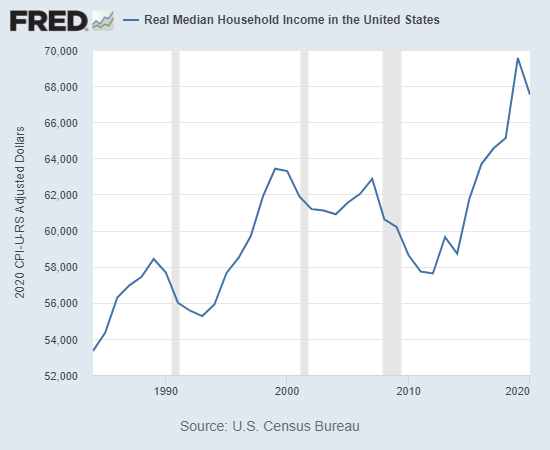
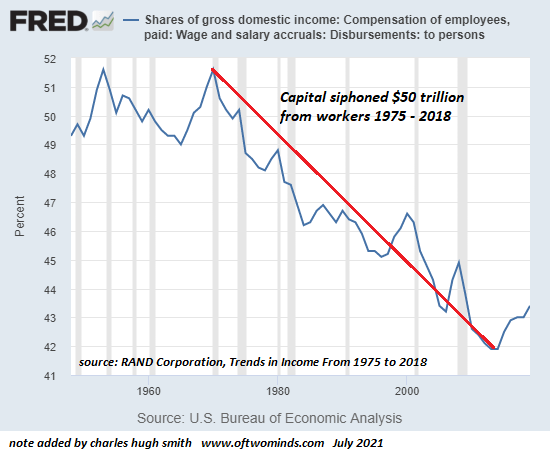
While average Americans paid a heavy price for the restrictions, Big Tech oligarchs quickly emerged as the pandemic’s winners. In 2020, billionaires increased their wealth by 54 percent. In fact, the top 1% of U.S. households now officially control more money than the entire middle class, or the middle 60 percent of households by income, in the US.
While the pandemic response has adversely affected working people and small businesses worldwide, lifting restrictions is in fact against major corporate interests: Amazon’s stock even fell seven percent in July as re-openings stalled pandemic-related online buying.
As lockdowns took their psychological toll on the US population, opioid-related deaths surged to record levels – up 30% from the previous year across the country and up 40% in 10 states. The sharpest rise in deaths occurred in Black Americans, along with those aged 35 to 44.
Lockdowns and excessive closures have also contributed to an international rise in domestic violence.
Despair rose in a significant way with the crisis: according to the CDC, 25.5 percent of survey respondents aged 18-24 reported seriously considering suicide within the previous 30 days by the end of June 2020. The same study indicated adults were more than twice as likely to report considering suicide when compared to those surveyed before the onset of coronavirus.
Professor Stephen Reicher, a behavioral scientist who advised the UK government on Covid policy, commented: “The problem with lockdown is isolation; being cut off from people is bad for you psychologically and physically. It is the equivalent of smoking 15 cigarettes a day.”
The impact of restrictions on young people, adolescents and babies who are at very little risk of illness with serious COVID-19, with a one in 50,000 chance of hospitalization and a two in one million chance of death for children, cannot be overstated. Babies and young infants, after all, require regular socialization and interaction for healthy development. Many of them, however, were only able to visit their closest family members over the past year and a half. Ultimately, extended periods of social isolation or loneliness can negatively impact a young individual’s health even decades later.
The overall outlook for young people, as suggested by the 2020 CDC study referenced above, is and remains grim. In Las Vegas, Nevada, schools opened in December of 2020 after an unprecedented 18 adolescent suicides were recorded in the district since March of the same year. And in the state of Victoria, Australia, about 340 teenagers each week were hospitalized due to mental health emergencies as of August 2021.
For many among the urban laptop class, including a large swath of the hyper-online Western left which still clamors for national school closures and demands lockdowns in the face of a handful of new cases (while crudely painting critics of official Covid policy as Nazis), quarantine orders merely enforced an already sedentary lifestyle that revolves around Zoom meetings, ordered food and Amazon deliveries. The restrictions further eliminated tedious commutes to work while providing those able to work remotely with the satisfying sense that staying home was a bold act of social solidarity.
Under this spectacular arrangement, which assumed individual behavior could slow down or contribute to the spread of a virus, isolation was framed as a moral choice that led many of those willingly confined to their homes to fear or vilify a working class that frequently provided them with vital services. And while non-pharmaceutical interventions have generally proven futile against COVID-19, the stentorian demands to socially distance and attendant shaming of those who fail to obey has done little more than generate hostility between friends, families, and communities.
“Lockdowns are a luxury of the rich,” Bhattacharya said, “and affect a certain class of people at the expense of others. A lockdown doesn’t mean all of society stops and we all sit in cages alone while we wait for the fires to go away. The poor and working class, many of them vulnerable and older, are asked to risk themselves, while another class of people stays at home protected.”
This was particularly true in the Global South, where class divisions are clearly drawn and most people live dangerously close to the poverty line.
Lockdowns drive debt, dependency and death across the Global South
The legacy of colonialism and imperialism has split the world economy into a “core” of wealthy economies and a periphery of poor economies that are largely dependent on exporting cheap raw materials and low-value added manufactured goods. When the wealthy core economies locked down in 2020, international trade contracted, triggering a violent economic whiplash in developing countries as their earnings from exports and tourism suddenly collapsed.
As a result, developing country debt has risen from an average of about 40 percent of overall GDP to over 60 percent. Throughout 2020, developing economies were forced to pay out 194 billion to their creditors, even as their economies contracted dramatically. This forced poor countries to cut deeply into social spending to maintain debt servicing from institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Since the COVID-19 pandemic was declared, the IMF has doled out “Covid funds” to 85 countries around the world. An analysis by Oxfam found that 85% of the 107 loans provided to these countries require them to impose austerity until well into the future to pay them back. Now, devastating impacts on future health and social spending in poor countries is practically inevitable.
With surging unemployment, reduced incomes, and fewer social services, the populations of poor countries in the Global South have experienced massive increases in hunger.
As early as July 2020, the Associated Press reported that an additional 10,000 children were dying of hunger every month “due to the virus.” In fact, the deaths were the result of governments’ choice to lock down. Indeed, the coronavirus has had very little effect on the health of children, except indirectly through bad policy. Thus, millions of children across the Global South who were not hungry in 2019 are hungry today because of the lockdowns.
In all, about 2.37 billion people – or about 30 percent of the world population and 320 million more people than in the previous year – did not have access to adequate food at some point during 2020.
As Nash Landesman reported for The Grayzone, extensive lockdowns with little social support by the US-backed government of Colombia led to mass unemployment, evictions, and widespread hunger throughout 2020, especially in working class neighborhoods of Bogotá, where residents placed red flags outside their homes to signal their sense of despair.
Mexicans similarly protested lockdown measures, with one vendor affixing a sign to her stall reading: “Mexico is NOT Europe. If you don’t work, you don’t eat.”
And in Honduras, which has been ruled for over a decade by a corrupt US-backed government installed through a military coup, citizens facing food and water shortages due to lockdown took to the streets in protest in March 2020, encountering heavy police repression. The protests continued into September, with drivers blocking roads to demand compensation for wages lost during the forced quarantine.
In India, meanwhile, where GDP shrank a record 7.3 percent from March 2020 to March 2021, a study of Uttar Pradesh state households found incomes contracting about 75 percent. Anthropologist Dr. Chandana Mathur of Maynooth University reported that the strict, yet poorly planned lockdowns in India kept millions of migrant workers away from income sources, forcing them into homes that were thousands of kilometers away from work or simply non-existent.
Just two days before the March 2020 lockdown, many transportation services in India ground to a halt, stranding and starving thousands of people at a time when strict stay-at-home rules were declared. To enforce the orders, police brutally beat those considered insufficiently compliant. One estimate found that about 1,000 people died from March to July 2020 due to the displacement.
In fact, mass suffering was anticipated by some governments and experts when the restrictions began. In March 2020, a cost-benefit analysis by the Dutch government’s Ministry of Economic Affairs and Climate Policy concluded health damage from lockdown would be six times greater than the benefit. Similarly, a 2020 Actuarial Society of South Africa model posited that a lockdown in the country may lead to 29 times more deaths than the restrictions can prevent.
And indeed, when lockdowns and other stringent interventions were applied in South Africa, many suffered enormously. Researchers estimate that 47 percent of South Africans ran out of money for food in April 2020. While rates of deprivation have decreased, estimates of hunger in the country remained steady at 17 percent of households throughout April and May 2021.
South Africans also faced a decrease in overall life expectancy due to other restriction-perpetuated factors, such as an increase in HIV and tuberculosis related health issues thanks to treatment stoppages, outbreaks of other infectious diseases especially associated with malnutrition, poverty and suspension of relevant vaccination programs, and interruptions in maternal and infant care.
Despite such excessive restrictions in the country, which previously included a curfew, a ban on gatherings and even on alcohol sales, some estimates found that 80 percent of South Africans were still infected with COVID-19.
A recently published study by researchers at the University of Johannesburg and the University of the Free State, COVID-19 in South Africa, found that “no changes in the shape of the [epidemiological] curve can be attributed to the introduction or easing of any regulation at [the current time].”
Instead of flattening the proverbial curve, restrictions induced economic and social deterioration which killed millions in the name of public health, while depriving an entire generation of the global poor of the right to education.
Lockdowns brutalized the world’s poor while depriving generations of education
For governments across the world, Covid provided an opportunity to pummel their most vulnerable residents, as well as those who dissented from the official order. As Amnesty International’s European bureau stated in a detailed but under-acknowledged June 2020 report, “The police enforcement of lockdowns disproportionately impacted poorer areas, which often have a higher proportion of residents from minority ethnic groups.”
Among Amnesty’s most disturbing findings was that police searches of Black Britons rose by a full third in the first month of the pandemic; Roma populations across Eastern Europe were placed under militarized quarantines and cut off from food supplies, causing deprivation on a mass scale; homelessness surged across the continent, and refugees and minority residents were subjected to police brutality on a regular basis.
Throughout 2020 in New York City, Black and Latino residents received a whopping 80% of police summonses for supposedly violating social distancing measures, leading civil rights groups including a local chapter of Black Lives Matter to complain that Covid restrictions were being exploited to bring back dreaded “stop and frisk” policies.
In Greece, such measures have been exploited to target refugees, migrants, and others living on the margins of society. Greek authorities have even fined refugees arriving by boat to Chios island 5000 euros each for not providing proof of negative coronavirus tests in late August 2021.
Many refugees that I, Stavroula, am personally acquainted with in Greece avoided spending time outside during the country’s six month lockdown from November 2020 to May 2021 out of fear of arrest and deportation. The lockdowns, which often confined people to a few miles from their home, and which imposed curfews as early as 6pm, required everyone to possess a government-issued identification and a text message or written note explaining their reason for being in public.
Penalties for violating the restrictions could mean fines of 300 euros, about half a monthly salary in the country, which could financially ruin many Greeks. For those in the country without papers, not having the required documentation during an encounter with police could even lead to deportation.
Across the globe, tens of thousands of people, mostly poor and working class, have been arrested for violating quarantine and been locked up in crowded unsanitary jails where Covid infections run rampant.
In Washington DC’s municipal jail, 1500 inmates were held in de facto solitary confinement for over 400 days without basic services throughout 2020 and early 2021. Though most inmates had already contracted COVID-19, developing durable natural immunity to the virus, the lockdown was justified on the grounds of “slowing the spread.”
“An overwhelming majority of the jail’s inmates are Black, and many have not yet been found guilty of the crimes for which they were arrested,” the Washington Post noted.
Similarly, St Louis city jail was the site of four prisoner uprisings since December 2020, with inmates forced into de facto solitary confinement for over a year with no trials. “People currently incarcerated…are tired of living in fear of COVID-19 and not being brought to trial,” one prisoner stated.
School-aged children and students around the world also suffered enormously under the weight of closures, particularly those in impoverished communities. In Uganda, citizens have spent large parts of the past two year under various forms of lockdown, with schools and recreation centers closed under orders of the US-backed leader Gen. Yoweri Museveni.
“An entire generation of our children is being plunged into the bottomless abyss of illiteracy and ignorance. I saw a docile wasted generation of young defenseless victims of Gen. Museveni’s warped COVID-19 directives loitering about and dwindling in hopelessness,” wrote dissident Kakwenza Bashaija after a visit to eastern Uganda.
The New York Times reported this November that Uganda’s ongoing school closures have consigned the county’s youth to possibly lifelong poverty. With educational institutions still off limits, the Times wrote, “young women, abandoning hopes of going to school, are getting married and starting families instead. School buildings are being converted into businesses or health clinics. Teachers are quitting, and disillusioned students are taking menial jobs like selling fruit or mining for gold.”
Poor and working class youth across the United States experienced similar educational setbacks as closures forced them out of the classroom. In the state of Virginia, for example, math achievement scores in 2021 were down by over 40% for eighth graders in comparison to 2018-19. Less than half of Black students from third to sixth grade were able to pass reading tests, while the math scores of disabled youth declined precipitously.
Glen Youngkin, a Republican who ran for governor in Virginia this year, highlighted these dismaying figures and slammed school closures in his closing campaign message. By capitalizing on the pent-up anger of parents in the state’s swing districts, Youngkin scored a surprise victory against a seasoned and well-funded opponent in a heavily Democratic state.
Meanwhile, in the Democratic bastion of New Jersey, incumbent Governor Phil Murphy nearly lost to a lesser known Republican challenger who hammered him over his support for some of the most stringent lockdown measures in the country. Murphy was walloped in Atlantic County, home of the Atlantic City resort and casino city where lockdowns pushed one third of small businesses into permanent collapse.
As the Biden administration considers new restrictions for US travelers, including placing the unvaccinated on a domestic no-fly list, the impact of lockdown policies has helped disrupt the international supply chain, driving inflation and shortages in supplies, gasoline, and even certain food items.
With the US government collaborating desperately with major corporations and retailers to repair the existing supply bottlenecks, some in the media class have urged convenience-accustomed Americans to simply lower their expectations.
While these lockdowns were implemented to supposedly blunt the impact of a public health danger, mainstream media have generally avoided a discussion of how well they mitigated the perceived crisis or of the severe social and economic harm they did to working people.
Despite the mass job loss, economic destruction, and increased hunger that non-pharmaceutical interventions have inflicted on the global population, the effectiveness of efforts such as lockdowns, curfews, school closures, and the constant PCR testing of healthy people are dubious at best.
Unpacking the misconception lockdowns work against COVID-19
Many credited lockdowns in China, Greece, Vietnam, and Australia with early COVID successes, contributing to a widespread perception that lockdowns are vital to saving lives, and, therefore, a compassionate choice. Such reasoning has led governments internationally to proceed with lengthy closures of daily life.
According to Dr. Bhattacharya, these policies might be appropriate to halt the spread of a given virus depending on its profile and status. “There are diseases that are incredibly deadly, but not particularly infectious, where quarantining and sharp lockdowns locally can be quite effective,” Bhattacharya explained. “For instance, we limited the Ebola [virus] outbreaks in this way.”
Could COVID-19 have been addressed through sharp interventions as Ebola was? The answer depends in part on the properties of the virus, such as how deadly it is and how and how easily it spreads. Oftentimes, more lethal diseases spread less easily than their weaker counterparts, and that’s because the host will either die or know what they have and isolate themselves accordingly, thus halting transmission. Despite significantly higher fatality rates (25-90%, depending on the outbreak) in relation to COVID-19, Ebola is less infectious than other diseases and does not spread through the air: in fact, it typically dies within thirty seconds outside bodily fluids.
In contrast, COVID-19 is a respiratory virus that likely spreads through aerosol transmission. Echoing the now-discredited modelling from the Imperial College of London, media coverage from early 2020 made the coronavirus appear more deadly than it turned out to be, with some reports suggesting the fatality rate could rise to as high as seven percent. In reality, the coronavirus is a less lethal disease that spreads easily, making it harder to contain with human interventions.
Because COVID-19 is a seasonal virus that tends to flourish in winter, much like the flu, early COVID “victors” like New Zealand and Australia were fortunate to get hit with it during their respective summers. They also are geographically isolated. The rest of the world was not so lucky.
Drawing on studies of virus prevalence in California urban areas in March 2020, for example, Bhattacharya concluded it was “too late” for the coronavirus measures that state officials issued to help eliminate the virus, with about 3-4% of survey respondents reporting they already had COVID-19 antibodies.
Such numbers suggest that the virus was present much earlier in many parts of the world than originally believed, rendering subsequent preventive pandemic measures futile in eliminating or slowing the virus despite their stringency. In other words, based on the nature of its spread and its widespread establishment in many communities, the virus had already taken root in an irreversible way.
“You don’t get up to 2 to 4 percent disease spread [of COVID-19] unless you’ve had it spreading for a while,” Bhattacharya said in reference to the California seroprevalence study. “That means 96 percent of the population [at the time was] still susceptible to the virus, and far from endemic. But way too far gone to actually have hope that any lockdowns will stop the disease.”
Despite the tendency to resort to them when cases rise, the evidence of lockdowns’ effectiveness in inhibiting the spread of coronavirus is threadbare.
Peru, which boasts the world’s highest COVID-19 death rate despite imposing hard lockdowns, was a case in point. Meanwhile, Greece locked down in November 2020 at around 2,500-3,000 cases daily, only to open again for tourism six months later with similar case numbers. Then there was Belarus, a country of over 9 million which did not lock down or introduce a mask mandate, and boasted one of Europe’s lowest COVID death rates all the way up to the Delta surge in Eastern Europe.
The International Monetary Fund, or IMF, reportedly offered Belarusian President Aleksandr Lukashenko $940 million in COVID assistance on the condition that he imposed harsh pandemic restrictions. Lukashenko said he refused, proclaiming, “the IMF continues to demand from us quarantine measures, isolation, and a curfew. This is nonsense. We will not dance to anyone’s tune.”
By June 2021, only a minority of Belarusian citizens told pollsters they favored more COVID-19 restrictions.
Despite their widespread utilization as a non-pharmaceutical intervention against COVID-19, the shaky evidence for lockdowns does not end with anecdotes and country-specific strategies: dozens of academic and scientific studies call into question their efficacy or otherwise argue that the social, economic, and health related harms they pose significantly outweigh the risks. Their conclusions include the following (thread compiled by twitter user @the_brumby):
- In Did Lockdown Work? An Economist’s Cross-Country Comparison, Aarhus University Economics Professor Christian Bjørnskov writes that after “[u]sing two indices from the Blavatnik Centre’s Covid 19 policy measures and comparing weekly mortality rates from 24 European countries in the first halves of 2017-2020, and addressing policy endogeneity in two different ways, I find no clear association between lockdown policies and mortality development.”
- In Assessing mandatory stay-at-home and business closure effects on the spread of COVID-19, Eran Bendavid, Christopher Oh, Jay Bhattacharya, and John P. A. Ioannidis, a team of Stanford University academics and research data scientists, conclude that “there is no evidence that more restrictive nonpharmaceutical interventions (“lockdowns”) contributed substantially to bending the curve of new cases in England, France, Germany, Iran, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, or the United States in early 2020.”
- Medical researchers and doctors Rabail Chaudhry, MD, Justyna Bartoszko, MD and Sheila Riazi, MD (University of Toronto Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine), George Dranitsaris, MD (University of Ioannina Department of Hematology) and Talha Mubashir, MD (previously University of Toronto Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, now at the University of Texas McGovern Medical School Department of Anesthesiology) write in A country level analysis measuring the impact of government actions, country preparedness and socioeconomic factors on COVID-19 mortality and related health outcomes that “government actions such as border closures, full lockdowns, and a high rate of COVID-19 testing were not associated with statistically significant reductions in the number of critical cases or overall mortality.”
- In Stay-at-home policy is a case of exception fallacy: an internet-based ecological study, academics and researchers at Brazil-based institutions, including the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, R. F. Savaris, G. Pumi, J. Dalzochio & R. Kunst address early data favoring lockdowns and stay-at-home policies through an analysis of mathematical models and data from 87 regions worldwide. In “yielding 3,741 pairwise comparisons for linear regression analysis…[they] were not able to explain if COVID-19 mortality is reduced by staying at home in ~ 98% of the comparisons.”
- In Covid-19 Mortality: A Matter of Vulnerability Among Nations Facing Limited Margins of Adaptation, French medical researchers Quentin De Larochelambert, Andy Marc, Juliana Antero, Eric Le Bourg and University of Paris Professor of Physiology Jean-François Toussaint write that the “[s]tringency of the measures settled to fight pandemia, including lockdown, did not appear to be linked with death rate.” Instead, they conclude that nations with stagnating life expectancies and high rates of income and non-communicable disease —in other words, existing characteristics of a nation’s demographics— faced higher mortality rates regardless of government interventions.
- And in Government mandated lockdowns do not reduce Covid-19 deaths: implications for evaluating the stringent New Zealand response, University of Waikato Economics Professor John Gibson concludes that “Lockdowns do not reduce Covid-19 deaths…[t]he apparent ineffectiveness of lockdowns suggests that New Zealand suffered large economic costs for little benefit in terms of lives saved.”
These dozens of studies are consistent with pre-COVID-19 pandemic literature emphasizing the ineffectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions like lockdowns.
“Almost all [pre-pandemic planning guides before the coronavirus] emphasized respect for civil rights, disrupting societies as little as possible, protecting the vulnerable, and not spreading panic,” said Dr. Bhattacharya. “The lockdowns and the media narrative and the public health narrative of March 2020 violated all those principles.”
In a 2006 paper, Disease Mitigation Measures in the Control of Pandemic Influenza, academics at the Center for Biosecurity of the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (now known as the John Hopkins Center for Health Security) in Baltimore, Maryland, wrote: “Experience has shown that communities faced with epidemics or other adverse events respond best and with the least anxiety when the normal social functioning of the community is least disrupted.”
Documents as recent as the 2019 World Health Organization (WHO) guide, Non-pharmaceutical public health measures for mitigating the risk and impact of epidemic and pandemic influenza, furthermore, state that the “evidence base on the effectiveness of [Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions] in community settings is limited, and the overall quality of evidence was very low for most interventions.”
While already-existing pandemic literature naturally could not make COVID-19 specific recommendations, a well-established understanding of the general ineffectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions for respiratory viruses largely went unheeded as media and government-driven fear gripped the population in early 2020. Everyday people paid and continue to pay the price.
“Making poor people a lot poorer” and shortening life spans
While they may not be effective at limiting the spread of coronavirus, lockdowns are effective at destroying the economy, people’s livelihoods, and perhaps the social fabric itself as individuals grow used to remaining distant from friends, coworkers, family and community.
And while income and education losses, extensive isolation, and other COVID-related disruptions are devastating in the short-term, they also can inflict long-term adverse impacts on the length and quality of life, even decades later.
Childhood years are vital to shaping an adult’s overall well being, and adverse events that elicit extended stress responses throughout one’s youth can have significant impacts on lifespan, and risk of mental health issues and chronic physical health issues in the long term.
Long-term unemployment, a common phenomenon during COVID-19, can also shorten life expectancy, with Daniel Sullivan and Till von Wachter concluding in 2009 that mortality rates are 50 to 100 percent higher for individuals the year after involuntary income loss, and 10 to 15 percent higher overall for the next 20 years of life.
Consistent stress itself, certainly exacerbated by ongoing coronavirus restrictions, can also trigger or exacerbate long-term health problems. Highlighting such issues in detail in COVID-19: Rethinking the Lockdown Groupthink, University of Alberta Clinical Professor in the Department of Pediatrics Dr. Ari Joffe concluded that aggressive interventions such as lockdowns will cost society far more WELLBY, or Well-Being-Years, than foregoing them over time.
Generally, extreme restrictions hit marginalized populations and working class people the hardest, especially in places where many were employed informally, and must therefore leave their homes illegally to work during stay-at-home orders. Fines for breaking restrictions and curfews are often prohibitive, moreover, and fail to address that many people are inadequately housed and cannot consistently follow such rules.
Even the WHO has appealed against lockdowns, acknowledging the strain lockdowns place on the disadvantaged. “We really do appeal to all world leaders, stop using lockdown as your primary method of control,” WHO COVID-19 envoy Dr. David Nabarro told British broadcaster Andrew Neil. “Lockdowns have just one consequence that you must never ever belittle, and that is making poor people an awful lot poorer.”
As the logic behind “stopping the spread” through indefinite lockdowns is questioned even by top public health authorities, the policy has reappeared with a vengeance in Europe, where it has been weaponized against non-compliant populations and to intimidate citizens into line with government policy. A winter of lockdowns, coercion and threats begins
The government of Austria triggered waves of national protest this November when it became the first in the world to announce a lockdown exclusively imposed on unvaccinated people. Just days before resigning, then-Austrian Chancellor Alexander Schallenberg said he aimed to establish a “threatening backdrop” for those who refused to take the jab, promising that “Christmas will be uncomfortable” for them.
Days later, Schallenberg extended the lockdown to all citizens, imposing fines of up to $1660 for anyone who violates the restriction, per violation, and announced a policy of compulsory vaccination for all. For those unable to pay fines for remaining unvaccinated, their refusal “can be converted into a prison sentence,” as The Guardian reported. Those who did not take the jab by December 12 would remain under lockdown, underscoring the punitive agenda behind the policy.
Slovakia followed Austria’s lead, imposing a lockdown on unvaccinated citizens on November 18 before it expanded the policy to the entire population. The next country to impose an unvaccinated-only lockdown is Germany, where public health officials blame a “pandemic of the unvaccinated” for the fourth wave of COVID-19 cases. “Probably by the end of this winter, as is sometimes cynically said, pretty much everyone in Germany will be vaccinated, cured or dead,” remarked German Minister of Health Jens Spahn.
However, in Portugal, which has run out of people to vaccinate due to the country’s near-total uptake, infections are also surging, prompting the government to declare a state of emergency and impose a new bevy of restrictions. And in Gibraltar, officially the most jabbed place on the planet, with a 99% vaccination rate, authorities cancelled official Christmas festivities following a surge of COVID-19 cases. The news confirmed a November 2021 study from the US CDC that found that vaccinated people are “no less infectious” than those who are unvaccinated.
Just as the failure of vaccines to prevent the spread of COVID-19 became apparent, international media began filling up with panicked headlines about a terrifying new variant. Labeled “Omicron” by the World Health Organization on November 26, 2021, the variant reportedly originated in southern Africa. The doctor who discovered the variant has said all cases tend to be mild so far. According to the government of Botswana, it arrived thanks to four fully vaccinated travelers.
Among the first prominent public health pundits to hype the supposed danger of Omicron was Tom Peacock, a virologist from the Imperial College of London’s department of infectious diseases – a wing of the same Bill Gates-sponsored institution responsible for the discredited models that influenced the UK and US government’s first lockdowns by grossly overestimating the death toll from COVID-19.
Even before the threat from the so-called Omicron variant is known, the US and EU have enacted new restrictions which are certain to ravage the already weathered economies of southern Africa. On November 26, the Biden administration issued a ban on flights from South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Lesotho, Eswatini, Mozambique, and Malawi. (At the time of publication, several of these countries have yet to register a single Omicron case).
“We are now entering a world where borders close for every variant,” Toby Green, author of The Covid Consensus, commented to The Grayzone. “It’s quite clear that Western governments and media don’t care at all about lives and livelihoods in poor countries. Tour guides, hotel porters, restaurateurs, those who depend on international conferences and study abroad visits – a large proportion of service industries in the Global South – will be devastated. And who benefits? Service industries in rich countries, where the profiteering of the last 20 months will get spent.”
For millions at the mercy of the new wave of restrictions, a dark winter has just begun.