By Charles Hugh Smith
Source: Of Two Minds
The Great Moderation of low inflation and soaring assets has ended. Welcome to the death by a thousand cuts of stagflation. It was all so easy in the good old days of the past 25 years: just keep pushing interest rates lower to reduce the cost of borrowing and juice credit expansion ((financialization) and offshore industrial production to low-cost nations with few environmental standards and beggar-thy-neighbor currency policies (globalization).
Both financialization and globalization are deflationary forces, as they reduce costs. They are also deflationary to the wages of bottom 90%, as wages are pushed down by cheap global labor and stripmined by financialization, which channels the vast majority of the economy’s gains into the top tier of the workforce and those who own the assets bubbling up in financialization’s inevitable offspring, credit-asset bubbles.
To keep the party going, central banks and governments pushed both forces into global dominance: hyper-financialization and hyper-globalization. Policy extremes were pushed to new extremes: “temporary” zero-rate interest policy (ZIRP) stretched on for 6 years as every effort was made to lower the cost of credit to bring demand forward and inflate yet another credit-asset bubble, as the “wealth effect” of the top 5% gaining trillions of dollars in unearned wealth as asset bubbles inflated pushed consumption higher.
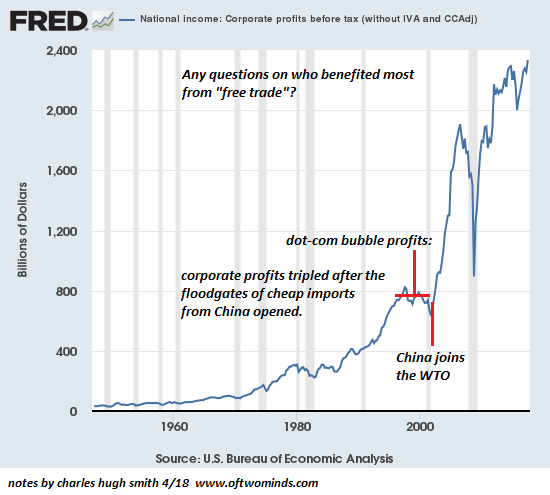
Corporate profits soared as credit became essentially free and super-abundant and globalization lowered costs and institutionalized planned obsolescence, the engineered replacement of goods and software that forces consumers to replace their broken / outdated products every few years.
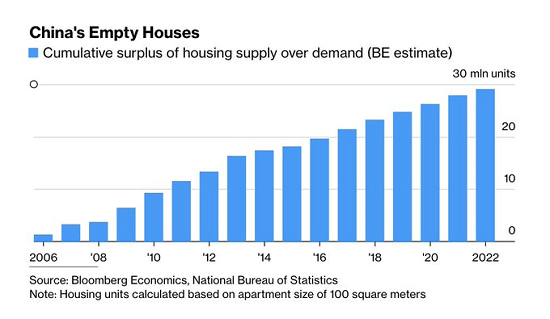
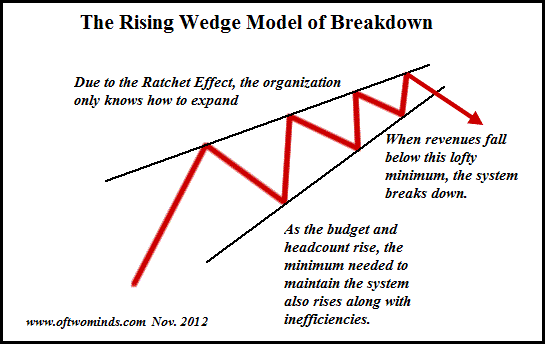
Every economic lever was pulled to extend the vast profits generated by hyper-financialization and hyper-globalization. Currencies were manipulated lower to boost exports, cheap credit kept zombie companies alive, bridges to nowhere and millions of empty flats were built to boost jobs and profits, and so on.
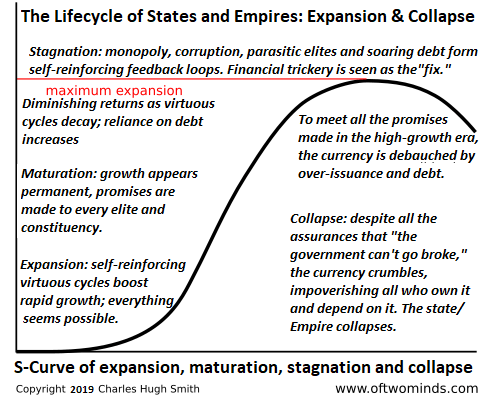
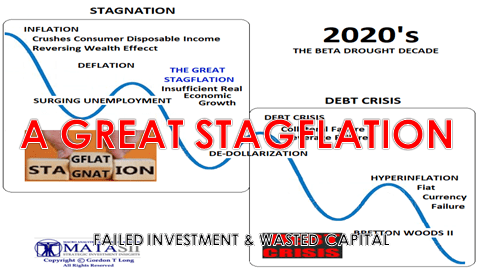
At long last, all these gimmicks have reversed or reached marginal returns: they no longer keep inflation suppressed, asset bubbles inflating and profits expanding. The malinvestment of global capital will be revealed and the costs of the policy gimmickry will be paid by years of stagflation: high inflation, low or negative growth and endless debt crises as the reliance on cheap credit to boost profits comes home to roost.
It turns out that the inevitable offspring of hyper-financialization and hyper-globalization are inflation, credit crises and the undermining of national security as the self-serving goal of pushing corporate profits higher via globalization led to fatal dependencies on competing powers for the essentials of modern life.
Correcting these decades-long extremes will take at least a decade as long-suppressed inflation becomes endemic, supply-chain disruptions become the norm and capital has to be invested in long-term national projects such as reshoring and the engineering of a new more efficient energy mix–projects that will only be expenses for many years.
This demand for structural investments with no immediate profit payoff is what drove the stagflation of the 1970s, a factor I explain in The Forgotten History of the 1970s and The 1970s: From Rotting Carcasses Floating in the River to Kayak Races.
The gains will not even be measured by our current outdated economic metrics of GDP and profits. The gains will be in the national security of essential supply chains and production and in the relocalizing of jobs and capital, not corporate profits.
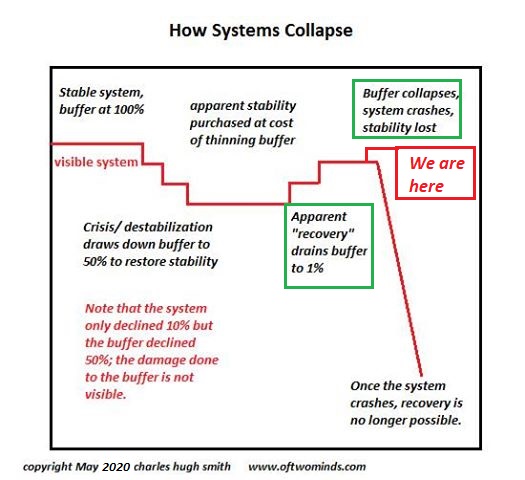
Our reliance on the endless expansion of credit, leverage and credit-asset bubbles will have its own high cost: the collapse not just of the current Everything Bubble but of the engines that inflated one bubble after another.
Central bank and state authorities are thrashing about cluelessly, as all their gimmicks are now problems rather than solutions. The current policy gimmicks laid the foundations for a decade or more of high inflation, low growth and credit crises as the phantom “wealth” of credit-asset bubbles evaporates.
This will drive a reverse Wealth Effect as the top spenders are crushed by the collapse of asset bubbles. Long-term trends in demographics (shrinking workforces and the skyrocketing population of elderly) and depletion of resources will add fuel to the inflationary / low growth / credit crises bonfires.
Gordon Long and I discuss all these mutually reinforcing trends in A Great Stagflation (36 min). This is the culmination of our decade of programs about all the policy gimmicks that were pushed to extremes to maintain the illusion of stability and growth–an illusion that’s evaporating as it makes contact with stagflationary realities.