By Michael Hudson and Vlado Plaga
Source: Unz Review
Interview with Vlado Plaga in the German magazine FAIRCONOMY, September 2017.
Originally, you didn’t want to become an economist. How did it come that you changed your plans and digged so deep into economics?
I found economics aesthetic, as beautiful as astronomy. I came to New York expecting to become an orchestra conductor, but I met one of the leading Wall Street economists, who convinced me that economics and finance was beautiful.
I was intrigued by the concept of compound interest and by the autumnal drain of money from the banking system to move the crops at harvest time. That is when most crashes occurred. The flow of funds was the key.
I saw that these economic cycles were mainly financial: the build-up of debt and its cancellation or wipe-out and bankruptcy occurring again and again throughout history. I wanted to study the rise and fall of financial economies.
But when you studied at the New York University you were not taught the things that really interested you, were you?
I got a PhD as a union card. In order to work on Wall Street, I needed a PhD. But what I found in the textbooks was the opposite of everything that I experienced on Wall Street in the real world. Academic textbooks describe a parallel universe. When I tried to be helpful and pointed out to my professors that the textbooks had little to do with how the economy and Wall Street actually work, that did not help me get good grades. I think I got a C+ in money and banking.
So I scraped by, got a PhD and lived happily ever after in the real world.
So you had to find out on your own… Your first job was at the Savings Banks Trust Company, a trust established by the 127 savings banks that still existed in New York in the 1960s. And you somehow hit the bull’s eye and were set on the right track, right from the start: you’ve been exploring the relationship between money and land. You had an interesting job there. What was it?
Savings banks were much like Germany’s Landesbanks. They take local deposits and lend them out to home buyers. Savings and Loan Associations (S&Ls) did the same thing. They were restricted to lending to real estate, not personal loans or for corporate business loans. (Today, they have all been turned into commercial banks.)
I noticed two dynamics. One is that savings grew exponentially, almost entirely by depositors getting dividends every 3 months. So every three months I found a sudden jump in savings. This savings growth consisted mainly of the interest that accrued. So there was an exponential growth of savings simply by inertia.
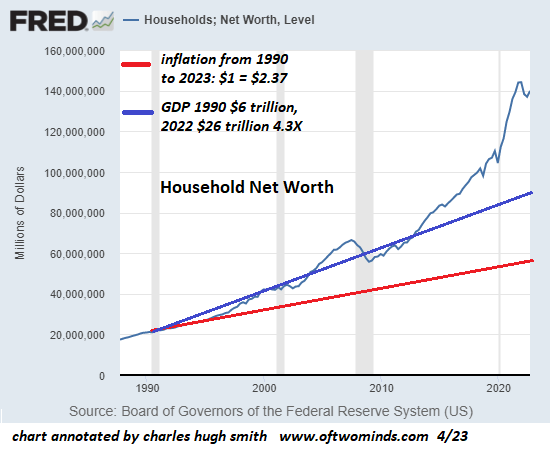
The second dynamic was that all this exponential growth in savings was recycled into the real estate market. What has pushed up housing prices in the US is the availability of mortgage credit. In charting the growth of mortgage lending and savings in New York State, I found a recycling of savings into mortgages. That meant an exponential growth in savings to lend to buyers of real estate. So the cause of rising real estate prices wasn’t population or infrastructure. It was simply that properties are worth whatever banks are able and willing to lend against them.
As the banks have more and more money, they have lowered their lending standards.
It’s kind of automatic, it’s just a mathematical law…
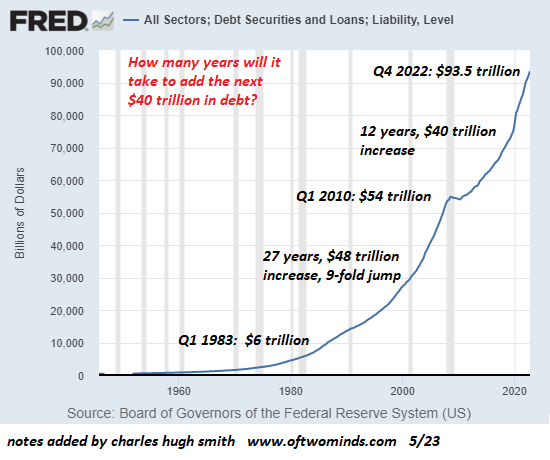
Yes, a mathematical law that is independent of the economy. In other words, savings grow whether or not the economy is growing. The interest paid to bondholders, savers and other creditors continues to accrue. That turns out to be the key to understanding why today’s economy is polarizing between creditors and debtors.
You wrote in “Killing the Host” that your graphs looked like Hokusai’s “Great Wave off Konagawa” or even more like a cardiogram. Why?
Any rate of interest has a doubling time. One way or another any interest-bearing debt grows and grows. It usually grows whenever interest is paid. That’s why it looks like a cardiogram: Every three months there’s a jump. So it’s like the Hokusai wave with a zigzag to reflect the timing of interest payments every three months.
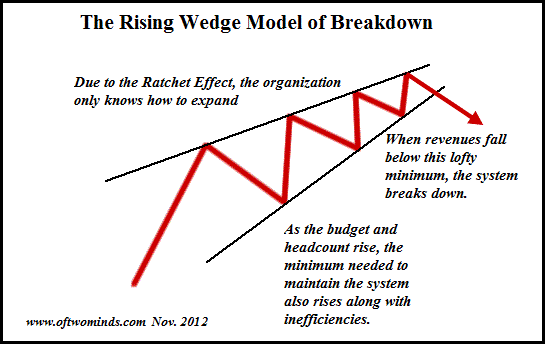
The exponential growth of finance capital and interest-bearing debt grows much faster then the rest oft he economy, which tends to taper off in an S-curve. That’s what causes the business cycle to turn down. It’s not really a cycle, it’s more like a slow buildup like a wave and then a sudden vertical crash downward.
This has been going on for a century. Repeated financial waves build up until the economy becomes so top-heavy with debt that it crashes. A crash used to occur every 11 years in the 19th century. But in the United States from 1945 to 2008, the exponential upswing was kept artificially long by creating more and more debt financing. So the crash was postponed until 2008.
Most crashes since the 19th century had a silver lining: They wiped out the bad debts. But this time the debts were left in place, leading to a massive wave of foreclosures. We are now suffering from debt deflation. Instead of a recovery, there’s just a flat line for 99% of the economy.
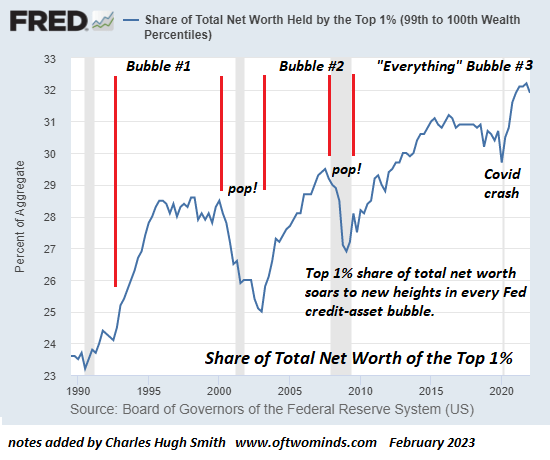
The only layer of the economy that is growing is the wealthiest 5% layer – mainly the Finance, Insurance and Real Estate (FIRE) sector. That is, creditors living of interest and economic rent: monopoly rent, land rent and financial interest. The rest of the economy is slowly but steadily shrinking.
And the compound interest that was accumulated was issued by the banks as new mortgages. Isn’t this only logical for the banks to do?
Savings banks and S&Ls were only allowed to lend for mortgages. Commercial banks now look for the largest parts of the economy as their customers. Despite the fact that most economic textbooks describe industry and manufacturing as being the main part of economy, real estate actually is the largest sector. So most bank lending is against real estate and, after that, oil, gas and mining.
That explains why the banking and financial interests have become the main lobbyists urging that real estate, mining and oil and gas be untaxed – so that there’ll be more economic rent left to pay the banks. Most land rent and natural resource rent is paid out as interest to the banks instead of as taxes to the government.
So instead of housing becoming cheaper and cheaper it turns out to be much less affordable in our days than in the 1960s?
Credit creation has inflated asset prices. The resulting asset-price inflation is the distinguishing financial feature of our time. In a race tot he bottom, banks have steadily lowered the terms on which they make loans. This has made the economy more risky.
In the 1960s, banks required a 25-30% down payment by the buyer, and limited the burden of mortgage debt service to only 25% of the borrower’s income. But interest is now federally guaranteed up to 43% of the home buyer’s income. And by 2008, banks were making loans no down payment at all. Finally, loans in the 1960s were self-amortizing over 30 years. Today we have interest-only loans that are never paid off.
So banks loan much more of the property’s market price. That is why most of the rental value of land isn’t paid to the homeowner or commercial landlord any more. It’s paid to the banks as interest.
Was this the reason for the savings and loan crisis that hit the US in 1986 and that was responsible for the failure of 1,043 out of the 3,234 savings and loan associations in the United States from 1986 to 1995?
The problem with the savings and loan crisis was mainly fraud! The large California S&L’s were run by crooks, topped by Charles Keating. Many were prosecuted for fraud and sent to jail. By the 1980s the financial sector as a whole had become basically a criminalized sector. My colleague Bill Black has documented most of that. He was a prosecutor of the S&L frauds in the 1980s, and wrote a book “The best way to rob a bank is to own one”.
That’s a famous quotation, I also heard that.
Fraud was the main financial problem, and remains so.
Since 2007 Americans were strangled by their mortgages in the sub-prime crisis…
These were essentially junk mortgages, and once again it was fraud. Already in 2004 the FBI said that the American economy was suffering the worst wave of bank fraud in history. Yet there was no prosecution. Essentially in the United States today, financial fraud is de-criminalized. No banker has been sent to jail, despite banks paying hundreds of billions of dollars of fines for financial fraud. These fines are a small portion of what they took illegally. Such payments are merely a cost of doing business. The English language was expanded to recognize junk loans. Before the financial crash the popular press was using the word “junk mortgages” and “Ninjas”: “No Income, No Jobs, no Assets”. So everybody knew that there was fraud, and the bankers knew they would not go to jail, because Wall Street had become the main campaign contributor to the leading politicians, especially in the Democratic party. The Obama Administration came in basically as representatives of the bank fraudsters. And the fraud continues today. The crooks have taken over the banking system. It is hard for Europeans to realize that that this really has happened in America. The banks have turned into gangsters, which is why already in the 1930s President Roosevelt coined the word “banksters”.
I also heard the nice English sayings “Too big to fail” or “Too big to jail”…
But what has become of those 10 million households that ended up losing their homes to foreclosure? How are their economic and living conditions today? What has become of their houses? The economy has recovered…
Most of the houses that were foreclosed on have been bought out by hedge funds for all cash. In the wake of 2008, by 2009 and 2010 hedge funds were saying “If you have $5,000,000 to invest, we’re going to buy these houses that are being sold at distress prices. We’re going to buy foreclosed properties for all cash, because we can make a larger rate of return simply by renting them out.” So there has been a transfer of property from homeowners to the financial sector. The rate of home-ownership in America is dropping.
The economy itself has not recovered. All economic growth since 2008 has accrued only to the top 5% of the economy. 95% of the economy has been shrinking by about 3% per year… and continues to shrink, because the debts were kept in place. President Obama saved the banks and Wall Street instead of saving the economy.
That’s why we live in an “age of deception” as the sub-title of your latest book suggests, I guess?
“People have the idea that when house prices go up, somehow everybody’s getting richer. And it’s true that the entry to the middle class for the last hundred years has been to be able to own your own home…”
What is deceptive is the fact that attention is distracted away from how the real world works, and how unfair it is. Economics textbooks teach that the economy is in equilibrium and is balanced. But every economy in the world is polarizing between creditors and debtors. Wealth is being sucked up to the top of the economic pyramid mainly by bondholders and bankers. The textbooks act as if the economy operates on barter. Nobel prices for Paul Samuelson and his followers treat the economy as what they call the “real economy,” which is a fictitious economy that in theory would work without money or debt. But that isn’t the real economy at all. It is a parallel universe. So the textbooks talk about a parallel universe that might exist logically, but has very little to do with how the real economy works in today’s world.
If you had a picture you’d see me nodding all the time, because that’s what I also found out: if you look at the mathematics, it is polarizing all the time, it is de-stabilizing. Without government interference we’d have crash after crash… It is not under control anymore.
But you also suggest that there’s another factor that makes housing prices go up – and that’s property tax cuts. Why?
“Taxes were shifted off the Donald Trumps of the world and onto homeowners….”
Whatever the tax collector relinquishes leaves more rental income available to be paid to the banks. Commercial real estate investors have a motto: “Rent is for paying interest.” When buyers bid for an office building or a house, the buyer who wins is the one who is able to get the largest bank loan. And that person is the one who pays all the rent to the bank. The reason why commercial investors were willing to do this for so many decades is that they wanted to get the capital gain – which really was the inflation of real estate prices as a result of easier credit. But now that the economy is “loan up,” prospects for further capital gains are gone. So the prices are not rising much anymore. There is no reason to be borrowing. So the system is imploding.
So, how could we change the situation and make land a public utility?
There are two ways to do this. One way is to fully tax the land’s rental value. Public investment in infrastructure – roads, schools, parks, water and sewer systems – make a location more desirable. A subway line, like the Jubilee tube line in London, increases real estate prices all along the line. The resulting rise in rents increases prices for housing. This rental value could be taxed back by the community to pay for this infrastructure. Roads and subways, water and sewer systems could be financed by re-capturing the rental value of the land that this public investment creates. But that is not done. A free lunch is left in private hands.
The alternative is direct public ownership of the land, which would be leased out to whatever is deemed to be most socially desirable, keeping down the rental cost. In New York City, for instance, restaurants and small businesses are being forced out. They’re closing down because of the rising rents. The character of the economy is changing. It is getting rid of the bookstores, restaurants and low-profit enterprises. Either there should be a land tax, or public ownership of the land. Those are the alternatives. If you tax away the land’s rent, it would not be available to be paid to the banks. You could afford to cut taxes on labor. You could cut the income tax, and you could cut taxes on consumption. That would reduce the cost of living.
To me that’s pretty close to the position of Georgists on how to handle land, isn’t it?
I don’t like to mention Henry George, because he didn’t have a theory of land rent or of the role of the financial sector and debt creation. The idea of land tax came originally from the Physiocrats in France, François Quesnay, and then from Adam Smith, John Stuart Mill, and in America from Thorstein Veblen and Simon Patten. All of these economists clarified the analysis of land rent, who ended up with it, and how it should be taxed. In order to have a theory of how much land rent there is to tax, you need a value and price theory. Henry George’s value theory was quite confused. Worst of all, he spent the last two decades of his life fighting against socialists and labor reformers. He was an irascible journalist, not an economist.
The classical economists wrote everything you need to know about land rent and tax policy. That was the emphasis of Adam Smith, John Stuart Mill… all the classical economists. The purpose of their value and price theory was to isolate that part of the economy’s income that was unearned: economic rent, land rent, monopoly rent, and financial interest. I think it is necessary to put the discussion of tax policy and rent policy back in this classical economic context. Henry George was not part of that. He was simply a right-wing journalist whom libertarians use to promote neoliberal Thatcherite deregulation and anti-government ideology. In Germany, his followers were among the first to support the Nazi Party already in the early 1920s, for instance, Adolf Damaschke. Anti-Semitism also marked George’s leading American followers in the 1930s and ‚40s.
So I guess I have to go back a bit further in history, to read the original Physiocrats as well…
John Stuart Mill is good, Simon Patten is good, Thorstein Veblen is wonderful. Veblen was writing about the financialization of real estate in the 1920s in his Absentee Ownership. I recently edited a volume on him: Absentee Ownership and its Discontents (ISLET, Dresden, 2016).
Germany’s land tax reform seems to go in the wrong direction. Germany has to establish new rules for it’s “Grundsteuer” that in fact is a mingled tax on land and the buildings standing on it, based on outdated rateable values of 1964 (in the West) and 1935 (in the East). The current reform proposals of the federal states will maintain this improper mingling and intend a revenue neutral reform of this already very low tax. It brings about 11 billion Euro to the municipal authorities, but this is only 2% of the total German tax revenue, whereas wage tax and sales tax make up for 25% each. We need a complete tax shift, don’t we?
Germany is indeed suffering from rising housing prices. I think there are a number of reasons for this. One is that Germans have not had a real estate bubble like what occurred in the US or England. They did lose money in the stock market, and many decided simply to put their money in their own property. There is also a lot of foreign money coming into Germany to buy property, especially in Berlin.
The only way to keep housing prices down is to tax away the rise in the land value. If this is done, speculators are not going to buy. Only homeowners or commercial users will buy for themselves. You don’t want speculators or bank credit to push up prices. If Germany lets its housing prices rise, it is going to price its labor out of the market. It would lose its competitive advantage, because the largest expense in every wage-earner’s budget is the cost of housing. In Ricardo’s era it was food; today it is housing. So Germany should focus on how to keep its housing prices low.
I’d like to come back to the issue of interest once more. The English title of “Der Sektor” is “Killing the host – How Financial Parasites and Debt Bondage Destroy the Global Economy”. It’s much more coming to the point. It struck me that you mention John Brown. He wrote a book called “Parasitic wealth or Money Reform” in 1898. I came across his book some years ago and thought that he was somehow America’s Helmut Creutz of the 19th century. He was a supporter of Henry George, but in addition John Brown analyzed and criticized the interest money system and its redistribution of wealth. He said that labour is robbed of 33% of its earnings by the parasitic wealth with subtle and insidious methods, so that it’s not even suspected. Why does almost nobody know this John Brown?
John Brown’s book is interesting. It is somewhat like that of his contemporary Michael Flürscheim. Brown’s book was published by Charles Kerr, a Chicago cooperative that also published Marx’s Capital. So Brown was a part of the group of American reformers who became increasingly became Marxist in the 19th and early 20thcentury. Most of the books published by Kerr discussed finance and the exponential growth of debt.
The economist who wrote most clearly about how debt grew by its own mathematics was Marx in Vol. III of Capital and his Theories of Surplus Value . Most of these monetary writers were associated with Marxists and focused on the tendency of debt and finance to grow exponentially by purely mathematical laws, independently of the economy, not simply as a by-product of the economy as mainstream economics pretends.
So you recommend reading his book?
Sure, it is a good book, although only on one topic. Also good is Michael Flürscheim’s Clue to the Economic Labyrinth (1902). So is Vol. III of Capital.
Brown’s plan of reforms included the nationalization of banks and the establishment of a bank service charge in lieu of interest. The latter sounds remarkably up-to-date. In Germany the banks are raising charges because of the decrease in their interest margins. How is your view on the matter of declining interest rates?
Well, today declining interest rates are the aim of central bank Quantitative Easing. It hasn’t helped. The most important question to ask is: what are you going to make your loans for? Most lending at these declining interest rates has been parasitic and predatory. There’s a lot of corporate take-over lending to companies that borrow to buy other companies. There is an enormous amount of stock market credit that has helped bid up stock prices with low-interest credit and arbitrage. This has inflated asset prices for stocks, bonds and real estate. If the result of low interest rates is simply to inflate asset prices, the only way this can work is to have a heavy tax on capital gains, that is asset price gains. But in the US, England, and other countries there are very low taxes on capital gains, and so low interest rates simply make housing more expensive, and make stocks and buying a flow retirement income (in the form of stocks or bonds that yield dividends and interest) much more expensive.
I guess Brown is getting to the positive aspects of low interest also.
What Brown was talking about were the problems of finance. In the final analysis there is only one ultimate solution: to write down the debts. Nobody really wants to talk about debt cancellation, because they try to find a way to save the system. But it can’t be fixed so that debts can keep growing at compound rates ad infinitum. Any financial system tends to end in a crash. So the key question is how a society is NOT going not to pay debts that go bad. Will it let creditors foreclose, as has occurred in the US? Or are you going to write down the debts and wipe out this overgrowth of creditor claims? That’s the ultimate policy that every society has to face.
Very topical, the German Bundesbank sees the combination of low interest rates and a booming housing market as a dangerous cocktail for the banking sector. “The traffic lights have jumped to yellow or even to dark yellow”, Andreas Dombret said, after the Bundesbank had denied the problem in the last years by dismissing it as Germany’s legitimate catch-up effects. The residential property prices have gone up by 30% since 2010, in the major cities even by more than 60%. The share of real estate loans in the total credit portfolio is significantly rising. The mortgage loans of the households have increased in absolute terms as well as relative to their income. It’s only due to the low interest rates that the debt service has not increased yet. But the banks and savings companies are taking on the risk: the mortgages with terms of more than ten years have risen to more than 40% of the residential real estate loans. The interest-change risks lie with the banks. Don’t we have to face up to the truth that interest rates shouldn’t go up again?
What should be raised are taxes on the land, natural resource rent and monopoly rent. The aim should be to keep housing prices low instead of speculation. Land rent should serve as the tax base, as the classical economists said it should. Adam Smith, John Stuart Mill… all urged that the basis of the tax system should be real-estate and natural resource rent, not income taxes (which add to the cost of labor), the cost of labor and not value-added taxes (which increase consumer prices). So tax policy and debt write-downs today are basically the key to economic survival.
Banking should be a public utility. If you leave banking in the present hands, you’re leaving it in the hands of the kind of crooks that brought about the financial crisis of 2008.
Couldn’t the subprime-crisis have been prevented if the Fed had introduced negative interest rates in the 1990s?
No. The reason there was the crash was fraud and speculation. It was junk mortgages and the financialization of the economy. Pension funds and people’s savings were turned over to the financial sector, whose policy is short-term. It seeks gains mainly by speculation and asset price inflation. So the problem is the financial system. I think the Boeckler foundation has annual meetings in Berlin that focus on financialization and explain what the problem is.
Yes, that’s a big topic. The financial sector is interested, as you said, in short-term gains, but people who want to save for their retirement are interested in long-term stability – that is contradictory. Do you know the “Natural Economic Order by Free Land and Free Money” by Silvio Gesell?
It is not practical for today’s world, it is very abstract. The solution to the financial problem really has to be ultimately a debt write-down, and a shift to the tax system, as the classical economists talked about.
Gesell was also advocating the taxing of land. I think he had something in mind with bidding for the land, letting the market fix the prices.
He did not go beneath the surface to ask what kind of market do you want. Today, the market for real estate is a financialized market. As I said, the basic principle is that most rent is paid out as interest. The value of real estate is whatever a bank will lend against it. Unless you have a theory of finance and the overall economy, you really don’t have a theory of the market.
You are advocating a revival of classical economics. What did the classical economists understand by a free economy?
They all defined a free economy as one that is free from land rent, free from unearned income. Many also said that a free economy had to be free from private banking. They advocated full taxation of economic rent. Today’s idea of free market economics is the diametric opposite. In an Orwellian doublethink language, a free market now means an economy free for rent extractors, free for predators to make money, and essentially free for financial and corporate crime. The Obama Administration de-criminalized fraud. This has attracted the biggest criminals – and the wealthiest families – to the banking sector, because that’s where the money is. Crooks want to rob banks, and the best way to rob a bank is to own one. So criminals become bankers. You can look at Iceland, at HSBC, or at Citibank and Wells-Fargo in the news today. Their repeated lawbreaking and criminal activities have been shown to be endemic in the US. But nobody goes to jail. You can steal as much money as you want, and you’ll never go to jail if you’re a banker and pay off the political parties with campaign contribution. It’s much like drug dealers paying off crooked police forces. So crime is pouring into the financial system.
I think this is what’s going to cause a return to classical economics – the realization that you need government banks. Of course, government banks also can be corrupted, so you need some kind of checks and balances. What you need is an honest legal system. If you don’t have a legal system that throws crooks in jail, your economy is going to be transformed into something unpleasant. That’s what is happening today. I think that most Europeans don’t want to acknowledge that that’s what happened in America (USA). There is such an admiration of America that there is a hesitancy to see that it has been taken over by financial predators (a.k.a. “the market”).
We always hear that oligarchies are in the east, in Russia, but hardly anyone is calling America an oligarchy… although alternative media says that it’s just a few families that rule the country.
Yes.
Michael Hudson is the author of Killing the Host (published in e-format by CounterPunch Books and in print by Islet). His new book is J is For Junk Economics. He can be reached at mh@michael-hudson.com