By Brandon Smith
Source: Alt-Market.us
Economic issues are some of the most politically abused issues often because the data politicians exploit is easy to present out of context. The vast majority of the public doesn’t spend their time immersed in the intricacies of monetary policy, unemployment stats and the processes of inflation vs deflation. They hear a soundbite on the news or social media once in a while, assume it must be true and then go on with their day.
This is how economic crisis events always seem to take the population by surprise – The establishment tells people all is well and no one questions the narrative in the face of numerous warning signs. Sometimes, the populace continues to believe that everything is fine despite the financial framework burning down around them, all because the “experts” continue to convince them that recovery is “right around the corner.”
There are numerous incentives for government officials and mainstream economists to mislead the citizenry with tales of imminent prosperity in the midst of instability. Primarily, the goal is to keep the middle-class population as docile as possible so that they don’t revolt until it’s too late (the middle class being predominantly conservative, and the greatest threat to any corrupt regime). Understand that economics is the root of power, and economic perception is the key to influencing the masses.
Hidden Indicators And Rampant Money Printing
The reality is that the US was hurtling towards stagflationary disaster ever since the crash of 2008, when Barack Obama and Joe Biden (with the help of the Federal Reserve) oversaw the near doubling of the national debt from $10 trillion to almost $20 trillion – The most egregious abuse of monetary policy that the US had ever seen.
And, keep in mind this was only the officially reported cash. Because of pressure brought by people like Ron Paul in 2011, the government was forced to pursue a limited audit of the Federal Reserve bailouts at that time. This revealed at least $16 trillion created from nothing by the Fed to prop up the failing system.
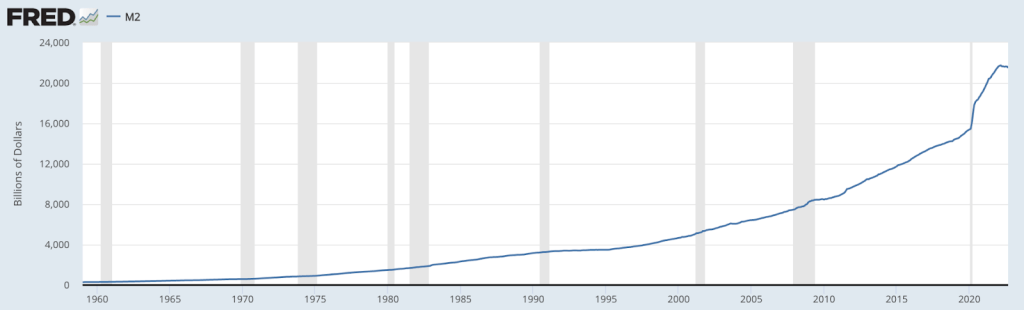
In 2006, right before the derivatives collapse, the Federal Reserve conveniently and abruptly ended their M3 money supply report. They now only report the M2 money supply, which does not include the vast assets held in corporate coffers, large time deposits in banks, institutional money market funds, short-term repurchase agreements (repo), and larger liquid assets. It was as if they knew an inflationary event was about to take place and they needed to obscure the evidence.
In other words, in economics there is the “official government data” and then there is the REAL data, which is sometimes so hidden it is impossible to quantify.
Even if we only go by the M2 report, the money supply skyrocketed starting in 2020, and rose exponentially through 2021 and 2022 – It jumped by 40% in only two years. This is why the cost of most necessities has risen 25% or more.
I’m sure most readers have noticed that inflation is not going away despite Joe Biden’s claims that he has “cut inflation in half” under his “Bidenomics” plan. This is because inflation is cumulative. The CPI might fluctuate, but the effects of inflation remain as prices tend to increase and stay high perpetually.
There Is No Such Thing As “Bidenomics”
The supposed financial progress that Biden is trying to take credit for has nothing to do with Biden’s policies. Not a thing. Unless, of course, you count market manipulation as a positive.
For example, the reduction in CPI is directly related to the continuous interest rate hikes of the Federal Reserve, which Biden has zero control over. The Fed is autonomous and makes its decisions independent of the White House or government. This is a fact openly admitted by former chairman Alan Greenspan. When the fed raises rates, debt becomes more expensive, lending slows down and thus the economy slows down.
One of the only ways that Biden can influence CPI is through artificial deflation of energy prices. The Biden Administration has been dumping US strategic oil reserves on the market for the past year as a means to suppress oil prices, thereby directly and indirectly keeping the CPI numbers down. This is not progress, it’s economic fraud.
The misuse of stats extends to other sectors, such as Biden’s attempt to take credit for the recent reduction in the US deficit. Again, this has nothing to do with Biden; the Fed’s interest rate hikes make it more expensive for the government to take on debt, therefore, debt spending drops.
It’s also not a situation that signals a recovery in the economy – The Fed continues to hike rates supposedly to stall inflation, but higher rates in a debt heavy environment lead to inevitable deflationary upheaval. As I predicted a year ago, the Fed is continuing to increase interest rates until this happens.
Employment Miracle Or Employment Scam?
This issue has been brought up by many analysts but I’ll touch on it again here because Biden is relentless in his falsehoods when it comes to employment data. FACT: 72% of all “new jobs” Biden takes credit for were originally lost during the pandemic lockdowns. The very lockdowns which Democrats avidly enforced and tried to keep in place perpetually. You can’t take credit for “creating” jobs that you are responsible for destroying.
In terms of higher labor demand, the pressure is in low wage service sector jobs and these are the majority of jobs added since Biden took office. And, this rush into retail/service was purchased with $8 trillion+ in covid stimulus cash along with a moratorium on rent and student loan payments. That much extra money in circulation buys at least a few years of consumer spending, propping up jobs numbers.
Throughout history, such gains from inflationary actions and government interventions are always short term, and they always end with a dramatic plunge in employment once the effects subside.
Biden’s Fake Manufacturing Boom
Biden has recently touted a jump in US manufacturing as the latest achievement of Bidenomics, but like every other claim he makes, you have to look at the context. These are not free market manufacturing facilities built according to market demand. Rather, Biden is pumping billions of taxpayer dollars into green tech, once again artificially engineering a “manufacturing boom” through government subsidies for products that have limited demand.
Biden wants to rig the demand, too, by enforcing climate laws which make gas, oil and coal sources too expensive and solar panels and wind turbines cheaper by comparison. For example, Biden is increasing costs for oil and gas exploration on federal lands, while greatly lowering the prices for building solar farms on federal lands. In other words, the government uses your money to create factories for green tech and then creates laws which force people to use that green tech.
In the meantime, Joe’s manufacturing “boom” paid for with tax dollars also comes at the cost of America’s oil, gas and coal industries, not to mention less energy freedom for the general public. It’s socialism, not a revolution in domestic manufacturing.
For Biden, The Key Is To Create As Many Government Cash Injections As Possible Until 2025
You want to know why Democrats are so angry that the Supreme Court blocked Biden’s plan to make taxpayers cover student loan debts? It’s not because they care about naive college kids who paid too much money for garbage degrees – It’s because student debt relief would immediately add trillions more in spending in the short term to the US economy.
An interesting side effect of the college loan moratorium is the surprising credit boost – As soon as college loan payments were put on hold, millions of former students had their credit ratings increase by default. Meaning, they could now hike their credit limits and spend MORE money they don’t have. It’s an incredibly sneaky way to artificially prop up the system WITHOUT using direct stimulus measures that rely on the central bank. This false boost will disappear by October of this year.
Biden’s constant attempts to introduce infrastructure programs are another way the government can create the illusion of recovery by using debt spending as a means to mitigate the signals of greater fiscal decline. Without Fed stimulus it’s the only option Biden has, and as rates rise it becomes costly.
The bottom line is this – The US economy is on a short timetable as long as the Fed continues to raise interest rates into weakness as a means to suppress inflation. As we witnessed in the spring, higher rates are already breaking the back of mid-tier banks across the western world and the Fed’s backstop funds are only enough to stall the debt crisis for a time. I continue to predict that once the Fed Funds Rate is raised to 6% or more, we will once again see a banking calamity similar to the 2008 crash, but this time if the Fed steps in with a bailout hyperinflation will be the immediate result.
Bidenomics is a sham in every respect. Anything that could be considered an economic improvement is due to the Federal Reserve playing the odds with interest rates. A massive 40% increase in the money supply sure helps in obscuring fiscal weakness as well. Luckily, nearly 60% of Americans in recent polls say they aren’t buying the Bidenomics fairytale – They see the dangers around them every day.
The covid event was a catalyst that revealed all the weaknesses of the US system that many of us in alternative economics have been warning about for years. And now it seems as if the establishment is trying to drag things along for just a little while longer. The reason why is up for speculation, but the fact remains that a broken structure cannot be propped up with stop gaps. I’m doubtful that Biden will be able to ride the wave created by covid stimulus until the end of 2024. Something has to give.