By Nicholas Baum
Source: Activist Post
Over the last few years, an unwelcome phrase has grown to plague American consumers and producers alike: supply chain issues. The recurring term is frequently offered by mainstream economists as the go-to explanation for record inflation, while the Biden Administration has seemingly twisted it into a sign of economic recovery. Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo states,
“What we have here is a demand issue. The economy is doing better… People have money in their pocket. They’re spending that money. Demand is through the roof… Supply has to catch up.”
Although Raimondo said this back in October 2021, inflation has only worsened from an annual rate of 6.2 percent to 7.7 percent more than twelve months later, leading one to wonder if the Secretary is right that inflation is a matter of supply chains adjusting to an increase in wealth. Yet as it turns out, in the words of the Mises Institute’s Ryan McMaken, “the administration’s defenders are right about consumer demand and spending – even if for the wrong reasons.”
That is, although we’re indeed witnessing a large spike in demand (which is perhaps best quantified by changes in nominal GDP), this increase in demand is a symptom of a larger problem: the massive expansion of the money supply under the watch of the Federal Reserve and the White House. The implications of this unprecedented expansion are two-fold, not only stirring this increase in “demand” but contributing to supply chain issues through the distortion of price signals.
The Money Supply and Demand
With state governments responding to the rise of Covid-19 by imposing lockdowns and forcibly closing “non-essential businesses,” both the Fed and the Trump and Biden Administrations stepped in with an extraordinarily expansive monetary and fiscal policy, respectively.
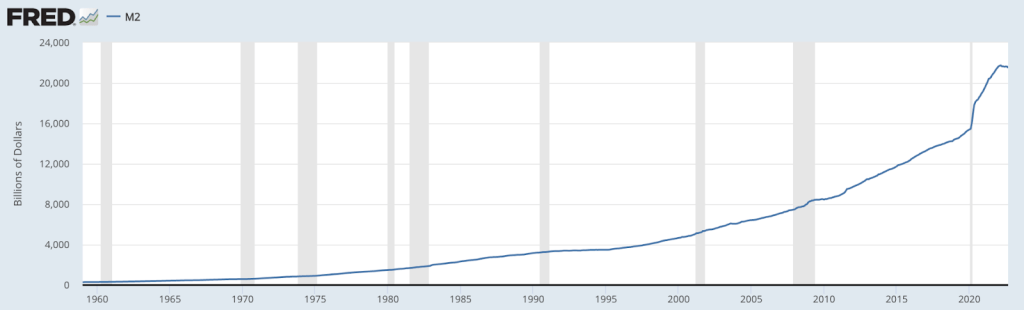
M2 is a figure for the money supply, which surged by more than $6.2 trillion, a 40 percent increase, between February 2020 and February 2022. This is the result of a variety of initiatives, from the Fed’s quantitative easing and purchase of over $2 trillion in assets to new federal programs such as stimulus checks, PPP loans, and the $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan Act.
Through these ventures that flooded the economy with new cash, Americans indeed had more money in their pockets. The problem is, obviously, that such money soon became worth a lot less. That’s because an increase in the money supply, without a corresponding increase in economic output, means an increase in prices, with more money chasing roughly the same quantity of goods.
This is where Raimondo serves to mislead viewers in her comments; just because Americans have more money, doesn’t mean they’re any wealthier. There certainly is a large spike in demand, but that doesn’t represent an increase in the real wealth of Americans, but an increase in the amount of money they have access to thanks to an unprecedented monetary expansion.
This is perhaps best represented by comparing nominal to real GDP per capita, which is a rough proxy for standard of living:
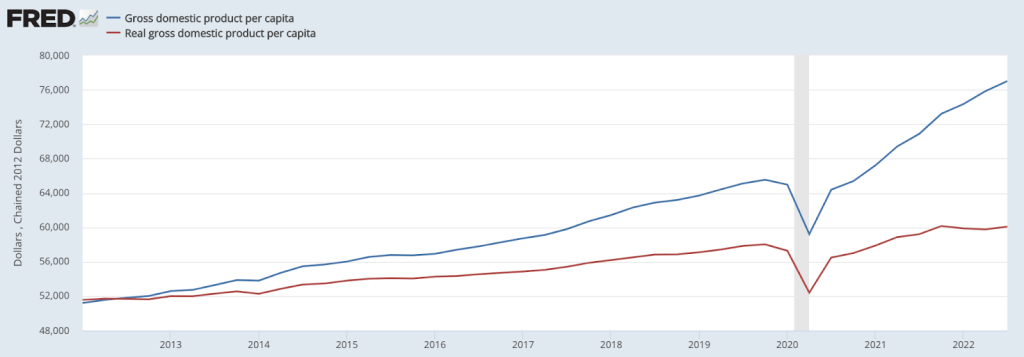
If you were to look only at nominal GDP per capita (the blue line) you would think that the average American’s wealth has increased greatly since the pandemic. This, however, is incredibly misleading, because it doesn’t take into account inflation and the decreasing value of the dollar.
Inflation and Price Signals
The large demand increase noted by Raimondo and other economists does not reflect a growing economy and an increase in wealth but an increase in the money supply which has created upward pressure on prices. Yet just as the Biden Administration declares that “supply has to catch up,” the ability for producers to do so has been greatly strained by inflation (not to mention the aforementioned lockdowns).
That’s because of the role prices—which economist Alex Tabarrok refers to as “a signal wrapped up in an incentive” —play in coordinating economic activity. Changes in prices usually convey changes in the scarcity and demand for different goods, products, and resources. When the price of something in a company’s supply chain increases, this hurts the company’s profitability and incentivizes it to economize and find a more efficient alternative.
On a macro scale, economic growth (or recovery) comes through thousands, if not millions, of businesses and firms finding new ways to innovate and maximize profits, which is the result of comparing the prices of alternative inputs and production methods. Inflation, by raising the general price level of the economy and often affecting the price of each good differently, can cause economic discoordination and confusion because prices no longer reflect changing efficiencies and scarcities.
Even if inflation impacted all prices equally, we still wouldn’t know to what extent a rise in the price of a certain resource reflects actually important information about it, given that the rate of inflation is always changing and can only be measured in hindsight.
In the context of the last few years, this has meant that firms have essentially been blindfolded, piecing back together supply chains forcibly closed during the pandemic without the ability for prices to convey the efficiency of competing alternatives. This is exactly why “supply chain issues” has continued to be a lingering excuse for inflation and shortages, with Volkswagen chief executive Oliver Blume going so far as to say that, “Challenges to our supply chains will become the rule, not the exception.”
Nor is this a relatively recent phenomenon. Paul Volcker, the late Fed Chairman notable for remedying the United States’ last encounter with runaway inflation in the late 1970s and early 1980s, observed that, “The inflationary process itself brought so many dislocations, and stresses and strains that you were going to have a recession sooner or later.”
Given the fact that the United States technically entered a recession during the first half of 2022—at least according to a common definition of recession—Volcker’s words proved prescient. Not only has an unprecedented monetary expansion under the purview of the Fed and White House triggered a dangerous period of inflation; the inflation has also caused disruptions to the supply chain, which agencies (ironically) use as a scapegoat for inflation.
Now, with economic growth stagnant and inflation persisting at high levels, the fate of supply, demand, and the price signals that they convey rests in the hands of the problems’ culprits.