By Paul Craig Roberts
Source: PaulCraigRoberts.com
According to official US government economic data, the US economy has been growing for 10.5 years since June of 2009. The reason that the US government can produce this false conclusion is that costs that are subtrahends from GDP are not included in the measure. Instead, many costs are counted not as subtractions from growth but as additions to growth. For example, the penalty interest on a person’s credit card balance that results when a person falls behind his payments is counted as an increase in “financial services” and as an increase in Gross Domestic Product. The economic world is stood on its head.
It is aggregate demand that drives the economy. Payments made on a rise in interest rates on credit card balances from 19% to a 29% penalty rate reduce consumers’ ability to contribute to aggregate demand by purchasing goods and the services of doctors, lawyers, plumbers, electricians, and carpenters. Contrary to logic, the fee is magically counted in the “financial services” category as a contributor to GDP growth. The extortion of a fee that reduces aggregate demand lowers GDP, but builds paper wealth in the financial services sector.
GDP growth is also artificially inflated by counting as GDP abstract concepts that do not produce income streams. For example, for homeowners the US Department of Commerce estimates the rental values of owner-occupied housing, that is, the amount owners would be paying if they rented instead of owned their homes, and counts this imputed rent as GDP.
These and other absurdities have caused economist Michael Hudson to conclude correctly that the “financial reality of how the U.S. economy works is no longer captured in GDP statistics.”
https://michael-hudson.com/2019/10/asset-price-inflation-and-rent-seeking/
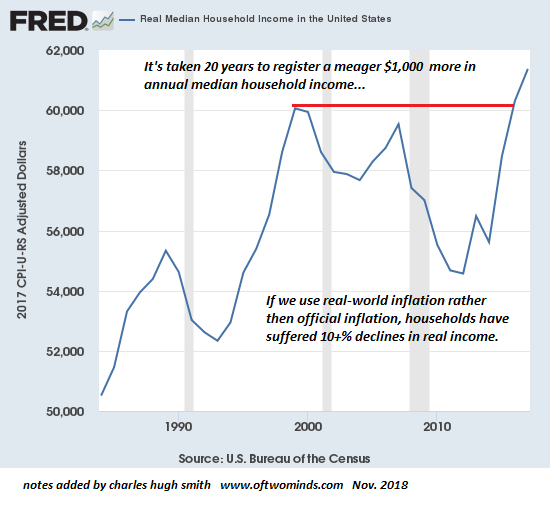
Today we have two economies. One is the real economy of production and consumption. The other is the financialized economy of paper wealth. The former is doing poorly, and the latter is doing well. The financialized economy is growing much faster than the real economy. Indeed, the real economy might not be growing at all.
Michael Hudson describes the difference. The stock market is at all time highs that have created massive wealth in financial assets for stock and bond owners. In the real economy the situation is totally different: “The Federal Reserve’s Report on the Economic Well-Being of U.S. Households in 2018 reports that 39% of Americans do not have $400 cash available for a medical or other emergency, and that a quarter of adults skipped medical care in 2018 because they could not afford it ( https://www.federalreserve.gov/publications/files/2018-report-economic-well-being-us-households-201905.pdf ). The latest estimates by the U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO) report that nearly half (48 percent) of households headed by someone 55 and older lack any retirement savings or pension benefits ( https://www.aarp.org/retirement/retirement-savings/info-2019/no-retirement-money-saved.html ). Even in what the press calls an economic boom, most Americans feel stressed and many are chronically angry and worried. According to a 2015 survey by the American Psychological Association, financial worry is the “number one cause of stress in America today” ( https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2015/02/money-stress ).
The data is completely clear. The rich are becoming much richer, and the rest are becoming poorer. Michael Hudson explains:
“The creation and trading of property and financial assets at rising prices has been fueled by rising debt levels owed to the financial sector. This sector’s returns therefore are best seen not as real wealth on the asset side of the balance sheet, but as overhead on the liabilities side. And the process is multi-layered: income accruing to the financial wealth owned by the top 10 Percent is paid mainly by the bottom 90 percent in the form of rising debt service and other returns to financial and other property.
“In the textbook models of industrial capitalism’s mass production and consumption, an asset’s price is determined by its cost of production. If the price rises above this level, competitors will offer it cheaper. But in the financialized economy an asset’s price is determined by how much credit buyers can borrow to buy it, not by its cost of production. A home is worth as much as a bank will lend to a bidder.
“The engine of industrial capitalism and its consumer society is a positive feedback loop in which widely shared income growth, expanding consumption and markets generated yet more investment and growth. By contrast, the feedback loop of financial capitalism is an exponential growth of credit-driven debt, driving up asset prices and hence requiring yet more borrowing to buy homes, retirement income and other assets. Corporate management and investment today is mainly about obtaining capital gains for real estate, stocks and bonds than about earning income.
“We illustrate this by charting the flow of income and capital gains in the real estate sector to show the dominance of asset-price gains over net rental income – and how rental income is used up paying interest in our financialized economy. Likewise, corporate income is spent (and new debt taken on) largely for stock buybacks to raise share prices. The resulting dynamic is exponential and destabilizing.”
This dynamic is destabilizing, because as more of consumers’ discretionary income is drawn off to service mortgage, credit card, automobile and student debt and for compulsory health insurance, less is left to purchase the goods and services in the real economy. Consequently, credit-driven debt grows faster than the income that services it, and this impoverishes the 90%. However, for the 10%, money creation by the Federal Reserve in order to protect the balance sheets of the “banks too big to fail or jail” drives up the values of financial assets. As a result the distribution of income and wealth becomes hightly polarized.
Think about the many Americans who meet their living expenses by making only the minimum payment on their credit card balance. At 19% interest their debt grows monthly. Eventually they hit a credit card debt cap and can no longer use the card to cover their living expenses. But they have the burden of a large debt balance to service without an income stream capable of servicing it.
Think about the corporation that decapitalizes itself in order to produce short to intermediate term capital gains for shareholders and executives by indebting the firm in order to buy back the firm’s shares. The end result is that all income goes for debt service.
In a financialized economy, the only possible outcomes are debt forgiveness or collapse.
As Michael Hudson makes clear, the combination of nonsensical categories in the National Income and Product Accounts and a financialized economy means we have no accurate picture of the economy’s condition. Michael Hudson has a proposal for correcting these problems and making GDP accounting more accurate, but as ecological economists such as Herman Daly have made clear, GDP measurement also omits the external costs of production. This means that we do not know whether GDP is growing or declining. It is entirely possible that the ecological and social costs of an increase in GDP (as currently measured) are greater than the value of the increased output. (See Paul Craig Roberts, The Failure of Laissez-Faire Capitalism, https://www.amazon.com/Failure-Laissez-Faire-Capitalism/dp/0986036250/ref=sr_1_2?crid=16NHZEQ9G3JRW&keywords=paul+craig+roberts+books&qid=1576440032&s=books&sprefix=Paul+Craig%2Caps%2C173&sr=1-2 )
Perhaps the major way in which GDP is overstated is the exclusion of external or social costs. External or social costs are costs of producing a product that the producer does not incur but imposes on third parties or on the environment. For example, untreated sewage dumped into a stream imposes costs on people downstream. Runoff of chemical fertilizers from commercial farming produces dead zones in the Gulf of Mexico and toxic algal blooms such as Red Tide that result in massive fish kills, make seafood unsafe, cause human ailments and adversely impact the tourist trade of beach areas. The result is lost incomes, ruined vacations, health expenses, and none of these costs are born by the commercial farmers.
Real estate development produces massive external costs. Scenic views from existing properties are blocked, thus reducing their values. Construction noise and congestion impose costs on existing residents and reduces the quality of their lives. Water runoff problems are often created. Infrastructure has to be provided, such as larger highways to provide evacuation from hurricane-impacted areas, usually financed by taxpayers. If the global warming case is correct, the external cost of human economic activity can be the life of the planet.
Lakshmi Sarah in the May/June, 2019, issue of the Sierra Club magazine provides an excellent detailed account of the external costs of coal-fired power plants being built in India by the Indian conglomerate Tata with a loan from the International Finance Corporation, a branch of the World Bank. The ground water in the area has been ruined and is no longer drinkable. Farmers are no longer able to grow crops on half of the area farmland. Heated wastewater that is dumped into the Gulf of Kutch is destroying fishing. The ecology and the livelihoods of the population are essentially destroyed. None of these costs are born by the private power companies.
Tired of being doormats for capitalists and the World Bank, the residents of the affected provinces rebelled. They have succeeded in getting their case before the US Supreme Court. It seems that the International Finance Corporation is so accustomed to financing projects that produce large external costs that it overlooked its obligation to examine the environmental impact of the projects it finances. This oversight resulted in Indian farmers and fishermen getting their case before the US Supreme Court. The International Finance Corporation’s lawyers argued that the World Bank lending agency had “absolute immunity.” The Supreme Court said no and remanded the case to the circuit court to rule on the damages.
Perhaps the most surprising thing about this apparent victory for ordinary faraway little people in an American court against the World Bank, a principle instrument of American imperialism, is that the Trump administration appeared in court as a friend of the Indian farmers and fishermen. The US Solicitor General, represented by Jonathan Ellis, rejected the notion that international orgnizations have absolute immunity. The Establishment exists on its immunity. Here we see the ultimate reason that the ruling Establishment wants rid of Trump.
Already the senior staff of the International Finance Corporation have come to the realization that they have other responsibilities than just to shuffle money out the lending shute. If the Indian farmers and fishermen succeed in protecting themselves from ruination by external costs, perhaps Americans who suffer external costs will follow their lead.
Perhaps economists will also come to the realization that they owe us accurate GDP accounting and not fanciful accounts that serve elite wealth in the financialized economy.